|
History Of Moncton
The history of Moncton extends back thousands of years, with its first inhabitants being the First Nations of the region, such as the Mi'kmaq. Located in New Brunswick, Moncton's motto is ''Resurgo'', which is Latin for ''I rise again''. This motto was originally chosen in celebration of the city's rebirth in 1875 after the recovery of the economy from the collapse of the shipbuilding industry. The city again lived up to its motto in more recent times, when the economy of the city was devastated once more during the 1980s as a result of the city's largest employers (the CN repair shops, the Eaton's catalogue division, and CFB Moncton) all departing the city in short order. The city has since rebounded due to growth in the light manufacturing, technology, distribution, tourism, and retail sectors of the economy and is now the fastest growing city in Canada east of Toronto. Aboriginal period The original aboriginal inhabitants of the Petitcodiac river valley were the Mi'kmaq. Mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moncton New Brunswick Location3
Moncton (; ) is the most populous city in the Canadian province of New Brunswick. Situated in the Petitcodiac River Valley, Moncton lies at the geographic centre of the Maritime Provinces. The city has earned the nickname "Hub City" because of its central inland location in the region and its history as a railway and land transportation hub for the Maritimes. As of the 2021 Census, the city had a population of 79,470, a metropolitan population of 157,717 and a land area of . Although the Moncton area was first settled in 1733, Moncton was officially founded in 1766 with the arrival of Pennsylvania German immigrants from Philadelphia. Initially an agricultural settlement, Moncton was not incorporated until 1855. It was named for Lt. Col. Robert Monckton, the British officer who had captured nearby Fort Beauséjour a century earlier. A significant wooden shipbuilding industry had developed in the community by the mid-1840s, allowing for the civic incorporation in 1855. But the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
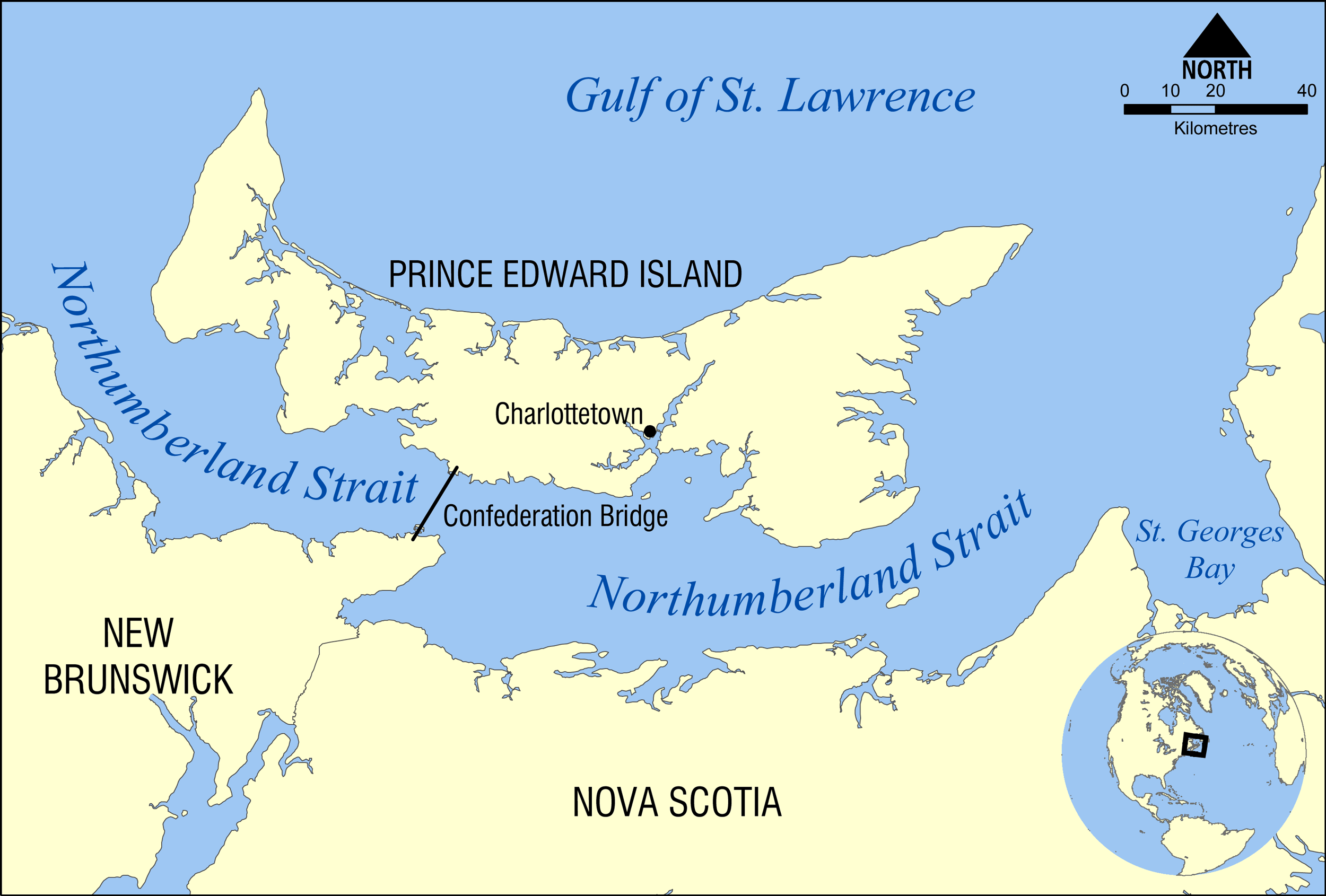
Northumberland Strait
The Northumberland Strait (French: ''détroit de Northumberland'') is a strait in the southern part of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in eastern Canada. The strait is formed by Prince Edward Island and the gulf's eastern, southern, and western shores. Boundaries The western boundary of the strait is delineated by a line running between North Cape, Prince Edward Island and Point Escuminac, New Brunswick while the eastern boundary is delineated by a line running between East Point, Prince Edward Island and Inverness, Nova Scotia. Hydrography The Northumberland Strait varies in depth between 17 and 65 metres, with the deepest waters at either end. The tidal patterns are complex; the eastern end has the usual two tides per day, with a tidal range of 1.2 to 1.8 metres, while the western end effectively has only one tide per day. The strait's shallow depths lend to warm water temperatures in summer months, with some areas reaching 25° C, or 77° F. Consequently, the strait is repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrochronology
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and atmospheric conditions during different periods in history from wood. Dendrochronology derives from Ancient Greek (), meaning "tree", (), meaning "time", and (), "the study of". Dendrochronology is useful for determining the precise age of samples, especially those that are too recent for radiocarbon dating, which always produces a range rather than an exact date. However, for a precise date of the death of the tree a full sample to the edge is needed, which most trimmed timber will not provide. It also gives data on the timing of events and rates of change in the environment (most prominently climate) and also in wood found in archaeology or works of art and architecture, such as old panel paintings. It is also used as a check in radiocar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steeves
Steeves (also Steves) is a surname. Notable people with the name include: * Burpee L. Steeves (1868–1933), American politician from Idaho; lieutenant governor of Idaho 1905–07 *David Steeves (1934–1965), U.S. Air Force officer cleared of giving a jet to the USSR *George Steeves (born 1945), Canadian art photographer *Harold Steves Canadian politician and activist *Manoah Steves (1828-1897), founder of Steveston, British Columbia * Tim Steeves (contemporary), Canadian comedian and writer *Wayne Steeves (born 1944), Canadian politician from New Brunswick; provincial legislator *William Steeves William Henry Steeves (May 20, 1814 – December 9, 1873) was a merchant, lumberman, politician and Father of Canadian Confederation. Life and career Born and raised in Hillsborough, New Brunswick, William Henry Steeves was a descendant of Hein ... (1814–1873), Canadian merchant and politician; one of the Fathers of Canadian Confederation References External links Steeves M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading intellectuals of his time, Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, a drafter and signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, and the first United States Postmaster General. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his studies of electricity, and for charting and naming the current still known as the Gulf Stream. As an inventor, he is known for the lightning rod, bifocals, and the Franklin stove, among others. He founded many civic organizations, including the Library Company, Philadelphia's first fire department, and the University of Pennsylvania. Isaacson, 2004, p. Franklin earned the title of "The First American" for his early and indefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Maryland to its south, West Virginia to its southwest, Ohio to its west, Lake Erie and the Canadian province of Ontario to its northwest, New York to its north, and the Delaware River and New Jersey to its east. Pennsylvania is the fifth-most populous state in the nation with over 13 million residents as of 2020. It is the 33rd-largest state by area and ranks ninth among all states in population density. The southeastern Delaware Valley metropolitan area comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the state's largest and nation's sixth most populous city. Another 2.37 million reside in Greater Pittsburgh in the southwest, centered around Pittsburgh, the state's second-largest and Western Pennsylvania's largest city. The state's su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Broussard
Joseph Broussard (1702–1765), also known as Beausoleil ( en, Beautiful Sun), was a leader of the Acadian people in Acadia; later Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and New Brunswick. Broussard organized a Mi'kmaq and Acadian militias against the British through King George's War, Father Le Loutre's War and during the French and Indian War. After Acadia was captured by the British, he eventually led the first group of Acadians to southern Louisiana in present-day United States. His name is sometimes presented as Joseph Gaurhept Broussard; this is likely the result of a transcription error. Broussard is widely regarded as a hero and an important historical figure by both Acadians and Cajuns. Life Broussard was born in Port-Royal, Acadia in 1702 to Jean-François Broussard and Catherine Richard. His father came from Poitiers and his mother was born in Port Royal. He lived much of his life at Le Cran (present-day Stoney Creek, Albert County, New Brunswick), along the Petitcodia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lawrence (British Army Officer)
Brigadier-General Charles Lawrence (14 December 1709 – 19 October 1760) was a British military officer who, as lieutenant governor and subsequently governor of Nova Scotia, is perhaps best known for overseeing the Expulsion of the Acadians and settling the New England Planters in Nova Scotia. He was born in Plymouth, England, and died in Halifax, Nova Scotia. According to historian Elizabeth Griffiths, Lawrence was seen as a "competent", "efficient" officer with a "service record that had earned him fairly rapid promotion, a person of considerable administrative talent who was trusted by both Cornwallis and Hopson." He is buried in the crypt of St. Paul's Church (Halifax). Early career Lawrence was born in Plymouth (Devon) on 14 December 1709. He followed his father, General Charles John Lawrence, who is said to have served in Flanders under John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, into a military career. Charles Lawrence's earlier life is obscure. He was commissioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Monckton
Lieutenant-General Robert Monckton (24 June 1726 – 21 May 1782) was an officer of the British Army and colonial administrator in British North America. He had a distinguished military and political career, being second in command to General James Wolfe at the battle of Quebec and later being named the Governor of the Province of New York. Monckton is also remembered for his role in a number of other important events in the French and Indian War (the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War), most notably the capture of Fort Beauséjour in Acadia, and the island of Martinique in the West Indies, as well as for his role in the deportation of the Acadians from British controlled Nova Scotia and also from French-controlled Acadia (present-day New Brunswick). The city of Moncton, New Brunswick, (about west of Fort Beauséjour) and Fort Monckton in Port Elgin, New Brunswick, are named for him. A second more important Fort Monckton in Portsmouth, England, is also named for him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
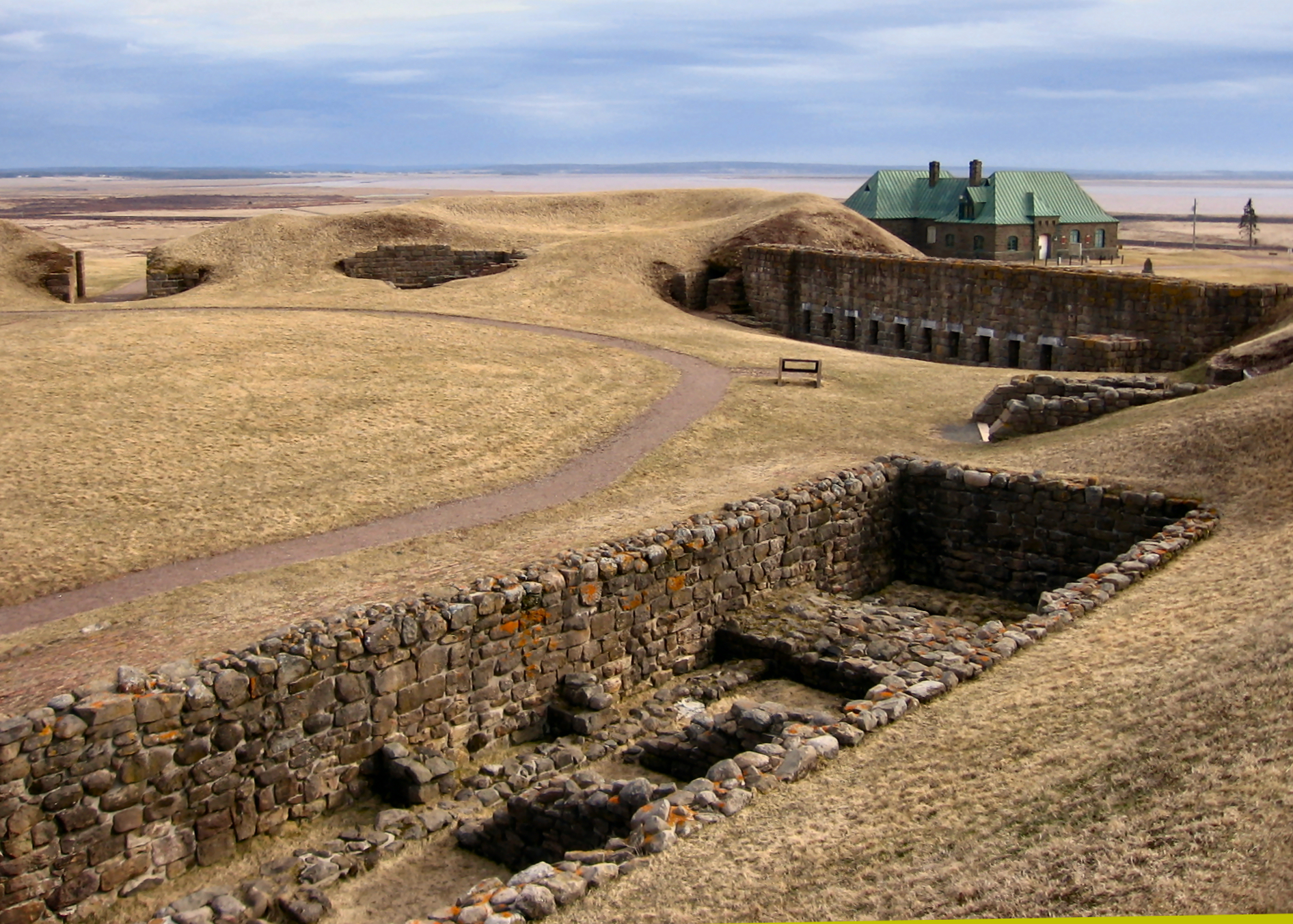
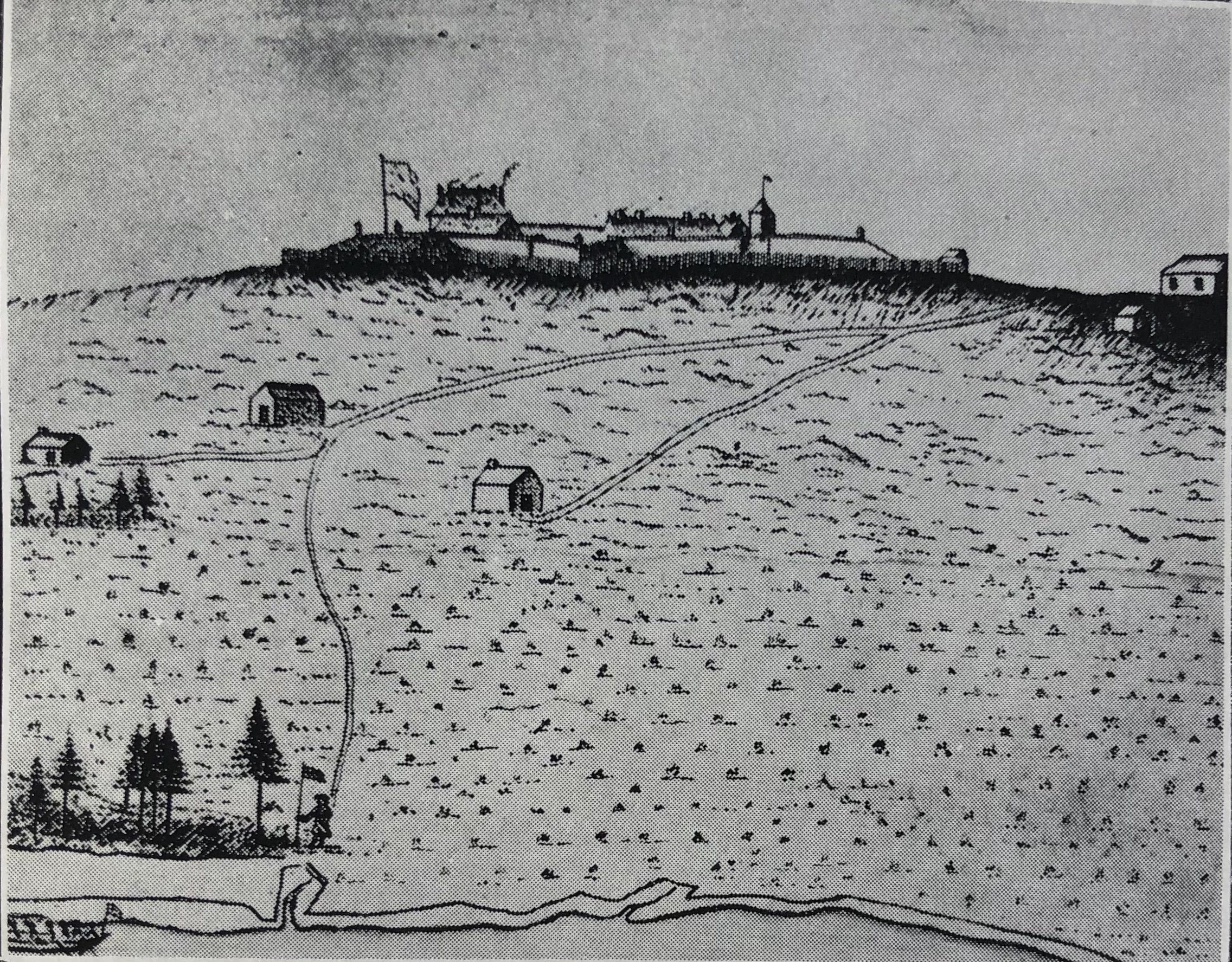
Fort Beauséjour
Fort Beauséjour (), renamed Fort Cumberland in 1755, is a large, five-bastioned fort on the Isthmus of Chignecto in eastern Canada, a neck of land connecting the present-day province of New Brunswick with that of Nova Scotia. The site was strategically important in Acadia, a French colony that included primarily the Maritimes, the eastern part of Quebec, and northern Maine of the later United States. The fort was built by the French from 1751 to 1752. They surrendered it to the British in 1755 after their defeat in the Battle of Fort Beauséjour, during the Seven Years' War. The British renamed the structure as Fort Cumberland. The fort was strategically important throughout the Anglo-French rivalry of 1749–63, known as the French and Indian Wars by British colonists. Less than a generation later, it was the site of the 1776 Battle of Fort Cumberland, when the British forces repulsed sympathisers of the American Revolution. Since 1920 the site has been designated as a National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_by_Dominic_Serres%2C_c._1765.jpg)

