|
Hideki Yukawa
was a Japanese theoretical physicist and the first Japanese Nobel laureate for his prediction of the pi meson, or pion. Biography He was born as Hideki Ogawa in Tokyo and grew up in Kyoto with two older brothers, two older sisters, and two younger brothers. He read the Confucian ''Doctrine of the Mean'', and later Lao-Tzu and Chuang-Tzu. His father, for a time, considered sending him to technical college rather than university since he was "not as outstanding a student as his older brothers". However, when his father broached the idea with his middle school principal, the principal praised his "high potential" in mathematics and offered to adopt Ogawa himself in order to keep him on a scholarly career. At that, his father relented. Ogawa decided against becoming a mathematician when in high school; his teacher marked his exam answer as incorrect when Ogawa proved a theorem but in a different manner than the teacher expected. He decided against a career in experimental physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Member Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki Ramakrishnan (2003), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
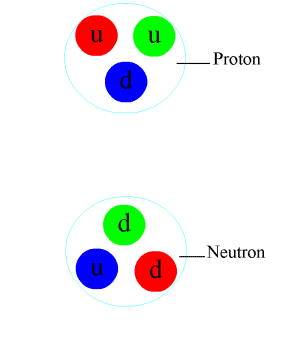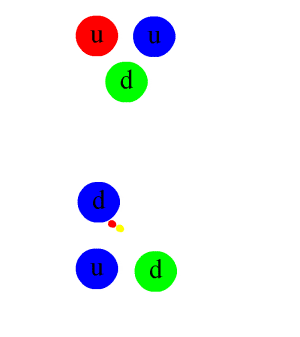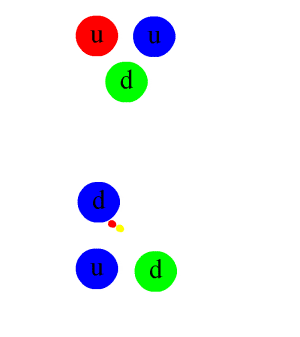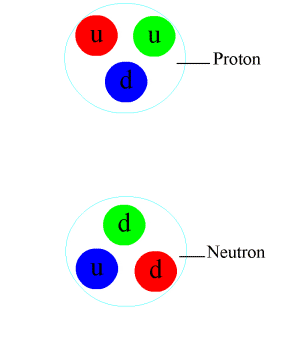
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ratio). Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons" (particles present in atomic nuclei). One or more protons are present in the nucleus of every atom. They provide the attractive electrostatic central force which binds the atomic electrons. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as the atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z''). Since each element has a unique number of protons, each element has its own unique atomic number, which determines the number of atomic electrons and consequently the chemical characteristics of the element. The word ''proton'' is Greek for "first", and this name was given to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meson
In particle physics, a meson ( or ) is a type of hadronic subatomic particle composed of an equal number of quarks and antiquarks, usually one of each, bound together by the strong interaction. Because mesons are composed of quark subparticles, they have a meaningful physical size, a diameter of roughly one femtometre (10 m), which is about 0.6 times the size of a proton or neutron. All mesons are unstable, with the longest-lived lasting for only a few hundredths of a microsecond. Heavier mesons decay to lighter mesons and ultimately to stable electrons, neutrinos and photons. Outside the nucleus, mesons appear in nature only as short-lived products of very high-energy collisions between particles made of quarks, such as cosmic rays (high-energy protons and neutrons) and baryonic matter. Mesons are routinely produced artificially in cyclotrons or other particle accelerators in the collisions of protons, antiprotons, or other particles. Higher-energy (more massive) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. Particles currently thought to be elementary include electrons, the fundamental fermions ( quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons, which generally are matter particles and antimatter particles), as well as the fundamental bosons ( gauge bosons and the Higgs boson), which generally are force particles that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be elementary particles – ''atomos'' meaning "unable to be cut" in Greek – although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1905, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Subatomic constituents of the atom were first identified in the early 1930s; the electron and the proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena. The advancement of science generally depends on the interplay between experimental studies and theory. In some cases, theoretical physics adheres to standards of mathematical rigour while giving little weight to experiments and observations.There is some debate as to whether or not theoretical physics uses mathematics to build intuition and illustrativeness to extract physical insight (especially when normal experience fails), rather than as a tool in formalizing theories. This links to the question of it using mathematics in a less formally rigorous, and more intuitive or heuristic way than, say, mathematical physics. For example, while developing special relativity, Albert Einstein was concerned wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuang Zhou
Zhuang Zhou (), commonly known as Zhuangzi (; ; literally "Master Zhuang"; also rendered in the Wade–Giles romanization as Chuang Tzu), was an influential Chinese philosopher who lived around the 4th century BCE during the Warring States period, a period of great development in Chinese philosophy, the Hundred Schools of Thought. He is credited with writing—in part or in whole—a work known by his name, the ''Zhuangzi'', which is one of the foundational texts of Taoism. Life The only account of the life of Zhuangzi is a brief sketch in chapter 63 of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'', and most of the information it contains seems to have simply been drawn from anecdotes in the ''Zhuangzi'' itself. In Sima's biography, he is described as a minor official from the town of Meng (in modern Anhui) in the state of Song, living in the time of King Hui of Liang and King Xuan of Qi (late fourth century BC). Sima Qian writes that Chuang-Tze was especially influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lao-Tzu
Laozi (), also known by numerous other names, was a semilegendary ancient Chinese Taoist philosopher. Laozi ( zh, ) is a Chinese honorific, generally translated as "the Old Master". Traditional accounts say he was born as in the state of Chu in the 6th centuryBC during China's Spring and Autumn Period, served as the royal archivist for the Zhou court at Wangcheng (modern Luoyang), met and impressed Confucius on one occasion, and composed the ''Tao Te Ching'' before retiring into the western wilderness. Chinese folk religion considers he then became an immortal hermit or a god of the celestial bureaucracy under the name Laojun, one of the Three Pure Ones. A central figure in Chinese culture, Laozi is generally considered the founder of philosophical and religious Taoism. He was claimed and revered as the ancestor of the 7th10th century Tang dynasty and similarly honored by modern Chinese with the surname Li. His work had a profound influence on subsequent Chinese re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctrine Of The Mean
The ''Doctrine of the Mean'' or ''Zhongyong'' is one of the Four Books of classical Chinese philosophy and a central doctrine of Confucianism. The text is attributed to Zisi (Kong Ji), the only grandson of Confucius (Kong Zi). It was originally a chapter in the ''Classic of Rites''. The phrase "doctrine of the mean" first occurs in Book VI, verse 29 of the '' Analects'' of Confucius, which states: The ''Analects'' never expands on what this term means, but Zisi's text, ''The Doctrine of the Mean'', explores its meaning in detail, as well as how to apply it to one's life. The application of Confucian metaphysics to politics and virtue ethics. The text was adopted into the canon of the Neo-Confucian movement, as compiled by Zhu Xi. While Burton Watson translated ''Zhōngyōng'' as ''Doctrine of the Mean'', other English-language translators have rendered it differently. James Legge called it ''Constant Mean'', Pierre Ryckmans (aka Simon Leys) used ''Middle Way'', while Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural processes wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)