|
Hindu Art
Hindu art encompasses the artistic traditions and styles culturally connected to Hinduism and have a long history of religious association with Hindu scriptures, rituals and worship. Background Hinduism, with its 1.2 billion followers, makes up about 15-16 % of the world's population and as such the culture that ensues it is full of different aspects of life that are effected by art. There are 64 traditional arts that are followed that start with the classics of music and range all the way to the application and adornment of jewellery. Since religion and culture are inseparable with Hinduism recurring symbols such as the gods and their reincarnations, the lotus flower, extra limbs, and even the traditional arts make their appearances in many sculptures, paintings, music, and dance. History Earliest depictions of Hindu deities (3rd-2nd centuries BCE) It is thought that before the adoption of stone sculpture, there was an older tradition of using clay or wood to represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism. Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within the Trimurti, the triple deity of supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva.Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme being who creates, protects, and transforms the universe. In the Shaktism tradition, the Goddess, or Adi Shakti, is described as the supreme Para Brahman, yet Vishnu is revered along with Shiva and Brahma. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power (Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the highest form of Ishvara is with qualities (Saguna), and have certain form, but is limitless, transcend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Greek
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent (parts of modern-day Pakistan and northwestern India). This kingdom was in existence from ca. 200 BC to ca. 1 BC. During its existence the kingdom was ruled over by 30 successive kings. Menander I, being the most well known amongst the Indo-Greek kings, is often referred to simply as ''“Menander,”'' despite the fact that there was indeed another Indo-Greek King known as Menander II. Menander I's capital was at Sagala in the Punjab region, Punjab (present-day Sialkot). The kingdom was founded when the Graeco-Bactrian king Demetrius I of Bactria, Demetrius (and later Eucratides I, Eucratides) invaded India from Bactria in 200 BC. The Greeks in the Indian Subcontinent were eventually divided from the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subhadra
Subhadra ( sa, सुभद्रा, Subhadrā) is a Hindu goddess mentioned in ancient Hindu scriptures like the ''Mahabharata'' and the ''Bhagavata Purana''. She is described as the favourite child of Vasudeva and the younger sister of deities Krishna and Balarama. According to the Mahabharata, Arjuna—one of the Pandava brothers—married her, with whom she bore one son, Abhimanyu. Subhadra is one of the three deities worshipped at the Jagannath Temple at Puri, along with Krishna (as Jagannatha) and Balarama (or Balabhadra). One of the chariots in the annual Ratha Yatra is dedicated to her. Etymology and epithets The word 'Subhadra' is made up of two words 'su' and 'bhadra'. Many scholars translate this name into 'glorious', 'fortunate', 'splendid' or 'auspicious'. * Chitra (चित्रा) - the text '' Harivamsa'' mentions Chitra (lit. bright, clear, excellent or colourful) as her birth name. * Bhadra (भद्रा) - sister of Balbhadra * Veer Sōdari ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linga
A lingam ( sa, लिङ्ग , lit. "sign, symbol or mark"), sometimes referred to as linga or Shiva linga, is an abstract or aniconic representation of the Hindu god Shiva in Shaivism. It is typically the primary ''murti'' or devotional image in Hindu temples dedicated to Shiva, also found in smaller shrines, or as self-manifested natural objects. It is often represented within a disc-shaped platform, the ''yoni'' – its feminine counterpart, consisting of a flat element, horizontal compared to the vertical lingam, and designed to allow liquid offerings to drain away for collection. Together, they symbolize the merging of microcosmos and macrocosmos, the divine eternal process of creation and regeneration, and the union of the feminine and the masculine that recreates all of existence. The original meaning of ''lingam'' as "sign" is used in Shvetashvatara Upanishad, which says "Shiva, the Supreme Lord, has no liūga", liuga ( sa, लिऊग ) meaning he is transcen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiva
Shiva (; sa, शिव, lit=The Auspicious One, Śiva ), also known as Mahadeva (; ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐ, or Hara, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions within Hinduism. Shiva is known as "The Destroyer" within the Trimurti, the Hindu trinity which also includes Brahma and Vishnu. In the Shaivite tradition, Shiva is the Supreme Lord who creates, protects and transforms the universe. In the goddess-oriented Shakta tradition, the Supreme Goddess ( Devi) is regarded as the energy and creative power (Shakti) and the equal complementary partner of Shiva. Shiva is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. Shiva has many aspects, benevolent as well as fearsome. In benevolent aspects, he is depicted as an omniscient Yogi who lives an ascetic life on Mount Kailash as well as a householder with his wife Parvati and his three children, Ganesha, Kartikeya and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. In ancient times, Mathura was an economic hub, located at the junction of important caravan routes. The 2011 Census of India estimated the population of Mathura at 441,894. In Hinduism, Mathura is birthplace of Krishna, which is located at the Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex. It is one of the Sapta Puri, the seven cities considered holy by Hindus, also called Mokshyadayni Tirth. The Kesava Deo Temple was built in ancient times on the site of Krishna's birthplace (an underground prison). Mathura was the capital of the kingdom of Surasena, ruled by Kansa, the maternal uncle of Krishna. Mathura is part of the Lord Krishna circuit (Mathura,Vrindavan, Barsana, Govardhan, Kurukshetra, Dwarka and Bhalka). Janmashtami is grandly celebrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodhisattva
In Buddhism, a bodhisattva ( ; sa, 𑀩𑁄𑀥𑀺𑀲𑀢𑁆𑀢𑁆𑀯 (Brahmī), translit=bodhisattva, label=Sanskrit) or bodhisatva is a person who is on the path towards bodhi ('awakening') or Buddhahood. In the Early Buddhist schools as well as modern Theravada Buddhism, a bodhisattva (Pali: ''bodhisatta'') refers to someone who has made a resolution to become a Buddha and has also received a confirmation or prediction from a living Buddha that this will be so. In Mahayana Buddhism, a bodhisattva refers to anyone who has generated ''bodhicitta'', a spontaneous wish and compassionate mind to attain Buddhahood for the benefit of all sentient beings. Mahayana bodhisattvas are spiritually heroic persons that work to attain awakening and are driven by a great compassion (''mahakaruṇā''). These beings are exemplified by important spiritual qualities such as the "four divine abodes" (''brahmaviharas'') of loving-kindness ('' metta''), compassion (''karuṇā''), empathet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattra
The ''chhatra'' (from sa, छत्र, meaning "umbrella") "jewelled/precious parasol" is an auspicious symbol in Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. The ''chhatra'' in various traditions According to Hindu mythology, it is the emblem of Varuna, also considered an embodiment of kingship. ''Chhatra'' is also a deity, yidam and ishta-devata. In various Dharmic traditions it is an accoutrement of ''chakravartin''. A number of deities are depicted with ''chhatra'', and they include Revanta, Surya, and Vishnu (in his Vamana avatar). The ''chhatra'' is cordoned amongst the symbols that approach universality within the numerous octavalent suites or sets of Ashtamangala, e.g., in the Digambar Jain tradition, and the Vajrayana tradition. In Dharmic tradition iconography, traditional Tibetan medicine thangkas and Ayurvedic diagrams, the ''chhatra'' is uniformly represented as the Sahasrara. In Vajrayana Buddhism, the umbrella or parasol is included in the 'Eight Auspicious Signs' or As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmund Bopearachchi
Osmund Bopearachchi (born 1949) is a Sri Lankan historian and numismatist who has specialized notably standardized the coinage of the Indo-Greek and Greco-Bactrian kingdoms. He is currently Emeritus Director of the CNRS at the École Normale Supérieure and Adjunct Professor of Central and South Asian Art, Archaeology, and Numismatics, University of California, Berkeley. Background Originally from Sri Lanka, Professor Bopearachchi received his Bachelor of Arts (General) Degree from the University of Kelaniya. In 1983 he joined a team of the CNRS at the École Normale Supérieure to further his studies. He received his Ph. D. in Art History and Archaeology from the Institute of Art and Archaeology at the Sorbonne University Paris I in 1987. In 1998, he completed his Habilitation at the Université de Paris-Sorbonne (Paris IV). Academic career In 1989, he became Research Specialist (''Chargé de Recherche'') at CNRS. In 1991, Osmund Bopearachchi published an extensive work on Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudarshana Chakra
Sudarshana Chakra (Sanskrit: सुदर्शन चक्र, lit. "disc of auspicious vision", IAST: Sudarśana Chakra) is a spinning, celestial discus with 108 serrated edges, attributed to Vishnu and Krishna in the Hindu scriptures. The Sudarshana Chakra is generally portrayed on the right rear hand of the four hands of Vishnu, who also holds the Panchajanya (conch), the Kaumodaki (mace), and the Padma (lotus). While in the Rigveda, the Chakra was Vishnu's symbol as the wheel of time and by the late period, the Sudarshana Chakra emerged as an ayudhapurusha (an anthropomorphic form), as a fierce form of Vishnu, used for the destruction of demons. As an ''ayudhapurusha'', the deity is known as Chakraperumal or Chakratalvar. Etymology The word ''Sudarshana'' is derived from two Sanskrit words – ''Su''(सु) meaning "good/auspicious" and ''Darshana'' (दर्शन) meaning "vision". In the Monier-Williams dictionary the word Chakra is derived from the root क्� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
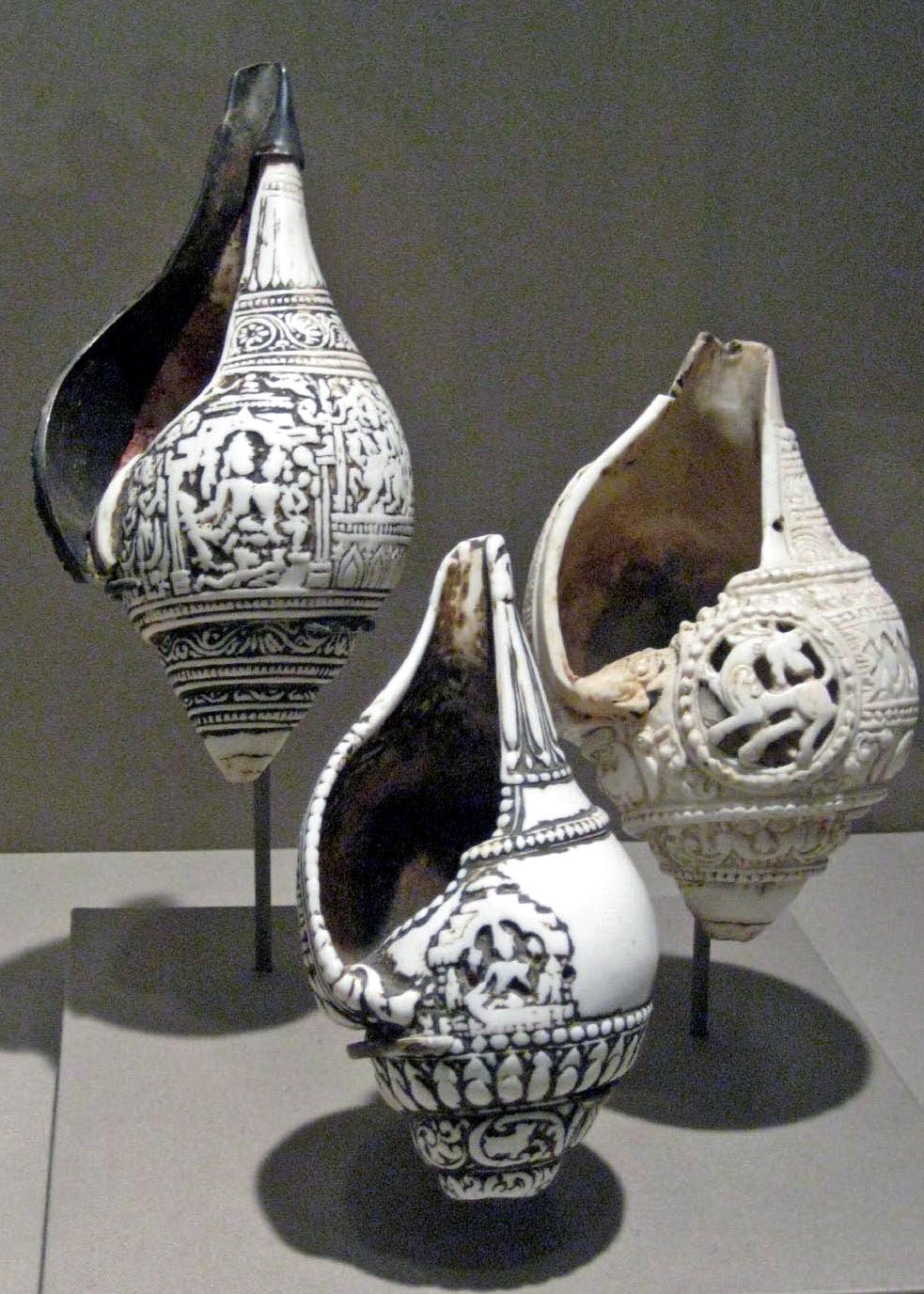
Shankha
A Shankha ( conch shell) has religious ritual importance in Hinduism. It is the shell of any suitable sea snail which had a hole made for the performer's embouchure. In Hindu history, the shankha is a sacred emblem of The Hindu preserver god Vishnu. It is still used as a trumpet in Hindu ritual, and in the past was used as a war trumpet. The shankha is praised in Hindu scriptures as a giver of fame, longevity and prosperity, the cleanser of sin and the abode of goddess Lakshmi, who is the goddess of prosperity and consort of Vishnu. The shankha is displayed in Hindu art in association with Vishnu. As a symbol of water, it is associated with female fertility and serpents (Nāgas). The shankha (representing the conch of the presiding deity of Padmanabhaswamy Temple is a part of the state emblem of the Indian state of Kerala. The symbol was derived from the erstwhile emblems of the Indian princely state of Travancore, and the Kingdom of Cochin. The shankha is one of the eight a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)