|
Helm Wind
The Helm Wind is a named wind in Cumbria, England, a strong north-easterly wind which blows down the south-west slope of the Cross Fell escarpment. It is the only named wind in the British Isles, although many other mountain regions in Britain exhibit the same phenomenon when the weather conditions are favourable. It may take its name from the helmet or cap of cloud which forms above Cross Fell, known as the Helm Bar, since a line of clouds over the fells can predict and accompany a Helm. Research into the helm wind was carried out by Gordon Manley in the 1930s. He interpreted the phenomenon in hydrodynamic terms as a " standing wave" and "rotor", a model confirmed in 1939 by glider flights. The dale at the head of the Eden Valley has its own Helm Wind, which sweeps over Mallerstang Mallerstang is a civil parish in the extreme east of Cumbria, and, geographically, a dale at the head of the upper Eden Valley. Originally part of Westmorland, it lies about south of the neares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first noticed by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a stationary med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winds
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet ( Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their spatial scale, their speed and direction, the forces that cause them, the regions in which they occur, and their effect. Winds have variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Cumbria
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
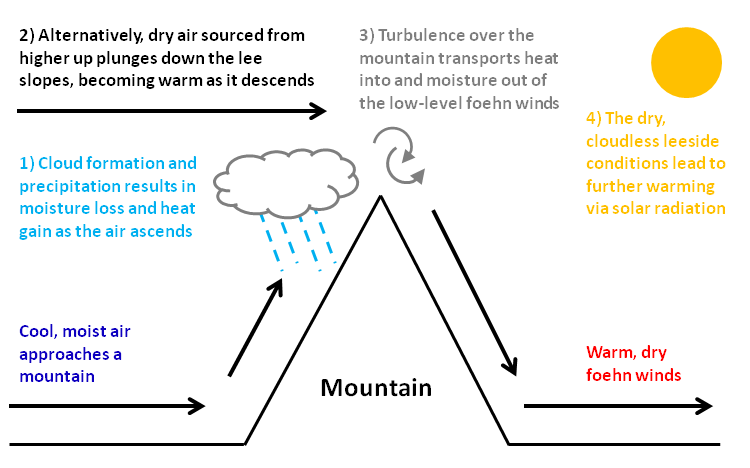
Föhn Effect
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range. It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Foehn winds can raise temperatures by as much as 14 °C (25 °F) in just a matter of hours. Switzerland, southern Germany and Austria have a warmer climate due to the Foehn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps. Etymology The name ''Foehn'' (german: Föhn, ) arose in the Alpine region. Originating from Latin ''(ventus) favonius'', a mild west wind of which Favonius was the Roman personification and probably transmitted by rm, favuogn or just ''fuogn'', the term was adopted as go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of England
The United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61°N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day. In general the climate of the UK is changeable, often cloudy especially in the more northerly areas of the country, with rain evenly distributed throughout the year. The climate in the United Kingdom is defined as a humid temperate oceanic climate, or ''Cfb'' on the Köppen climate classification system, a classification it shares with most of north-west Europe. Regional climates are influenced by the Atlantic Ocean and latitude. Northern Ireland, Wales and western parts of England and Scotland, being closest to the Atlantic Ocean, are generally the mildest, wettest and windiest regions of the UK, and temperature ranges there are seldom extreme. Eastern areas are drier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallerstang
Mallerstang is a civil parish in the extreme east of Cumbria, and, geographically, a dale at the head of the upper Eden Valley. Originally part of Westmorland, it lies about south of the nearest town, Kirkby Stephen. Its eastern edge, at Aisgill, borders on North Yorkshire; and since August 2016 it has been within the Yorkshire Dales National Park. At the 2011 census data for Wharton was included with Mallerstang, giving a total population of 173. The head of the Eden This narrow valley at the head of the River Eden is bounded by Wild Boar Fell and Swarth Fell to the west and Mallerstang Edge to the east. The highest point of Mallerstang Edge is the summit of High Seat; at this is a metre or so higher than the more prominent Wild Boar Fell. The other main high points on the eastern side of the dale are the curiously named Gregory Chapel, south of High Seat, and Hugh Seat to the south-east. The river Eden rises as Red Gill Beck in Black Moss, the peat bogs below Hugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dale (origin)
A dale is an open valley. ''Dale'' is a synonym of the word ''valley''. The name is used when describing the physical geography of an area. It is used most frequently in the Lowlands of Scotland and in the North of England; the term "fell" commonly refers to the mountains or hills that flank the dale. Etymology The word ''dale'' comes from the Old English Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ... word ''dæl'', from which the word " dell" is also derived. It is also related to Old Norse word ''dalr'' (and the modern Icelandic language, Icelandic word ''dalur''), which may perhaps have influenced its survival in northern England. The Germanic origin is assumed to be *''dala-''. ''Dal-'' in various combinations is common in placenames in Norway. Modern English valley a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Manley
Gordon Valentine Manley, FRGS (3 January 1902 – 29 January 1980) was a British climatologist who has been described as "probably the best known, most prolific and most expert on the climate of Britain of his generation". He assembled the Central England temperature (CET) series of monthly mean temperatures stretching back to 1659, which is the longest standardised instrumental record available for anywhere in the world. It provides a benchmark for proxy records of climatic change for the period covered, and is a notable example of scientific scholarship and perseverance (it took over thirty years to complete). His two papers describing the work are available online. Early life and career Gordon Manley was born at Douglas, Isle of Man. He was brought up in Blackburn, Lancashire, where he attended Queen Elizabeth's Grammar School. After obtaining degrees in engineering and geography at Victoria University of Manchester and Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge respectively, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. Cumbria's county town is Carlisle, in the north of the county. Other major settlements include Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal, Whitehaven and Workington. The administrative county of Cumbria consists of six districts ( Allerdale, Barrow-in-Furness, Carlisle, Copeland, Eden and South Lakeland) and, in 2019, had a population of 500,012. Cumbria is one of the most sparsely populated counties in England, with 73.4 people per km2 (190/sq mi). On 1 April 2023, the administrative county of Cumbria will be abolished and replaced with two new unitary authorities: Westmorland and Furness ( Barrow-in-Furness, Eden, South Lakeland) and Cumberland ( Allerdale, Carlisle, Copeland). Cumbria is the third largest ceremonial county in England by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenticular Cloud
Lenticular clouds (Latin: ''Lenticularis'' lentil-shaped, from ''lenticula'' lentil) are stationary clouds that form mostly in the troposphere, typically in parallel alignment to the wind direction. They are often comparable in appearance to a lens or saucer. Nacreous clouds that form in the lower stratosphere sometimes have lenticular shapes. There are three main types of lenticular clouds: altocumulus standing lenticular (ACSL), stratocumulus standing lenticular (SCSL), and cirrocumulus standing lenticular (CCSL), varying in altitude above the ground. Because of their unique appearance, they have been suggested as an explanation for some unidentified flying object (UFO) sightings. Formation and appearance As air travels along the surface of the Earth, obstructions are often encountered, including natural features, such as mountains or hills, and artificial structures, such as buildings and other constructions, which disrupt the flow of air into "eddies", or areas of tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pileus (meteorology)
A pileus (; Latin for "cap"), also called scarf cloud or cap cloud, is a small, horizontal, lenticular cloud appearing above a cumulus or cumulonimbus cloud. Pileus clouds are often short-lived, with the main cloud beneath them rising through convection to absorb them. They are formed by strong updraft at lower altitudes, acting upon moist air above, causing the air to cool to its dew point. As such, they are usually indicators of severe weather, and a pileus found atop a cumulus cloud often foreshadows transformation into a cumulonimbus cloud, as it indicates a strong updraft within the cloud. Pilei can also form above mountains, ash clouds, and pyrocumulus clouds from erupting volcanoes. Pilei form above some mushroom clouds of high- yield nuclear detonations. Appearance Sometimes several pileus clouds are observed above each other. The bright iridescent colors seen in pileus are sunlight diffracted in water vapor. Iridescent colors are strongest when the diffracting drop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |