|
Gordon Manley
Gordon Valentine Manley, FRGS (3 January 1902 – 29 January 1980) was a British climatologist who has been described as "probably the best known, most prolific and most expert on the climate of Britain of his generation". He assembled the Central England temperature (CET) series of monthly mean temperatures stretching back to 1659, which is the longest standardised instrumental record available for anywhere in the world. It provides a benchmark for proxy records of climatic change for the period covered, and is a notable example of scientific scholarship and perseverance (it took over thirty years to complete). His two papers describing the work are available online. Early life and career Gordon Manley was born at Douglas, Isle of Man. He was brought up in Blackburn, Lancashire, where he attended Queen Elizabeth's Grammar School. After obtaining degrees in engineering and geography at Victoria University of Manchester and Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge respectively, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Geographical Society
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). In English, an asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in sans-serif typefaces, six-pointed in serif typefaces, and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk has already been used as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helm Bar Mallerstang
Helm may refer to: Common meanings * a ship's steering mechanism; see tiller and ship's wheel * another term for helmsman * an archaic term for a helmet, used as armor Arts and entertainment * Matt Helm, a character created by Donald Hamilton * Helm (Forgotten Realms), a god in the Forgotten Realms campaign setting for the game ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * Helm, a character from the 2000AD comic strip ''Rogue Trooper'' * ''Helm'' (album), released by Lebanese singer Carole Samaha * ''Helm'', a novel by Steven Gould HELM * Hierarchical editing language for macromolecules, a method of describing complex biological molecules * Holomorphic embedding load flow method, a mathematical technique for solving AC power flow People * Helm (given name) * Helm (surname) Places United States * Helm, California, an unincorporated community * Helm, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * Helm, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Helm Canal, California, an aqueduct Antarctica * Helm Glac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Naturalist
The New Naturalist Library (also known as ''The New Naturalists'') is a series of books published by Collins in the United Kingdom, on a variety of natural history topics relevant to the British Isles. The aim of the series at the start was: "To interest the general reader in the wild life of Britain by recapturing the inquiring spirit of the old naturalists."Guy Mountfort, ''The Hawfinch''. Collins, 1957. An editors' preface to a 1952 monograph says: "An object of the ''New Naturalist'' series is the recognition of the many-sidedness of British natural history, and the encouragement of unusual and original developments of its forgotten or neglected facets." The first volume to appear was E.B. Ford's ''Butterflies'' in 1945. The authors of this series are usually eminent experts, often professional scientists. This gives the series authority, and many are or have been authoritative introductory textbooks on a subject for some years. The books are written in scientific style, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its surrounding areas) is home to over 65% of the population. Iceland is the biggest part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge that rises above sea level, and its central volcanic plateau is erupting almost constantly. The interior consists of a plateau characterised by sand and lava fields, mountains, and glaciers, and many glacial rivers flow to the sea through the lowlands. Iceland is warmed by the Gulf Stream and has a temperate climate, despite a high latitude just outside the Arctic Circle. Its high latitude and marine influence keep summers chilly, and most of its islands have a polar climate. According to the ancient manuscript , the settlement of Iceland began in 874 AD when the Norwegian chieftain Ingólfr Arnarson became the first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degree-awarding examination board for students holding certificates from University College London and King's College London and "other such other Institutions, corporate or unincorporated, as shall be established for the purpose of Education, whether within the Metropolis or elsewhere within our United Kingdom". This fact allows it to be one of three institutions to claim the title of the third-oldest university in England, and moved to a federal structure in 1900. It is now incorporated by its fourth (1863) royal charter and governed by the University of London Act 2018. It was the first university in the United Kingdom to introduce examinations for women in 1869 and, a decade later, the first to admit women to degrees. In 1913, it appointe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Meteorological Society
The Royal Meteorological Society is a long-established institution that promotes academic and public engagement in weather and climate science. Fellows of the Society must possess relevant qualifications, but Associate Fellows can be lay enthusiasts. Its Quarterly Journal is one of the world's leading sources of original research in the atmospheric sciences. The chief executive officer is Liz Bentley. Constitution The Royal Meteorological Society traces its origins back to 3 April 1850 when the British Meteorological Society was formed as "a society the objects of which should be the advancement and extension of meteorological science by determining the laws of climate and of meteorological phenomena in general". Along with nine others, including James Glaisher, John Drew, Edward Joseph Lowe, The Revd Joseph Bancroft Reade, and Samuel Charles Whitbread, Dr John Lee, an astronomer, of Hartwell House, near Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire founded in the library of his house the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedford College (London)
Bedford College was in York Place after 1874 Bedford College was founded in London in 1849 as the first higher education college for women in the United Kingdom. In 1900, it became a constituent of the University of London. Having played a leading role in the advancement of women in higher education and public life in general, it became fully coeducational (i.e. open to men) in the 1960s. In 1985, Bedford College merged with Royal Holloway College, another constituent of the University of London, to form Royal Holloway and Bedford New College. This remains the official name, but it is commonly called Royal Holloway, University of London (RHUL). History Foundation The college was founded by Elizabeth Jesser Reid (''née'' Sturch) in 1849, a social reformer and anti-slavery activist, who had been left a private income by her late husband, Dr John Reid, which she used to patronise various philanthropic causes. Mrs Reid and her circle of well-educated friends believed firmly in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Air Squadron
Cambridge University Air Squadron, abbreviated CUAS, formed in 1925, is the training unit of the Royal Air Force at the University of Cambridge and forms part of the Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve. It is the oldest of 15 University Air Squadrons in the UK. For many years it was based at Cambridge Airport at Teversham. History The unit was formed in 1925 and initially operated out a runway located next to RAF Engineering school at Fen causeway in Cambridge. After a brief spell at RAF Duxford, the squadron moved in 1949 to a new home at Cambridge "Marshall's" or "Teversham" Airport where it remained until 1999 and its transfer away to RAF Wyton. 15 years later, the squadron was moved again, to RAF Wittering. Present day Cambridge University Air Squadron offers basic flying training and adventure training to undergraduates and graduates and encourages members to take up a career as an officer in one of the branches of the Royal Air Force. Student members hold the title of Offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge logo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotor (meteorology)
In meteorology, lee waves are Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric stationary waves. The most common form is mountain waves, which are atmospheric internal gravity waves. These were discovered in 1933 by two German glider pilots, Hans Deutschmann and Wolf Hirth, above the Krkonoše. They are Frequency, periodic changes of atmospheric pressure, temperature and orthometric height in a Air current, current of air caused by vertical displacement, for example orographic lift when the wind blows over a mountain or mountain range. They can also be caused by the surface wind blowing over an escarpment or plateau, or even by upper winds deflected over a thermal updraft or cloud street. The vertical motion forces periodic changes in speed and Boxing the compass, direction of the air within this air current. They always occur in groups on the Windward and leeward, lee side of the terrain that triggers them. Sometimes, mountain waves can help to enhance precipitation amounts downwind of mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
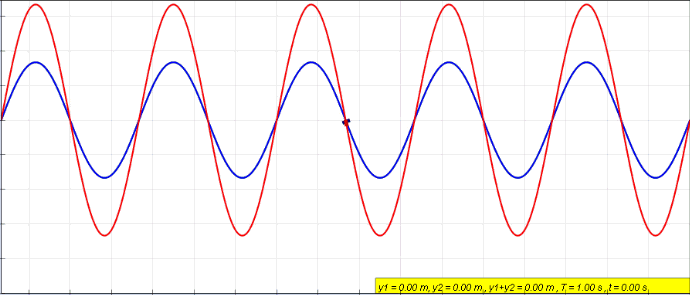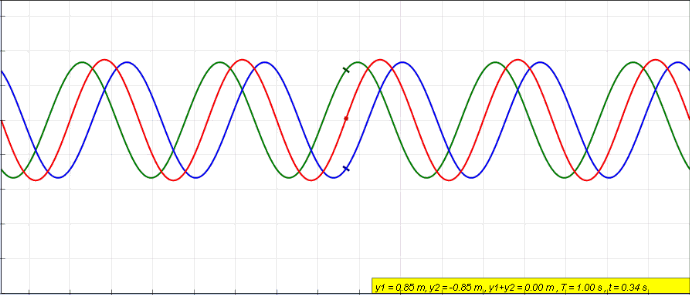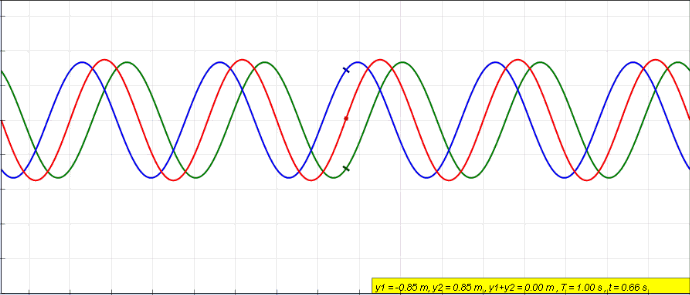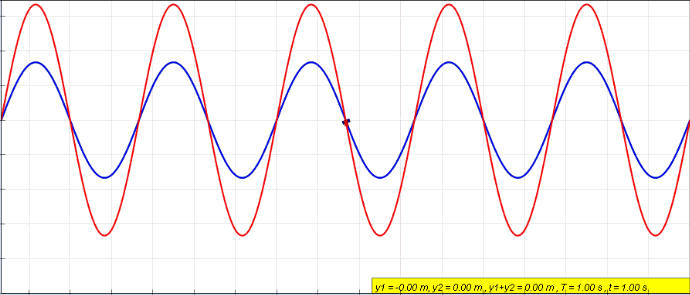
Standing Wave
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first noticed by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in a stationary medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |