|
Henry Norris (engineer)
Henry Norris (1816–1878) was a British civil engineer born in Poplar, London, the son of several generations of house carpenters. He was the resident engineer for lighthouse construction projects under contract to Trinity House from civil engineers James Walker (engineer), Messrs. Walker & Burges, the firm of James Walker (engineer), James Walker and Alfred Burges, and later on oversaw the building of Souter Lighthouse, the world's first lighthouse specifically designed & built to be powered by electricity. He died at Stratford, London and is buried at Tower Hamlets Cemetery. His grave was located during ground clearing work in 2013 a few metres from that of John Buckley (VC). Henry Norris noted projects around the coast of England and Wales, included: Projects *Eddystone Lighthouse repairs to Smeaton's Tower in 1841 "The Eddystone Lighthouse has within the past few months undergone a complete renovation, under the direction of Mr. Henry Norris, engineer, from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tower Hamlets Cemetery
Tower Hamlets Cemetery Park is a local nature reserve and historic cemetery in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets within the East End of London. It is regarded as one of the seven great cemeteries of the Victorian era, the "Magnificent Seven cemeteries, Magnificent Seven", instigated because the normal (until that time) church burial plots had become overcrowded. The cemetery opened in 1841 and closed for burials in 1966. The cemetery park today encompasses the original cemetery, bounded by historic walls, and additional pockets of land including "Scrapyard Meadow" and the Ackroyd Drive Greenlink. It was originally named The City of London and Tower Hamlets Cemetery but was called Bow Cemetery by locals for its Bow, London, locality. The cemetery pre-dates the creation of the modern Borough of Tower Hamlets in 1965, and instead takes its name from the original, older and somewhat larger, Tower division, Tower Hamlets (or Tower division) – from which the modern borough also t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
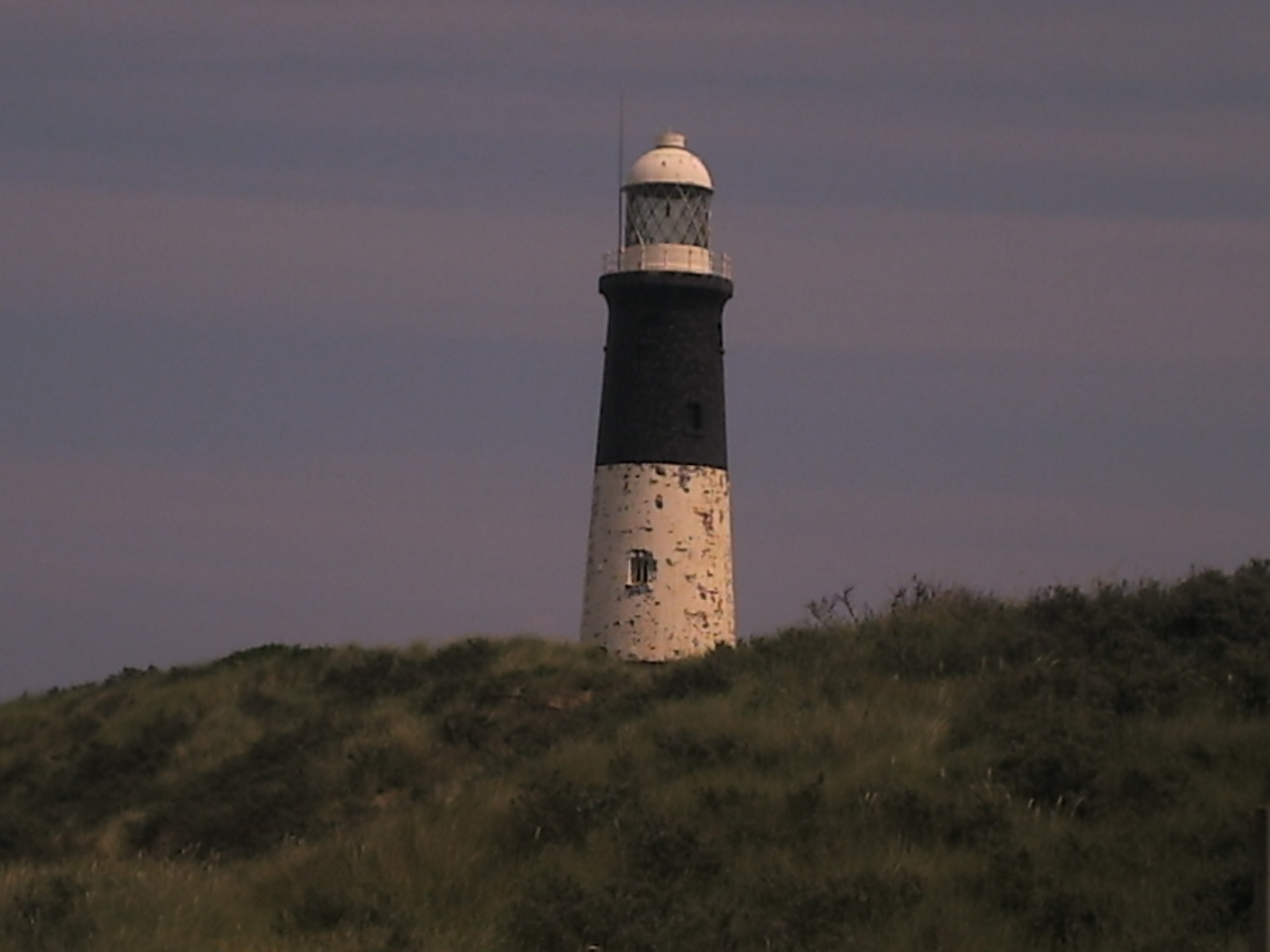
Spurn
Spurn is a narrow sand tidal island located off the tip of the coast of the East Riding of Yorkshire, England that reaches into the North Sea and forms the north bank of the mouth of the Humber Estuary. It was a spit with a semi-permanent connection to the mainland, but a storm in 2013 made the road down to the end of Spurn impassable to vehicles at high tide. The island is over long, almost half the width of the estuary at that point, and as little as wide in places. The southernmost tip is known as Spurn Head or Spurn Point and is the home to an RNLI lifeboat station and two disused lighthouses. It forms part of the civil parish of Easington. Spurn Head covers above high water and of foreshore. It has been owned since 1960 by the Yorkshire Wildlife Trust and is a designated national nature reserve, heritage coast and is part of the Humber Flats, Marshes and Coast Special Protection Area. History Spurn Head was known to classical authors, such as Ptolemy as ''Oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingdom. Located in the south-east of Wales and in the Cardiff Capital Region, Cardiff is the county town of the historic county of Glamorgan and in 1974–1996 of South Glamorgan. It belongs to the Eurocities network of the largest European cities. A small town until the early 19th century, its prominence as a port for coal when mining began in the region helped its expansion. In 1905, it was ranked as a city and in 1955 proclaimed capital of Wales. Cardiff Built-up Area covers a larger area outside the county boundary, including the towns of Dinas Powys and Penarth. Cardiff is the main commercial centre of Wales as well as the base for the Senedd. At the 2021 census, the unitary authority area population was put at 362,400. The popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workhouse
In Britain, a workhouse () was an institution where those unable to support themselves financially were offered accommodation and employment. (In Scotland, they were usually known as poorhouses.) The earliest known use of the term ''workhouse'' is from 1631, in an account by the mayor of Abingdon reporting that "we have erected wthn our borough a workhouse to set poorer people to work". The origins of the workhouse can be traced to the Statute of Cambridge 1388, which attempted to address the labour shortages following the Black Death in England by restricting the movement of labourers, and ultimately led to the state becoming responsible for the support of the poor. However, mass unemployment following the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, the introduction of new technology to replace agricultural workers in particular, and a series of bad harvests, meant that by the early 1830s the established system of poor relief was proving to be unsustainable. The New Poor Law of 1834 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merthyr Tydfil
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydfil, daughter of Brychan Brycheiniog, King Brychan of Brycheiniog, who according to legend was slain at Merthyr by pagans about 480 CE. generally means "Martyr of the Faith, martyr" in modern Welsh, but here closer to the Latin : a place of worship built over a martyr's relics. Similar place names in south Wales are Merthyr Cynog, Merthyr Dyfan and Merthyr Mawr. History Pre-history Peoples migrating north from Europe had lived in the area for many thousands of years. The archaeological record starts from about 1000 BC with the Celts. From their language, the Welsh language developed. Hillforts were built during the British Iron Age, Iron Age and the tribe that inhabited them in the south of Wales was called the Silures, according to Tacitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiff Docks
Cardiff Docks ( cy, Dociau Caerdydd) is a port in southern Cardiff, Wales. At its peak, the port was one of the largest dock systems in the world with a total quayage of almost . Once the main port for the export of South Wales coal, the Port of Cardiff remains active in the import and export of containers, steel, forest products and dry and liquid bulks. History Following the development of the coal found in the Cynon Valley, Rhondda Valley, and Merthyr areas of South Wales, the export of both coal and iron products required a sea connection to the Bristol Channel if economic volumes of product were to be extracted. In 1794, the Glamorganshire Canal was completed, linking the then small town of Cardiff with Merthyr, and in 1798 a basin was built, connecting the canal to the sea. By the 1830s, Cardiff became the pre-eminent iron-exporting port, shipping almost half of British overseas iron exports; between 1840 and 1870, the volume of coal exports increased from 44,350 to 2.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Merryn
St Merryn ( kw, S. Meryn) is a civil parish and village in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is about south of the fishing port of Padstow and northeast of the coastal resort of Newquay. The village has a primary school, a veterinary practice, various shops, restaurants, and two public houses. The population at the 2011 census was 1,692. Geography The 3,798 acre parish of St Merryn is bounded by a millstream to the south that separates it from the St Ervan and St Eval parishes; more than of coastline along the Atlantic Ocean; and the Padstow parish and Lyn stream. The Seven Bays region of St Merryn includes (from west to east) Porthcothan Bay, Treyarnon Bay, Constantine Bay, Booby's Bay, Mother Ivey's Bay, Harlyn Bay and Trevone Bay.''Welcome to St Merryn Online.'' St Merryn Online. Retrieved 17 September 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, with the River Tamar forming the border between them. Cornwall forms the westernmost part of the South West Peninsula of the island of Great Britain. The southwesternmost point is Land's End and the southernmost Lizard Point. Cornwall has a population of and an area of . The county has been administered since 2009 by the unitary authority, Cornwall Council. The ceremonial county of Cornwall also includes the Isles of Scilly, which are administered separately. The administrative centre of Cornwall is Truro, its only city. Cornwall was formerly a Brythonic kingdom and subsequently a royal duchy. It is the cultural and ethnic origin of the Cornish dias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevose Head
Trevose Head ( kw, Penn Trenfos, meaning ''farm of the wall's headland'') () is a headland on the Atlantic coast of north Cornwall, United Kingdom. It is situated approximately west of Padstow. The South West Coast Path runs around the whole promontory and is within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and the Trevose Head Heritage Coast. In clear weather, visitors to Trevose Head can see virtually the whole length of the north Cornwall coast; to the north, the view extends beyond the Cornwall county boundary to Hartland Point (), Devon; to the south, it extends beyond St Ives to the headland at Pendeen Watch (). History The ruins of St Constantine's chapel can be visited at hole 3 of Trevose Golf Club along an ancient right of way. The club is situated between Constantine Bay and Mother Ivey's Bay, behind Booby's Bay. Trevose Head Lighthouse, maintained by Trinity House, is on the north-west corner of the headland and the Padstow lifeboat is stationed on the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevose Head Lighthouse
Trevose Head Lighthouse is a lighthouse on Trevose Head on the north Cornish coast at lying to the WSW of Padstow and was sited here as there was previously no light from Land's End to Lundy and it would be visible from Cape Cornwall to Hartland Point. The tower is tall, and has a range of , but, on a clear night, you can just spot the light from Pendeen Lighthouse, over away. History Construction The site was surveyed by order of the Trinity Board in July 1844 with a design submitted that November and approved February 1845. Building began in that May with the laying out of the road and contract entered into with the builders the next month. During gales on 20–21 November 1846 scaffolding attached to the tower was blown away. After completion of the first tower, it was determined that the light was under certain circumstances liable to be mistaken by mariners. A second lower light was therefore proposed and (the decision having been taken in June 1847) it was co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
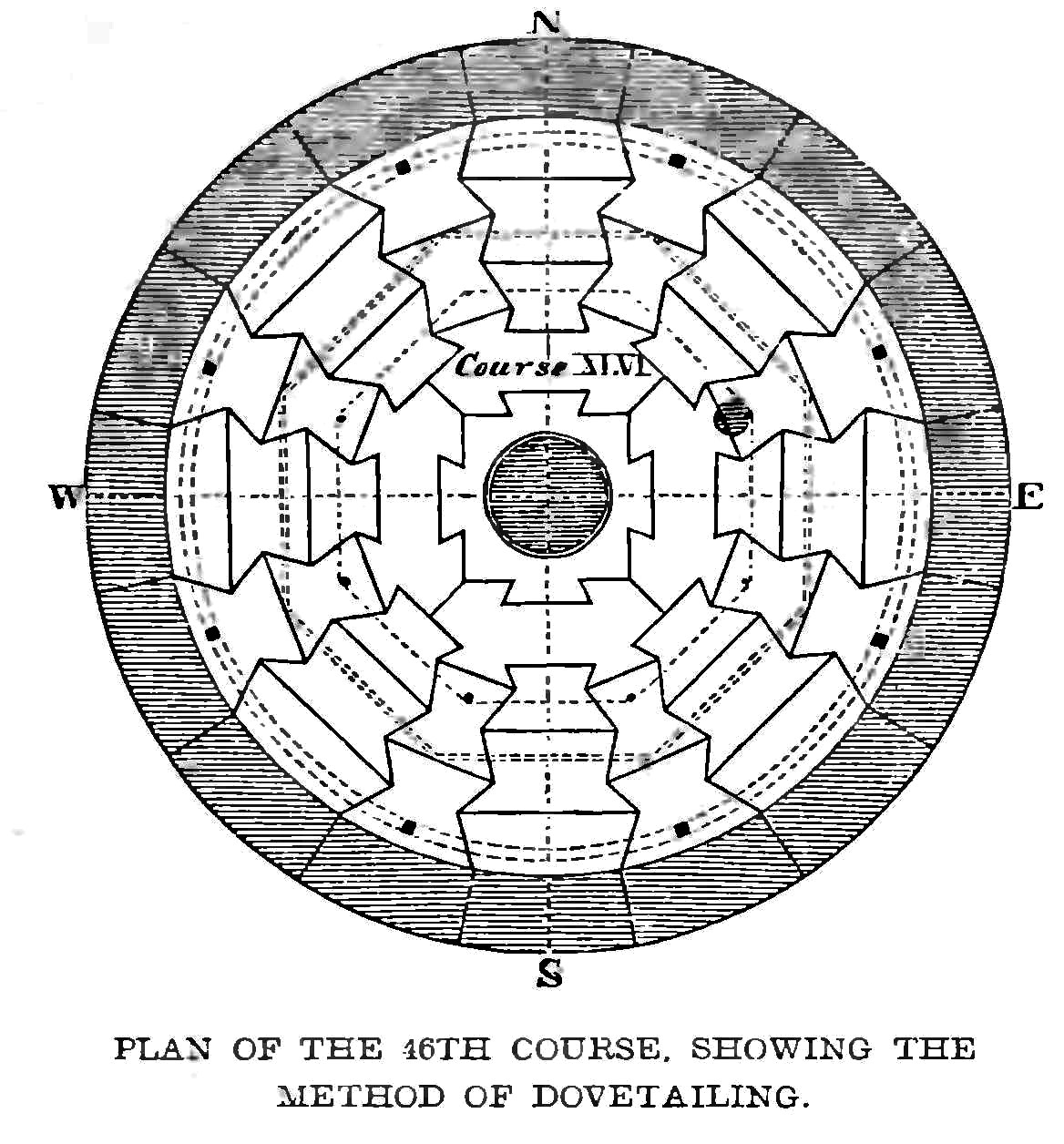
Smeaton's Tower
Smeaton's Tower is a memorial to civil engineer John Smeaton, designer of the third and most notable Eddystone Lighthouse. A major step forward in lighthouse design, Smeaton's structure was in use from 1759 to 1877, until erosion of the ledge it was built upon forced new construction. The tower was largely dismantled and rebuilt on Plymouth Hoe in Plymouth, Devon, where it stands today. History Background England’s coasts are notorious for rough weather, dangerous seas and deathly obstacles. The Eddystone rocks are among them. There were several attempts were made to place a marker on these reefs. The first attempt was called the Winstanley Lighthouse. After it was destroyed in the 1703 storm, a second one called the Rudyard lighthouse was built. This one was also destroyed, this time by a fire in 1755. Born in Austhorpe, Yorkshire, England in 1724, John Smeaton is considered the father of civil engineering. Recognized for his scientific achievements, including the increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |