|
Herki (tribe)
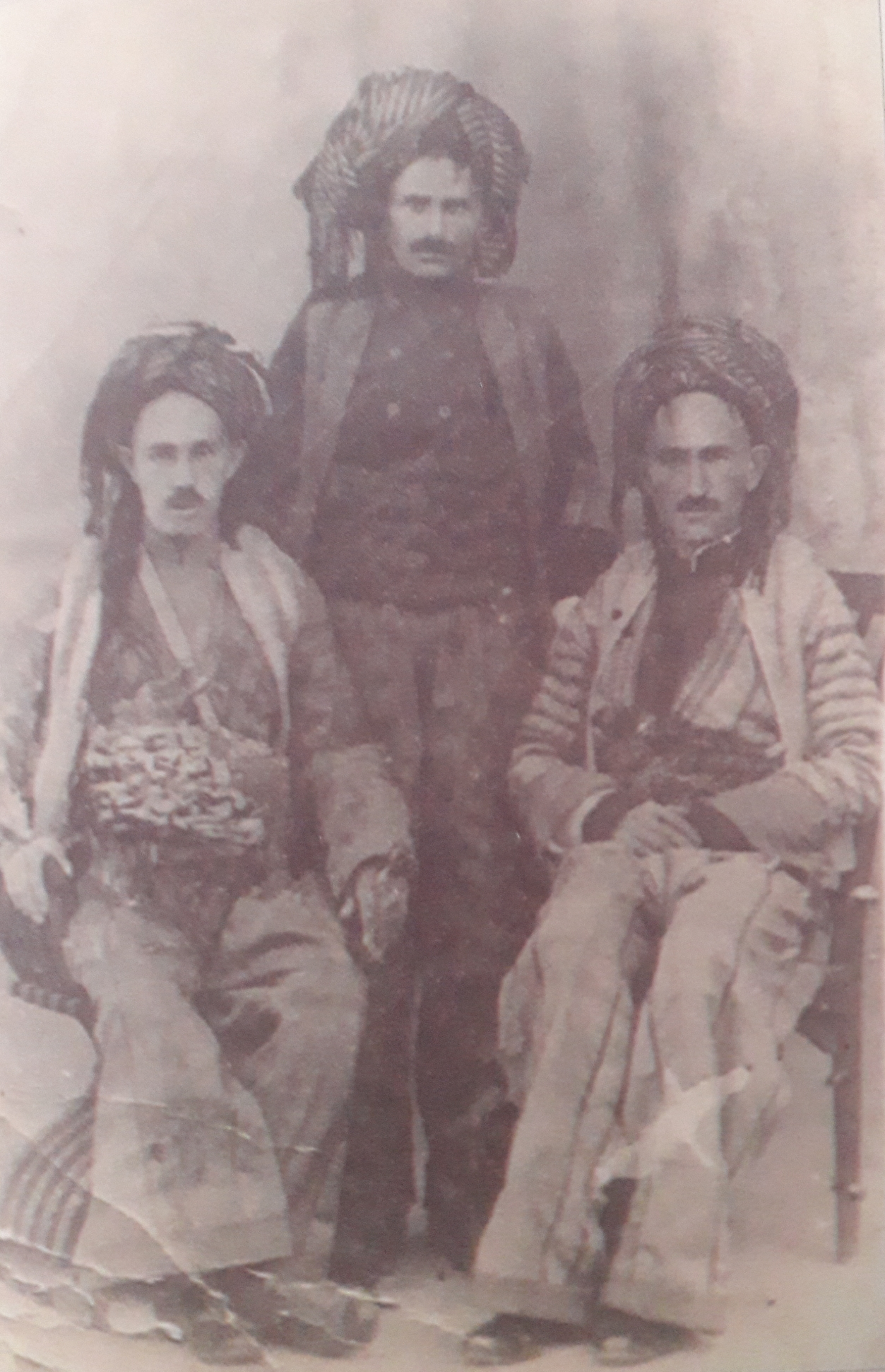
Herki, also spelled Harki () is a large tribe in Kurdistan. The largest part of this tribe live in Iraqi Kurdistan and a significant number live in Iranian Kurdistan. They are also found in Northern Kurdistan. Sub-tribes The Herkis are divided in three sub-tribes: Menda, Sida and Serhati. History According to tradition, the Herkis descend from a man named Babekr Agha. There are claims, however, like that of Dr.Zirar Siddiq Tewfiq, author of the book ''The Kurdish Tribes and Tribal Leaders in the Middle Ages,'' believes that the Harkis were present in the middle ages, possibly as 'Arji'. It seems that the Arji dwelt around Amadiya during the Abbasid period. An attested individual who belonged to the Arji is a man named Baw Al-Arji, who was one of Abu'l-Haija bin Abdullah Al-Hakkari's men, a contemporary of Imad al-Din Zengi. However, this is unlikely, considering the tribe's family tree from the founder till recent times does not go that far into the past. , in his masterpiece , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, Kurdish languages, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros Mountains, Zagros and the eastern Taurus Mountains, Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey (Turkish Kurdistan, Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Iraqi Kurdistan, Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran (Iranian Kurdistan, Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria (Syrian Kurdistan, Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern South Caucasus, Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalism, Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraqi Kurdistan
Iraqi Kurdistan or Southern Kurdistan ( ku, باشووری کوردستان, Başûrê Kurdistanê) refers to the Kurdish-populated part of northern Iraq. It is considered one of the four parts of "Kurdistan" in Western Asia, which also includes parts of southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdistan), northern Syria (Western Kurdistan), and northwestern Iran (Eastern Kurdistan). Much of the geographical and cultural region of Iraqi Kurdistan is part of the Kurdistan Region (KRI), an autonomous region recognized by the Constitution of Iraq. As with the rest of Kurdistan, and unlike most of the rest of Iraq, the region is inland and mountainous. Etymology The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan'' is an Iranian term for region. The literal translation for Kurdistan is "Region of Kurds". The name was also formerly spelled ''Curdistan''. One of the ancient names of Kurdistan is '' Corduene''.A.D. Lee, ''The Role of Hostages in Roman Diplomacy with Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Kurdistan
Iranian Kurdistan or Eastern Kurdistan ( ku, ڕۆژھەڵاتی کوردستان, translit=Rojhilatê Kurdistanê) is an unofficial name for the parts of northwestern Iran with either a majority or sizable population of Kurds. Geographically, it includes the West Azerbaijan Province, Kurdistan Province, Kermanshah Province, Ilam Province and parts of Hamadan Province and Lorestan Province. In totality, Kurds are about 10% of Iran's total population. According to the last census conducted in 2006, the four main Kurdish-inhabited provinces in Iran – West Azerbaijan, Kermanshah Province, Kurdistan Province and Ilam Province – had a total population of 6,730,000. Kurds generally consider northwestern Iran (Eastern Kurdistan) to be one of the four parts of a Greater Kurdistan, which under that conception are joined by parts of southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdistan), northern Syria (Western Kurdistan), and northern Iraq (Southern Kurdistan). Outside the traditional Kurdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Kurdistan
Turkish Kurdistan or Northern Kurdistan () refers to the southeastern part of Turkey, where Kurds form the predominant ethnic group. The Kurdish Institute of Paris estimates that there are 20 million Kurds living in Turkey, the majority of them in the southeast. Southeastern Turkey (Northern Kurdistan) is considered to be one of the four parts of Kurdistan, which also includes parts of northern Syria (Western Kurdistan), northern Iraq (Southern Kurdistan) and northwestern Iran (Eastern Kurdistan). The term Turkish Kurdistan is often used in the context of Kurdish nationalism, which makes it a controversial term among proponents of Turkish nationalism. The term has different meaning depending on context. Geography The Encyclopaedia of Islam delineates the geography of Turkish Kurdistan as following: Nonetheless, it is emphasized that "the imprecise limits of the frontiers of Kurdistan hardly allow an exact appreciation of the area." The region forms the south-eastern edge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amadiya
Amedi or Amadiya ( ku, ئامێدی, Amêdî, ; Syriac: , Amədya), is a town in the Duhok Governorate of Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It is built on a mesa in the broader Great Zab river valley. Etymology According to Ali ibn al-Athir, the name Amadiya is eponymous to Imad al-Din Zengi who built a fortress there in 1142. Another theory is that the name is named after Imad al-Dawla, but this theory is less likely. According to Professor Jeffrey Szuchman, Amedi is of Hurrian or Urartian origin. History From Early Bronze Age until it came under the control of the Mitanni Empire in the 16th century BCE, Amedi region was part of the kingdom of Kurda and it was entirely inhabited by non Semitic Subarians. During the rule of the Mittanian Empire the inhabitants of this region were known as Zubarians. After the fall of the Mittanian Empire, the city of Amedi was conquered by Ashurnasirpal I of Assyria in 11th century BCE after he fought the Nairi and Barzani people. After the fall of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian Empire, Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture and List of inventions in the medieval Islamic world, invention in what became known as the Islamic Golden Age, Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imad Al-Din Zengi
Imad al-Din Zengi ( ar, عماد الدین زنكي; – 14 September 1146), also romanized as Zangi, Zengui, Zenki, and Zanki, was a Turkmen atabeg, who ruled Mosul, Aleppo, Hama, and, later, Edessa. He was the namesake of the Zengid dynasty. Early life Zengi's father, Aq Sunqur al-Hajib, governor of Aleppo under Malik-Shah I, was beheaded by Tutush I for treason in 1094. At the time, Zengi was about 10 years old and brought up by Kerbogha, the governor of Mosul. Zengi against Damascus Following the death in 1128 of Toghtekin, ''atabeg'' of Damascus, a power vacuum threatened to open Syria to renewed Crusader aggression. Zengi became ''atabeg'' of Mosul in 1127 and of Aleppo in 1128, uniting the two cities under his personal rule, and was formally invested as their ruler by the Sultan Mahmud II. Zengi had supported the young sultan against his rival, the caliph al-Mustarshid. In 1130 Zengi allied with Taj al-Mulk Buri of Damascus against the Crusaders, but this wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurmanji
Kurmanji ( ku, کورمانجی, lit=Kurdish, translit=Kurmancî, also termed Northern Kurdish, is the northern dialect of the Kurdish languages, spoken predominantly in southeast Turkey, northwest and northeast Iran, northern Iraq, northern Syria and the Caucasus and Khorasan regions. It is the most widely spoken form of Kurdish. The earliest textual record of Kurmanji Kurdish dates back to approximately the 16th century and many prominent Kurdish poets like Ehmedê Xanî (1650–1707) wrote in this dialect. Kurmanji Kurdish is also the common and ceremonial dialect of Yazidis. Their sacred book '' Mishefa Reş'' and all prayers are written and spoken in Kurmanji. Phonology Phonological features in Kurmanji include the distinction between aspirated and unaspirated voiceless stops and the presence of facultative phonemes. For example, Kurmanji Kurdish distinguishes between aspirated and unaspirated voiceless stops, which can be aspirated in all positions. Thus contrasts wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pastoral tribes slowly decreased, reaching an estimated 30–40 million nomads in the world . Nomadic hunting and gathering—following seasonally available wild plants and game—is by far the oldest human subsistence method. Pastoralists raise herds of domesticated livestock, driving or accompanying them in patterns that normally avoid depleting pastures beyond their ability to recover. Nomadism is also a lifestyle adapted to infertile regions such as steppe, tundra, or ice and sand, where mobility is the most efficient strategy for exploiting scarce resources. For example, many groups living in the tundra are reindeer herders and are semi-nomadic, following forage for their animals. Sometimes also described as "nomad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well as creating large occupation zones within the Ottoman Empire. It was one of a series of treaties that the Central Powers signed with the Allied Powers after their defeat in World War I. Hostilities had already ended with the Armistice of Mudros. The treaty was signed on 10 August 1920 in an exhibition room at the Manufacture nationale de Sèvres porcelain factory in Sèvres, France. The Treaty of Sèvres marked the beginning of the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire. The treaty's stipulations included the renunciation of most territory not inhabited by Turkish people and their cession to the Allied administration. The ceding of Eastern Mediterranean lands saw the introduction of novel polities, including the British Mandate for Palestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish People
ug:كۇردلار Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northern Syria. There are exclaves of Kurds in Central Anatolia Region, Central Anatolia, Khorasan Province, Khorasan, and the Caucasus, as well as significant Kurdish diaspora communities in the cities of western Turkey (in particular Istanbul) and Western Europe (primarily Kurds in Germany, in Germany). The Kurdish population is estimated to be between 30 and 45 million. Kurds speak the Kurdish languages and the Zaza–Gorani languages, which belong to the Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian branch of the Iranian languages. After World War I and the defeat of the Ottoman Empire, the victorious Allies of World War I, Western allies made provision for a Kurdish state in the 1920 Treaty of Sevres, Treaty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
.jpg)


.jpg)