Mathura on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the
 Mathura, which lies at the centre of the cultural region of
Mathura, which lies at the centre of the cultural region of
/ref> which was found in
 Mathura is a holy city in Hinduism and is considered the heart of Brij Bhoomi, the land of Krishna. The twin-city to Mathura is
Mathura is a holy city in Hinduism and is considered the heart of Brij Bhoomi, the land of Krishna. The twin-city to Mathura is
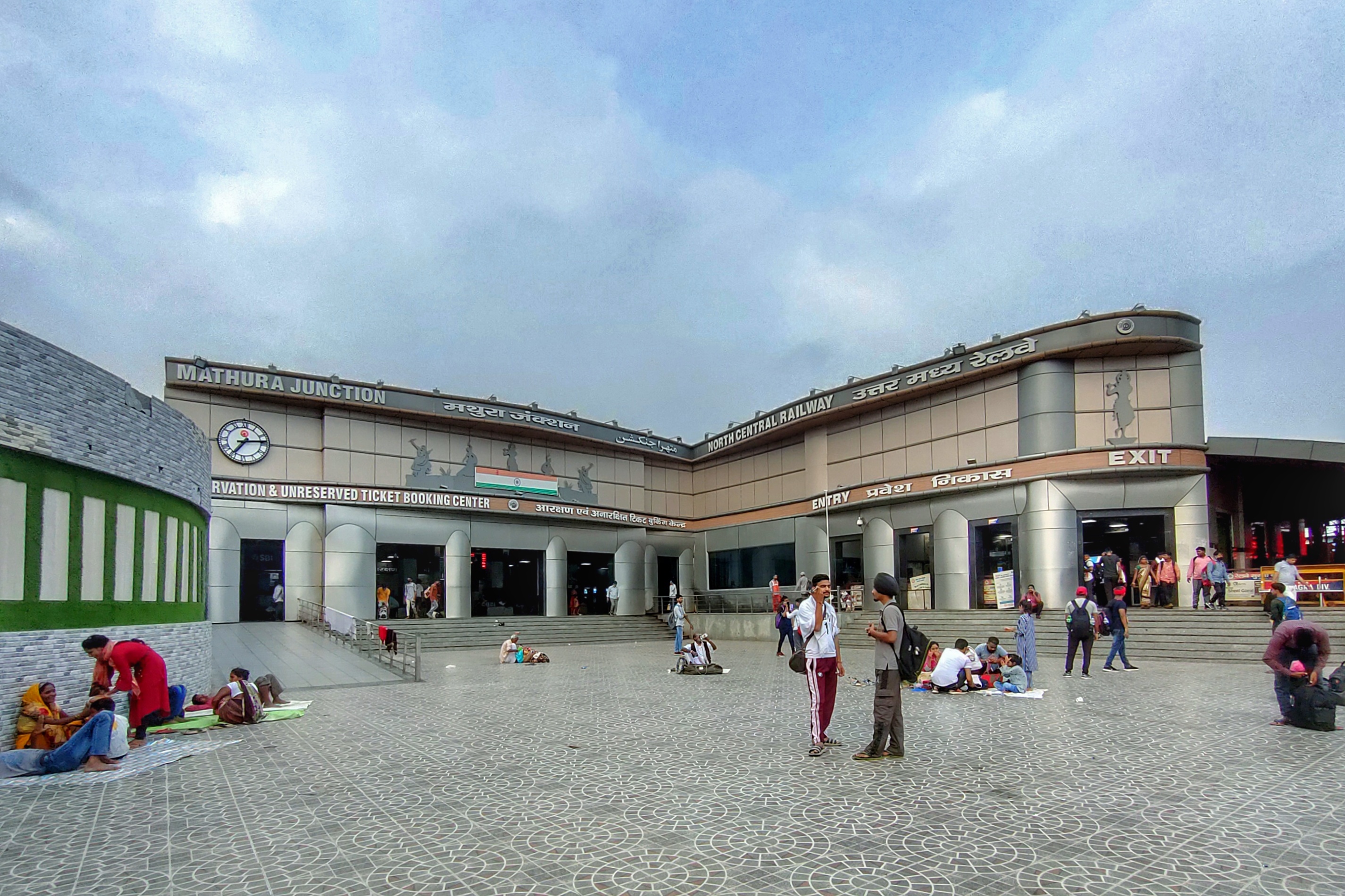 Mathura Junction railway station is situated on the major Delhi-Mumbai rail route. Both Central Railway and Western Railway routes pass through Mathura. Trains from NCR (north-central railway) to ER (eastern railway) also pass through the Mathura junction. Mathura Cantt railway station is a major route for eastern and central railway.
Important trains that originate/terminate at Mathura are:
* Chambal Express, 12177/Howrah – Mathura Chambal Express.
Mathura Junction railway station is situated on the major Delhi-Mumbai rail route. Both Central Railway and Western Railway routes pass through Mathura. Trains from NCR (north-central railway) to ER (eastern railway) also pass through the Mathura junction. Mathura Cantt railway station is a major route for eastern and central railway.
Important trains that originate/terminate at Mathura are:
* Chambal Express, 12177/Howrah – Mathura Chambal Express.
''The Jain stûpa and other antiquities of Mathura''
by Smith, Vincent Arthur, 1848–1920. (1901)
1018: Mahmud Ghazni’s invasion of Mathura
* *
{{Authority control Mathura, Hindu holy cities Hindu pilgrimage sites in India Buddhist pilgrimage sites in India Cities and towns in Mathura district Former capital cities in India Cities in Uttar Pradesh Locations in Hindu mythology Holy cities Ancient Indian cities Hindu pilgrimages Krishna temples Hinduism Krishna Religious tourism in India
Indian state
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indepen ...
of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
. It is located approximately north of Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is ...
, and south-east of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
; about from the town of Vrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance in Hinduism as Krishna spent most of his childho ...
, and from Govardhan
Govardhan also called Giriraj, is a key pilgrimage centre in India and a municipal town; a nagar panchayat; seat of a MLA Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), Member of Legislative Assembly of Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Uttar Pr ...
. In ancient times, Mathura was an economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
hub, located at the junction of important caravan routes. The 2011 Census of India
The 2011 Census of India or the 15th Indian Census was conducted in two phases, house listing and population enumeration. The House listing phase began on 1 April 2010 and involved the collection of information about all buildings. Information ...
estimated the population of Mathura at 441,894.
In Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Mathura is birthplace of Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
, which is located at the Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex. It is one of the Sapta Puri
The Sapta Puri (Sanskrit: सप्त-पुरी ', a Sanskrit meaning "seven cities") are the seven holy pilgrimage centres in India. These are the seven holy pilgrimage sites in Hinduism, which bless the pilgrims with moksha (liberation from ...
, the seven cities considered holy by Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, also called Mokshyadayni Tirth. The Kesava Deo Temple was built in ancient times on the site of Krishna's birthplace (an underground prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correc ...
). Mathura was the capital of the kingdom of Surasena
Kingdom of Surasena (or Sourasena) (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian region corresponding to the present-day Braj region in Uttar Pradesh, with Mathura as its capital city. According to the Buddhist text '' Anguttara Nikaya'', Surasena was on ...
, ruled by Kansa, the maternal uncle of Krishna. Mathura is part of the Lord Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
circuit (Mathura,Vrindavan, Barsana, Govardhan
Govardhan also called Giriraj, is a key pilgrimage centre in India and a municipal town; a nagar panchayat; seat of a MLA Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), Member of Legislative Assembly of Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Uttar Pr ...
, Kurukshetra, Dwarka
Dwarka () is a city and a municipality of Devbhumi Dwarka district in the state of Gujarat in Western India. It is located on the western shore of the Okhamandal Peninsula on the right bank of the Gomti river at the mouth of the Gulf of Kut ...
and Bhalka). Janmashtami
Krishna Janmashtami , also known simply as Krishnashtami, Janmashtami, or Gokulashtami, is an annual Hindu festival that celebrates the birth of Krishna, the eighth avatar of Vishnu. According to the Hindu lunisolar calendar, it is observed ...
is grandly celebrated in Mathura every year.
Mathura has been chosen as one of the heritage cities for the Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana
National Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) was launched on 21 January 2015 with the aim of bringing together urban planning, economic growth and heritage conservation in an inclusive manner to preserve the heritage chara ...
scheme of Government of India.
History
Traditionally it is believed that it was founded by Satrughana after killingYadava
The Yadava (literally, descended from Yadu) were an ancient Indian people who believed to be descended from Yadu, a legendary king of Chandravamsha lineage. The community was formed of various clans, being the Abhira, Andhaka, Vrishni, and Sat ...
Lavana
The Lavana, Lohana , Lobana , Labana, are a Hindu caste found in the states of Rajasthan and Gujarat in India.P
History and origin
The Lavana are a branch of the larger community of North India. They are descent from the Indo-Scythians, and th ...
at the site of Madhuvana. According to Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
it was founded by Madhu
Madhu (Sanskrit: ) is a word used in several Indo-Aryan languages meaning ''honey'' or ''sweet''. It is ultimately derived from Proto-Indo-European ''*médʰu'', whence English '' mead''.
Metaphorical use
''Madhu'' has been used for millennia si ...
(a man of the Yadu tribe). Later on Madhu's son Lavanasura
Lavanasura () is an asura in Hinduism. He is slain by Shatrughna, the youngest brother of Rama, in the Hindu epic Ramayana.
Legend
During Rama's reign, while peace prevailed in most places, Lavanasura continued to torment the innocent and destroy ...
was defeated by Satrughana. Madhu says all the territory of Mathura belongs to Abhiras
The Abhira tribe is mentioned in the ancient Indian epic Mahabharata. A historical people of the same name are mentioned in the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea''. They are thought to be people who moved in from eastern Iran in the aftermath of ...
.
 Mathura, which lies at the centre of the cultural region of
Mathura, which lies at the centre of the cultural region of Braj
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhoomi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura- Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal and Ballabhgarh in Harya ...
has an ancient history and is also believed to be the homeland and birthplace of Krishna, who belonged to the Yadu dynasty. According to the Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexande ...
plaque at the Mathura Museum
__NOTOC__
Government Museum, Mathura, commonly referred to as Mathura museum, is an archaeological museum in Mathura city of Uttar Pradesh state in India. The museum was founded by then collector of the Mathura district, Sir F. S. Growse in 1 ...
, the city is mentioned in the oldest Indian epic, the ''Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
''. In the epic, the Ikshwaku
The Solar dynasty (IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98, 100-/1, 136 The dynasty is ...
prince Shatrughna
''Shatrughna'' ( sa, text=शत्रुघ्न, translit=śatrughna, lit=killer of enemies) is a prince of Ayodhya, King of Madhupura and Vidisha, and a brother of Prince Rama in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is also known as ''Ripudaman' ...
slays a demon called Lavanasura
Lavanasura () is an asura in Hinduism. He is slain by Shatrughna, the youngest brother of Rama, in the Hindu epic Ramayana.
Legend
During Rama's reign, while peace prevailed in most places, Lavanasura continued to torment the innocent and destroy ...
and claims the land. Afterwards, the place came to be known as Madhuvan
Madhu Forest or Madhuvana ( sa, मधुवन) was a dense forest in ancient northern India, west of Yamuna.
In the Ramayana and the Mahabharata
According to the Ramayana, an Asura named ''Madhu'', ruled this forest and its territory. He was def ...
as it was thickly wooded, then Madhupura and later Mathura.Pargiter, F.E. (1972). ''Ancient Indian Historical Tradition'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, p.170. The most important pilgrimage site in Mathura was Katra ('market place'), now referred to as Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
Janmasthan ('the birthplace of Krishna'). Excavations at the site revealed pottery and terracotta dating to the sixth century BCE, the remains of a large Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
complex, including a monastery called Yasha Vihara of the Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by se ...
period, as well as Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
sculptures of the same era.
Ancient history
Archaeological excavations at Mathura show the gradual growth of a village into an important city during theVedic age
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betw ...
. The earliest period belonged to the Painted Grey Ware culture
The Painted Grey Ware culture (PGW) is an Iron Age Indian culture of the western Gangetic plain and the Ghaggar-Hakra valley in the Indian subcontinent, conventionally dated 1200 to 600–500 BCE, or from 1300 to 500–300 BCE It is a successo ...
(1100–500 BCE), followed by the Northern Black Polished Ware
The Northern Black Polished Ware culture (abbreviated NBPW or NBP) is an urban Iron Age Indian culture of the Indian Subcontinent, lasting c. 700–200 BCE (proto NBPW between 1200 and 700 BCE), succeeding the Painted Grey Ware culture and Blac ...
culture (700–200 BCE). Mathura derived its importance as a center of trade due to its location where the northern trade route of the Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
met with the routes to Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syno ...
(central India) and the west coast West Coast or west coast may refer to:
Geography Australia
* Western Australia
*Regions of South Australia#Weather forecasting, West Coast of South Australia
* West Coast, Tasmania
**West Coast Range, mountain range in the region
Canada
* Britis ...
. Archaeologists have discovered a fragment of Mathura red sandstone from Rakhigarhi
Rakhigarhi or Rakhi Garhi is a village and an archaeological site belonging to the Indus Valley civilisation in Hisar District of the northern Indian state of Haryana, situated about 150 km northwest of Delhi. It was part of the mature ph ...
- a site of Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
dated to third millennium BCE - which was used as a grindstone; red sandstone was also a popular material for historic period sculptures.
By the sixth century BCE Mathura became the capital of the Surasena Kingdom. The city was later ruled by the Maurya
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
empire (fourth to second centuries BCE). Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; grc, Μεγασθένης, c. 350 BCE– c. 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, diplomat and Indian ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but ha ...
, writing in the early third century BCE, mentions Mathura as a great city under the name Μέθορα (''Méthora''). It seems it never was under the direct control of the following Shunga
is a type of Japanese erotic art typically executed as a kind of ukiyo-e, often in woodblock print format. While rare, there are also extant erotic painted handscrolls which predate ukiyo-e. Translated literally, the Japanese word ''shunga' ...
dynasty (2nd century BCE) as not a single archaeological remain of a Shunga presence were ever found in Mathura.
The Indo-Greeks
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, or Graeco-Indian Kingdom, also known historically as the Yavana Kingdom (Yavanarajya), was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of Afghanistan and the northwestern r ...
may have taken control, direct or indirect, of Mathura some time between 180 BCE and 100 BCE, and remained so as late as 70 BCE according to the Yavanarajya inscription
The Yavanarajya inscription, also called the Maghera Well Stone Inscription, was discovered in the village of Maghera, 17 kilometers north of Mathura, India in 1988. The Sanskrit inscription, carved on a block of red sandstone, is dated to the 1 ...
,History of Early Stone Sculpture at Mathura: Ca. 150 BCE – 100 CE, Sonya Rhie Quintanilla, BRILL, 2007, p.8-1/ref> which was found in
Maghera
Maghera (pronounced , ) is a small town at the foot of the Glenshane Pass in County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. Its population was 4,220 in the 2011 Census, increasing from 3,711 in the 2001 Census. It is situated within Mid-Ulster Distri ...
, a town from Mathura. The opening of the 3 line text of this inscription in Brahmi script
Brahmi (; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system of ancient South Asia. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' o ...
translates as: "In the 116th year of the Yavana
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for "Ionians" ( grc, ...
kingdom..." or '"In the 116th year of Yavana hegemony" ("''Yavanarajya''") However, this also corresponds to the presence of the native Mitra dynasty of local rulers in Mathura, in approximately the same time frame (150 BCE—50 BCE), possibly pointing to a vassalage relationship with the Indo-Greeks.
Indo-Scythians
After a period of local rule, Mathura was conquered by theIndo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
during the first century BCE. The Indo-Scythian satraps of Mathura are sometimes called the "Northern Satraps
The Northern Satraps (Brahmi: , ''Kṣatrapa'', "Satraps" or , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps"), or sometimes Satraps of Mathura, or Northern Sakas, are a dynasty of Indo-Scythian rulers who held sway over the area of Eastern Punjab and Math ...
", as opposed to the "Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
" ruling in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
and Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syno ...
. However, Indo-Scythian control proved to be short lived, following the reign of the Indo-Scythian ''Mahakshatrapa'' ("Great Satrap") Rajuvula
Rajuvula (Greek ; Brahmi: , ; Kharosthi: , ; , ; , ) was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (''Mahākṣatrapa''), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura in the northern Indian Subcontinent in the years around 10 CE. The M ...
, –25 CE. The Mora Well inscription of Mahakshatrapa Rajuvula
Rajuvula (Greek ; Brahmi: , ; Kharosthi: , ; , ; , ) was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (''Mahākṣatrapa''), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura in the northern Indian Subcontinent in the years around 10 CE. The M ...
, of the early decades of the first century CE, found in a village seven miles from Mathura, stated that images ''pratima(h)'' of the blessed (''bhagavatam'') five Vrishni heroes, were installed in a stone shrine of a person called Tosa. The heroes were identified from a passage in the Vayu Purana
The ''Vayu Purana'' ( sa, वायुपुराण, ) is a Sanskrit text and one of the eighteen major Puranas of Hinduism.
''Vayu Purana'' is mentioned in the manuscripts of the Mahabharata and other Hindu texts, which has led scholars to p ...
as Samkarsana, Vasudev, Pradyumna, Samba, and Aniruddha. The English translation of the inscription read:-
The Mathura inscription of the time of Mahakshatrapa Rajuvula
Rajuvula (Greek ; Brahmi: , ; Kharosthi: , ; , ; , ) was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (''Mahākṣatrapa''), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura in the northern Indian Subcontinent in the years around 10 CE. The M ...
's son, Mahakshatrapa Sodasa
Sodasa ( Kharosthi: , ; Middle Brahmi script: , , also , ) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap and ruler of Mathura during the later part of the 1st century BCE or the early part of 1st century CE. He was the son of Rajuvula, the Great Sat ...
recorded erection of a ''torana'' (gateway), ''vedika'' (terrace) and ''chatuhsala'' (quadrangle) at the ''Mahasthana'' (great place) of Bhagavat Vasudeva. Several male torsos representing the Vrisni heroes were also found in a shrine in Mora dating to the time of Mahakshatrapa Sodasa
Sodasa ( Kharosthi: , ; Middle Brahmi script: , , also , ) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap and ruler of Mathura during the later part of the 1st century BCE or the early part of 1st century CE. He was the son of Rajuvula, the Great Sat ...
.
Kushan Empire
During the rule of the great Kushanas, art and culture flourished in the region and reached new heights and is now famously known as the Mathura School of Art. The Kushans took control of Mathura some time after MahakshatrapaSodasa
Sodasa ( Kharosthi: , ; Middle Brahmi script: , , also , ) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap and ruler of Mathura during the later part of the 1st century BCE or the early part of 1st century CE. He was the son of Rajuvula, the Great Sat ...
, although several of his successors ruled as Kushans vassals, such as the Indo-Scythian "Great Satrap" Kharapallana
Kharapallana (Brahmi: , ; Greek: Ancient Greek: ) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap who ruled around c. 130 CE.
Name
Kharapallana's name is attested in the Greek form ( grc, Χαροβαλανο) and in the Brahmi form , which are derived fr ...
and the "Satrap" Vanaspara
Vanaspara (ruled circa 130 CE) was an Indo-Scythian Northern Satrap (''kshtrapa''). He is mentioned as a "Satrap" (Brahmi:, ''Kṣatrapa'', " Satrap") of Kushan ruler Kanishka I on an inscription discovered in Sarnath, and dated to the 3rd year o ...
, both of whom paid allegiance to the Kushans in an inscription at Sarnath
Sarnath (Hindustani pronunciation: aːɾnaːtʰ also referred to as Sarangnath, Isipatana, Rishipattana, Migadaya, or Mrigadava) is a place located northeast of Varanasi, near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pr ...
, dating to the third year of the reign of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire r ...
CE. Mathuran art and culture reached its zenith under the Kushan dynasty which had Mathura as one of its capitals. The preceding capitals of the Kushans included Kapisa (modern Bagram, Afghanistan), Purushapura
Peshawar (; ps, پېښور ; hnd, ; ; ur, ) is the sixth most populous city in Pakistan, with a population of over 2.3 million. It is situated in the north-west of the country, close to the International border with Afghanistan. It is ...
(modern Peshawar, Pakistan) and Takshasila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area an ...
/Sirsukh
Sirsukh ( ur, سر سکھ) is an ancient city that forms part of the ruins at Taxila, near the modern day city of Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
City
The city of Sirsukh is said to have been founded during the Kushan era after 80 CE, and is the last ...
/ (modern Taxila, Pakistan). Mathura ateliers were most active during the epoch of the great Kushan emperors Kanishka
Kanishka I (Sanskrit: कनिष्क, '; Greco-Bactrian: Κανηϸκε ''Kanēške''; Kharosthi: 𐨐𐨞𐨁𐨮𐨿𐨐 '; Brahmi: '), or Kanishka, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign (c. 127–150 CE) the empire ...
, Huvishka
Huvishka (Kushan: Οοηϸκι, ''Ooēški'', Brahmi: ', '; Kharosthi: 𐨱𐨂𐨬𐨅𐨮𐨿𐨐 ', ') was the emperor of the Kushan Empire from the death of Kanishka (assumed on the best evidence available to be in 150 CE) until the successio ...
, Vasudeva
According to Hindu scriptures, Vasudeva (Sanskrit: वसुदेव, IAST: ''Vasudeva''), also called Anakadundubhi, (''anakas'' and ''dundubhis'' both refer to ''drums'', after the musicians who played these instruments at the time of his ...
whose reign represents the Golden Age of Mathura sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
. During the third century, Nagas ruled Mathura after decline of Kushan Empire.
Gupta Empire
In the reign ofChandragupta Vikramaditya
Chandragupta II (r.c. 376-415), also known by his title Vikramaditya, as well as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, was the third ruler of the Gupta Empire in India, and was one of the most powerful emperors of the Gupta dynasty.
Chandragupta continue ...
, a magnificent temple of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
was built at the site of Katra Keshavadeva. Kalidasa, hailed as the greatest poet and dramatist in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, in the fourth-fifth century CE mentioned the groves of Vrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance in Hinduism as Krishna spent most of his childho ...
and Govardhan
Govardhan also called Giriraj, is a key pilgrimage centre in India and a municipal town; a nagar panchayat; seat of a MLA Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), Member of Legislative Assembly of Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Uttar Pr ...
hill as:
Chinese Buddhist Monk Faxian
Faxian (法顯 ; 337 CE – c. 422 CE), also referred to as Fa-Hien, Fa-hsien and Sehi, was a Chinese Buddhist monk and translator who traveled by foot from China to India to acquire Buddhist texts. Starting his arduous journey about age 60, h ...
mentions the city as a centre of Buddhism about 400 CE. He found the people were very well off, there were no taxes other than for those on farmers who tilled the royal land. He found that people did not kill animals, no one consumed wine, and did not eat onion or garlic. He found that engraved title deeds were issued to land owners. Visiting priests were provided with accommodation, beds, mats, food, drinks and clothes to perform scholarly works.
Harsha Empire
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of ...
, who visited the city in 634 CE, mentions it as Mot'ulo, recording that it contained twenty Buddhist monasteries and five Hindu temples. (Mathura) Later, he went east to Thanesar
Thanesar city or old Kurukshetra city is a historic town and an important Hindu pilgrimage centre in Kurukshetra district of the state of Haryana in northern India. It is located in Kurukshetra district, approximately 160 km northwest of D ...
, Jalandhar
Jalandhar is the third most-populous city in the Indian state of Punjab and the largest city in Doaba region. Jalandhar lies alongside the Grand Trunk Road and is a well-connected rail and road junction. Jalandhar is northwest of the state ...
in the eastern Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
, before climbing up to visit predominantly Theravada
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
monasteries in the Kulu valley
Kullu is a municipal council town that serves as the administrative headquarters of the Kullu district of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. It is located on the banks of the Beas River in the Kullu Valley about north of the airport at B ...
and turning southward again to Bairat
Viratnagar previously known as Bairat ( IAST: ) or Bairath ( IAST: ) is a town in northern Jaipur district of Rajasthan, India.
History
Ancient era
According to Huen Tsang, visitor to China, Tonk was under Bairath State or Viratnagar p ...
and then Mathura, on the Yamuna river
The Yamuna ( Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Ban ...
.
Medieval History and Islamic Invasions
Early Middle Ages
The famous femaleAlvar
An alvar is a biological environment based on a limestone plain with thin or no soil and, as a result, sparse grassland vegetation. Often flooded in the spring, and affected by drought in midsummer, alvars support a distinctive group of prair ...
saint, Andal visualized going to a pilgrimage which began at Mathura, then proceeded to Gokul
Gokul is a town in the Mathura district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Mathura. According to Bhagavata Purana, Krishna spent his childhood in Gokul.
Geography
The town has an average elevation of .
Demo ...
, the Yamuna
The Yamuna (Hindustani language, Hindustani: ), also spelt Jumna, is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in List of major rivers of India, India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a ...
, the pool of Kaliya, Vrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance in Hinduism as Krishna spent most of his childho ...
, Govardhan
Govardhan also called Giriraj, is a key pilgrimage centre in India and a municipal town; a nagar panchayat; seat of a MLA Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), Member of Legislative Assembly of Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, Uttar Pr ...
, and finished at Dwarka
Dwarka () is a city and a municipality of Devbhumi Dwarka district in the state of Gujarat in Western India. It is located on the western shore of the Okhamandal Peninsula on the right bank of the Gomti river at the mouth of the Gulf of Kut ...
. The eleventh century Kashmiri poet, Bilhana
Kaviraj, Kavi Bilhana was an 11th-century Kashmiri Pandits, Kashmiri poet. He is known for his love poem, the ''Caurapañcāśikā''.
According to legend, Bilhana fell in love with the daughter of King Madanabhirama, Princess Yaminipurnatilaka, ...
visited Mathura and Vrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance in Hinduism as Krishna spent most of his childho ...
after leaving Kashmir en route to Karnataka.
High Middle Ages
The city was sacked and many of its temples destroyed byMahmud of Ghazni
Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
in 1018 CE. The capture of Mathura by Maḥmūd Ibn Sebüktegīn is described by the historian al-Utbi (Abu Nasr Muhammad ibn Muhammad al Jabbaru-l 'Utbi) in his work Tarikh Yamini
The Tarikh i Yamini, or Kitab i Yamini, written in Arabic in an embellished, flowery rhetorical rhymed prose, is a history of the reigns of Sebuktigin and Mahmud.
Written by the historian Abu Nasr Muhammad ibn Muhammad al Jabbaru-l 'Utbi (or ''al ...
as follows:
The temple at Katra was sacked by Maḥmūd Ibn Sebüktegīn. A temple was built to replace it in 1150 CE. The Mathura ''prasasti'' (Eulogistic Inscription) dated Samvat (V.S.) 1207 (1150 CE), said to have been found in 1889 CE at the Keshava mound by Anton Fuhrer, German Indologist who worked with the Archaeological Survey of India, recorded the foundations of a temple dedicated to Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
at the Katra site:
Jajja was a vassal of the Gahadavalas in charge of Mathura, and the committee mentioned in the ''prasasti'' could have been of an earlier Vaishnava
Vaishnavism ( sa, वैष्णवसम्प्रदायः, Vaiṣṇavasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. It is also called Vishnuism since it considers Vishnu as the ...
temple. The temple built by Jajja at Katra was destroyed by the forces of Qutubuddin Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak ( fa, قطبالدین ایبک), (1150 – 14 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid king Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in ...
, though Firuz Shah Tughlaq, Feroz Tughlaq (r. 1351–88 CE) was also said to have attacked it. It was repaired and survived till the reign of Sikandar Lodi (r. 1489–1517 CE).
In the twelfth century, Bhatta Lakshmidhara, chief minister of the Gahadavala dynasty, Gahadavala king Govindachandra (Gahadavala dynasty), Govindachandra (r. 1114–1155 CE), wrote the earliest surviving collection of verses in praise of the sacred sites of Mathura in his work Krtyakalpataru, which has been described as "the first re-statement of the theory of ''Tirtha-yatra'' (pilgrimage)". In his Krtyakalpataru, Bhatta Lakshmidhara devoted an entire section (9) to Mathura.
Later on the city was sacked again by Sikandar Lodi, who ruled the Sultanate of Delhi from 1489 to 1517 CE. Sikandar Lodi earned the epithet of 'Butt Shikan', the 'Destroyer of Idols'. Firishta, Ferishta recorded that Sikandar Lodi was a staunch Muslim, with a passion for vandalizing heathen temples:
In Tarikh-i Daudi, of 'Abdu-lla (written during the time of Jahangir) said of Sikandar Lodi:
Vallabhacharya and Chaitanya Mahaprabhu arrived in the Braj region, in search of sacred places that had been destroyed or lost. In ''Shrikrsnashrayah'', that make up the ''Sodashagrantha'', Vallabha said of his age:
Late Middle Ages
The Portuguese people, Portuguese, Father Antonio Monserrate (1536 CE-1600 CE), who was on a Jesuit mission at the Mughal Court during the times of Akbar, visited Mathura in 1580–82, and noted that all temples built at sites associated with the deeds ofKrishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
were in ruins:-
The Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex, Keshavadeva temple was rebuilt by the Bundela Rajput Rajah Vir Singh Deo at a cost of thirty-three lakh rupees when the gold was priced at around ₹ 10/- per Tola (unit), ''tola''. And the grand structure of the temple in Mathura was regarded a "wonder of the age".
The Mughal Empire, Mughal Aurangzeb, Emperor Aurangzeb, built the Shahi-Eidgah Mosque during his rule, which is adjacent to Shri Krishna Janmabhoomi believed to be over a Hindu temple. He also changed the city's name to Islamabad. In 1669, Aurangzeb issued a general order for the demolition of Hindu schools and temples, in 1670, specifically ordered the destruction of the Keshavadeva temple. Saqi Mustaid Khan recorded:
The Muslim conquest resulted in the destruction of all Buddhism, Buddhist, Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
, and Hinduism, Hindu temples and monuments in and around Mathura. Buddhism, already in decline, never revived, and for the next four hundred years the Jainism, Jains and Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
were unable to erect any temples that were not sooner or later demolished. Many of the sites that had been places of religious importance were abandoned and gradually sank beneath the earth. But some of them were not forgotten, owing to the persistence of oral tradition, the refashioning of a temple into a mosque, or the presence of humble shrines, some of which housed sculptural fragments of earlier buildings. Several of them have survived as places of significance in the modern pilgrimage circuit.
"The rebellion in Mathurá district seems to have gained ground. 'On the 14th Rajab, 1080, [28 November 1669], his Majesty left Dihlí for Akbarábád, and almost daily enjoyed the pleasures of the chase. On the 21st Rajab, whilst hunting, he received the report of a rebellion having broken out at Mauza' Rewarah, Chandarkah, and Surkhrú. Hasan 'Ali Khán was ordered to attack the rebels at night, which he did, and the firing lasted till 12 o'clock the next day. The rebels, unable longer to withstand, thinking of the honour of their families, now fought with short arms, and many imperial soldiers and companions of Hasan ’Alí were killed. Three hundred rebels were sent to perdition, and two hundred and fifty, men and women, caught. Hasan ’Alí, in the afternoon, reported personally the result of the fight, and was ordered to leave the prisoners and the cattle in charge of Sayyid Zain ul-'Abidin, the jágirdár of the place. Çaf Shikan Khán also (who after ’Abdunnabí's death had been appointed Faujdár of Mathura) waited on the emperor, and was ordered to tell off two hundred troopers to guard the fields attached to the villages, and prevent soldiers from plundering and kidnapping children. Námdár Khán, Faujdár of Murádábád, also came to pay his respects. Çafshikan Khán was removed from his office, and Hasan 'Ali Khán was appointed Faujdár of Mathura, with a command of Three Thousand and Five Hundred, 2000 troopers, and received a dress of honour, a sword, and a horse. * * * On the 18th Sha'bán [1st January, 1670), his Majesty entered Agrah. Kokilá Ját, the wicked ringleader of the rebels of District*......, who had been the cause of ’Abdunnabí's death and who had plundered Parganah Sa'dábád, was at last caught by Hasan ’Alí Khán and his zealous peshkár, Shaikh Razíuddin, and he was now sent with the Shaikh to Agrah, where by order of his Majesty he was executed. Kokila's son and daughter were given to Jawahir Khán Nazir [a eunuch]. The girl was later married to Shah Quli, the well-known Chelah; and his son, who was called Fázil, became in time so excellent a Hafiz [one who knows the Qorán by heart], that his Majesty preferred him to all others and even chaunted passages to him. Shaikh Razíuddin, who had captured Kokila, belonged to a respectable family in Bhagalpur, Bihár, and was an excellent soldier, administrator, and companion; he was at the same time so learned, that he was ordered to assist in the compilation of the Fatáwá i 'Alamgiri [the great code of Muhammadan laws]. He received a daily allowance of three rupees.'+ (Haásir i ’Alamgiri, pp. 92 to 91.) Hasan ’Alí Khán retained his office from 1080 to Sha'bán 1087 (October, 1676), when Sulțán Qulí Khán was appointed Faujdír of Mathurá.", Asiatic Society of Bengal, ''Proceedings''
Early Modern History
According the biographer of Raja Jai Singh II, Jai Singh, Atmaram, when Jai Singh was campaigning against the Jat Raja Churaman, Churaman Singh, he bathed at Radha ''kund'' on the full moon of Kartik, went to Mathura in the month of Shravan in 1724, and performed the marriage of his daughter on Krishna Janmashtami, ''Janmashtami''. He then undertook a tour of the sacred forests ofBraj
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhoomi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura- Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal and Ballabhgarh in Harya ...
, and, on his return to Mathura, founded religious establishments and celebrated Holi.
Pilgrimage by the Family of Peshwa of Maratha Empire
During the period of the expansion of Maratha Empire, pilgrimage to the holy places in the north became quite frequent. Pilgrims required protection on the way and took advantage of the constant movement of troops that journeyed to and back from their homeland for military purposes. That is how the practice arose of ladies accompanying military expeditions. The mother of Peshwa Balaji Baji Rao, Kashibai, Kashitai performed her famous pilgrimage for four years in the north, visiting Mathura, Prayagraj, Prayag, Ayodhya, Varanasi, Banaras, and other holy places.Religious heritage
Vrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance in Hinduism as Krishna spent most of his childho ...
.
There are many places of historic and religious importance in Mathura and its neighbouring towns.
Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex is an important group of temples built around what is considered to be the birthplace of Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
. The temple complex contains Keshav Deva temple, Garbha Griha shrine, Bhagavata Bhavan and the Rangabhoomi where the final battle between Krishna and Kans took place.
The Dwarkadheesh temple Mathura, Dwarkadheesh Temple is one of the largest temples in Mathura. Vishram Ghat at the bank of river Yamuna is said to be the place were Krishna had rested after killing Kans.
Other notable Hindu religious sites and heritage locations includes the Gita Mandir, Govind Dev temple, ISKCON temple, Kusum Sarovar, Naam yog Sadhna Mandir, Peepleshwar Mahadeo Temple and Yum Yamuna Temple
Kankali Tila brought forth many treasures of Jain art. The archaeological findings testify the existence of two Jain temples and stupas. Numerous Jain sculptures, Ayagapatas (tablet of homage), pillars, crossbeams and lintels were found during archaeological excavations. Some of the sculptures are provided with inscriptions that report on the contemporary society and organization of the Jain community.
Most sculptures could be dated from the second century BC to the 12th century CE, thus representing a continuous period of about 14 centuries during which Jainism flourished at Mathura. These sculptures are now housed in the Lucknow State Museum and in the Mathura Museum.
The Mathura Museum
__NOTOC__
Government Museum, Mathura, commonly referred to as Mathura museum, is an archaeological museum in Mathura city of Uttar Pradesh state in India. The museum was founded by then collector of the Mathura district, Sir F. S. Growse in 1 ...
is notable for archaeological artefacts, especially those from the Kushan Empire, Kushan and Gupta
Gupta () is a common surname or last name of Indian origin. It is based on the Sanskrit word गोप्तृ ''goptṛ'', which means 'guardian' or 'protector'. According to historian R. C. Majumdar, the surname ''Gupta'' was adopted by se ...
empires. It has sculptures associated with Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.
Festivals
Krishna Janmashtami is grandly celebrated every year in Mathura. Every year 3 to 3.5 million devotees celebrate Janmashtami in Mathura, with the maximum number of devotees visiting the Keshav Deva temple and the Dwarkadheesh temple. Devotees generally observe a fast and break it at midnight when Krishna was believed to have been born. Devotional songs, dance performances, bhog and aartis are observed across Mathura-Vrindavan.Geography
Mathura is located at . It has an average elevation of 174 metres (570 foot (length), feet).Climate
Demographics
The 2011 census of India estimates the population of Mathura to be 441,894, with a decadal growth rate of 22.53 per cent. Males account for 54% (268,445) and females for 46% (173,449) of this population. Sex ratio of Mathura is 858 females per 1000 males, which has increased from 840 (2001). However, national sex ratio is 940. Population density in 2011 has increased from 621 per km2 in 2001 to 761 per km2. Mathura has an average literacy rate of 72.65 per cent which has increased from 61.46 percent (2001) but still lower than the national average of 74.04 per cent. Male and female literacy rate are 84.39 and 58.93 per cent respectively. 15.61 percent of Mathura's population is under 6 years of age. This figure was 19.56 per cent in 2001 census.Languages
According to the 2011 census on Mathura NPP, 95.4% of the people identified as Hindi speakers, 2.6% as Urdu speakers and 1.4% as speakers of Braj Bhasha (the local dialect). The city also lies within the cultural region ofBraj
Braj, also known as Vraj, Vraja, Brij or Brijbhoomi, is a region in India on both sides of the Yamuna river with its centre at Mathura- Vrindavan in Uttar Pradesh state encompassing the area which also includes Palwal and Ballabhgarh in Harya ...
.
Government and politics
Actress turned political leader, Hema Malini is the sitting MP of holy constituency Mathura in Uttar Pradesh.Transportation
Rail
 Mathura Junction railway station is situated on the major Delhi-Mumbai rail route. Both Central Railway and Western Railway routes pass through Mathura. Trains from NCR (north-central railway) to ER (eastern railway) also pass through the Mathura junction. Mathura Cantt railway station is a major route for eastern and central railway.
Important trains that originate/terminate at Mathura are:
* Chambal Express, 12177/Howrah – Mathura Chambal Express.
Mathura Junction railway station is situated on the major Delhi-Mumbai rail route. Both Central Railway and Western Railway routes pass through Mathura. Trains from NCR (north-central railway) to ER (eastern railway) also pass through the Mathura junction. Mathura Cantt railway station is a major route for eastern and central railway.
Important trains that originate/terminate at Mathura are:
* Chambal Express, 12177/Howrah – Mathura Chambal Express.
Road
Mathura is well-connected by road to the rest of India. National highways of India, National Highway NH-19(previously National Highway 2 (India), NH-2) from Delhi to Kolkata, with diversion for Chennai also passes through Mathura. Yamuna Expressway from Greater-Noida to Agra (165 km 6 lane access controlled express highway) also passes through, providing good connectivity to Noida, Agra, Kanpur and Lucknow.Tram
A tram network has been proposed in the city, which would make Mathura the second only city in India (besides Kolkata) to have a functional tram transport. In 2017, the local MLA Shrikant Sharma announced that the trams will be operational in Mathura andVrindavan
Vrindavan (; ), also spelt Vrindaban and Brindaban, is a historical city in the Mathura district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located in the Braj Bhoomi region and holds religious importance in Hinduism as Krishna spent most of his childho ...
by 2018.
Air
Currently the city has no airport. The nearest airports are the Agra Airport (about 60 km away) and the Indira Gandhi International Airport, Delhi Airport (about 160 km away) with major national and international air routes.The under-construction Jewar Airport in Greater Noida is approximately 75 km from Mathura and is expected to be country's largest airport when fully operational. Land has been earmarked, and construction is in progress near the Yamuna Expressway, with plans to open in the next five years with regular flights to major national and international air routes in future. In 2012, the then civil aviation minister Ajit Singh (Indian politician), Ajit Singh suggested Mathura's name for the site of a new greenfield international airport to the then chief minister ofUttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, Akhilesh Yadav. Mathura's name came to note when a group of ministers terminated the plan of building Taj International Airport at Agra.
Strategic importance
I Corps (India), I Corps (Strike Formation) within the Indian Army's Central Command (India), Central Command is based in Mathura, hosting Strike I Corps headquarters in a large classified area in the outskirts of the city known as Mathura Cantonment (Central Command is headquartered in Lucknow). It hosts Strike Infantry units, air defence units, armoured divisions, engineer brigades, artillery Units, and classified units of Strategic Forces Command. The I Corps is primarily responsible for the western borders of India. In 2007 during Exercise Ashwamedha, all the armoured, artillery, and infantry divisions performed a simulation of an overall NBC (nuclear-chemical-biological) environment. The aim was to show operational ability in high intensity, short duration and 'sudden' battleIndustries
Mathura Refinery located in the city is one of the biggest oil refineries of Asia with a refining capacity of 8.0 million tonnes per year. This oil refinery of Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. is a technologically advanced oil refinery and provides local employment opportunities as well. Its main focus is to meet the demands from the National Capital Region (India), NCR. The refinery had undertaken projects to upgrade its diesel and gasoline units to bring Sulphur levels down by nearly 80 percentMedia and communications
The city has a local station of the All India Radio.Educational institutions
* GLA University * Sachdeva Institute of Technology * Sanskriti University * U.P. Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Veterinary Science University and Cattle Research InstituteSee also
* Mathur (disambiguation) * Brij Bhoomi *Gokul
Gokul is a town in the Mathura district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Mathura. According to Bhagavata Purana, Krishna spent his childhood in Gokul.
Geography
The town has an average elevation of .
Demo ...
* Kankali Tila
* Nandgaon, Uttar Pradesh, Nandgaon
* Goverdhan
* Saunkh, Sonkh
References
Citations
Sources
* Mathura-The Cultural Heritage. Edited by Doris Meth Srinivasan, published in 1989 by AIIS/Manohar. * Konow, Sten. Editor. 1929. ''Kharoshthī Inscriptions with Exception of those of Ashoka''. Corpus Inscriptionum Indicarum, Vol. II, Part I. Reprint: Indological Book House, Varanasi, 1969. * Mukherjee, B. N. 1981. ''Mathurā and its Society: The Śaka-Pahlava Phase''. Firma K. L. M. Private Limited, Calcutta. * Sharma, R. C. 1976. ''Mathura Museum and Art''. 2nd revised and enlarged edition. Government Museum, Mathura. * Growse, F. S. 1882. " Mathura A District Memoir. * Drake-Brockman, D. L. 1911. "Muttra A Gaztteer".''The Jain stûpa and other antiquities of Mathura''
by Smith, Vincent Arthur, 1848–1920. (1901)
1018: Mahmud Ghazni’s invasion of Mathura
* *
External links
{{Authority control Mathura, Hindu holy cities Hindu pilgrimage sites in India Buddhist pilgrimage sites in India Cities and towns in Mathura district Former capital cities in India Cities in Uttar Pradesh Locations in Hindu mythology Holy cities Ancient Indian cities Hindu pilgrimages Krishna temples Hinduism Krishna Religious tourism in India