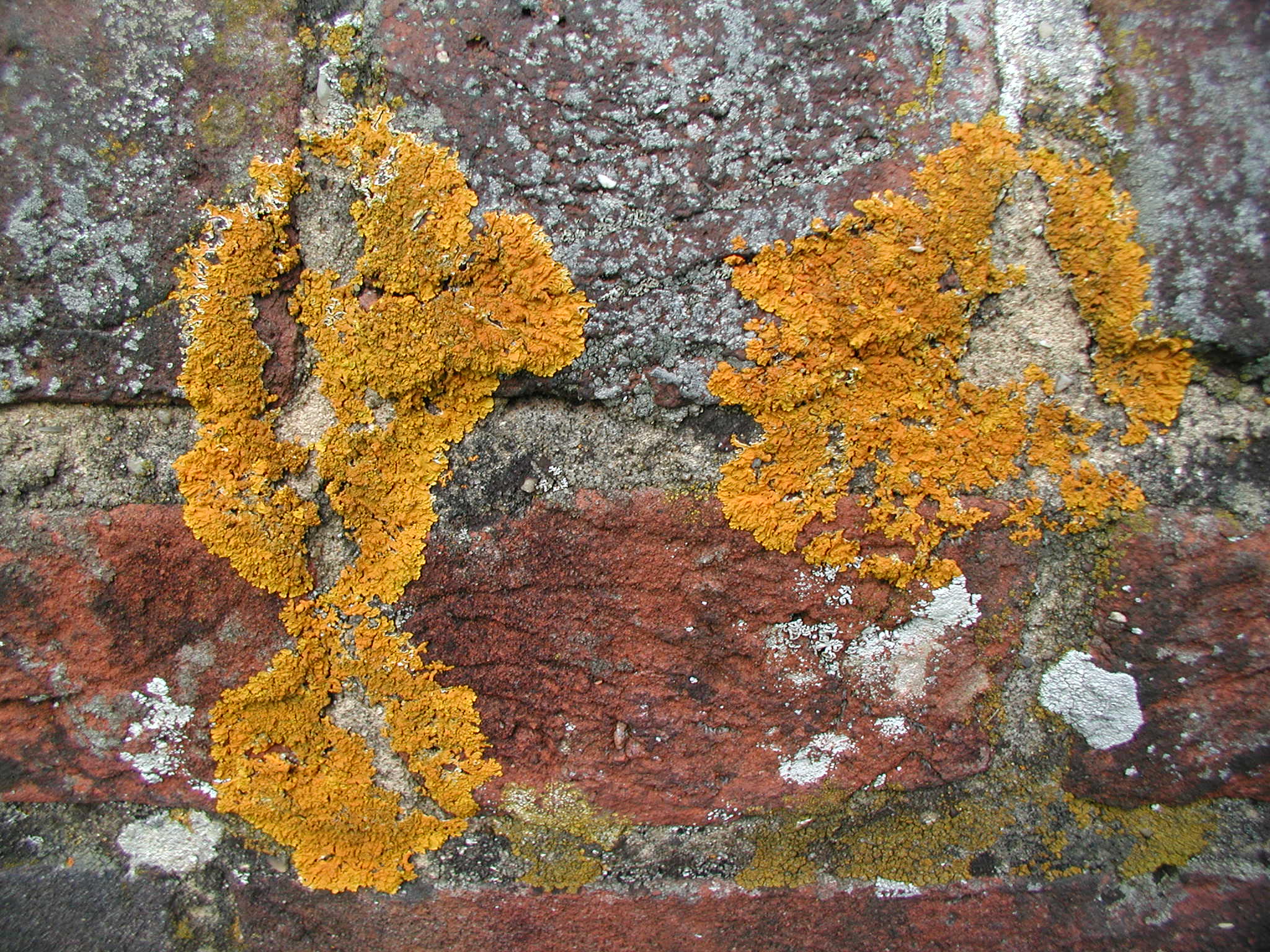|
Harpidiaceae
Harpidiaceae is a small family of lichen-forming fungi, containing two genera and five species. It is of uncertain classification in the Pezizomycotina. Taxonomy The Harpidiaceae was first informally proposed by Antonín Vězda in 1974 to contain genus '' Harpidium'', which he noted "is an extremely isolated genus, unrelated to the Lecanoraceae. It should be recognized as a separate monotypic family". It was formally published in 1984 by Josef Hafellner, along with several other families characterised mainly by differences in the amyloid reactions of structures of their asci. In 1988, Aino Henssen and colleagues published the results of a study of the thallus, apothecia, and pycnidia of the genera ''Harpidium'' and ''Euopsis'', and concluded that they corresponded to the genus '' Pyrenopsis'' and other genera of the Lichinaceae (order Lichinales, class Lichinomycetes). With this, they justified including ''Harpidium'' and ''Euopsis'' in the Lichinaceae, and amended the circumscr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichinaceae
The Lichinaceae are a family of ascomycete fungi. Most species are lichenized with cyanobacteria, and have a distribution largely in temperate regions. Taxonomy The family was circumscribed in 1854 by Finnish lichenologist William Nylander. His description of the family mentioned the obscure brown thallus resembling algae, with an overall morphology described as either filamentous or tufted (fruticose). The fruiting structures, the apothecia, are described as either endocarpous or biatorine. He included two tribes in the Lichinaceae: ''Ephebeae'', which contained the genera ''Ephebe'' and ''Gonionema'', and ''Lichineae'', which contained '' Lichina'', the type genus. In 1986, Aino Henssen and Burkhard Büdel proposed the order Lichinales to contain the Lichinaceae. In the 1980s and 1990s, several taxonomic and nomenclatural studies were the basis for the revision of many of the species in the family. Heppiaceae was a family proposed by Alexander Zahlbruckner in 1906 to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpidium Gavilaniae
''Harpidium'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Harpidiaceae. The genus contains three species. ''Harpidium'' was circumscribed in 1855 by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber, with '' Harpidium rutilans'' assigned as the type species. Species * '' Harpidium gavilaniae'' * '' Harpidium longisporum'' * '' Harpidium nashii'' * '' Harpidium rutilans'' The taxon In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ... ''Harpidium glaucophanum'' is now known as '' Rhizoplaca glaucophana''. References Pezizomycotina Ascomycota genera Lichen genera Taxa described in 1855 Taxa named by Gustav Wilhelm Körber {{Ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euopsis
''Euopsis'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Harpidiaceae. The genus contains two species. The genus was circumscribed by Finnish botanist William Nylander William Andrew Michael Junior Nylander Altelius (born 1 May 1996) is a Canadian-born Swedish professional ice hockey right winger for the Toronto Maple Leafs of the National Hockey League (NHL). Nylander was selected by the Maple Leafs in the ... in 1881. Species *'' Euopsis granatina'' *'' Euopsis pulvinata'' References Pezizomycotina Ascomycota families Taxa described in 1881 Taxa named by William Nylander (botanist) Lichen genera {{Ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpidium
''Harpidium'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Harpidiaceae. The genus contains three species. ''Harpidium'' was circumscribed in 1855 by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber, with '' Harpidium rutilans'' assigned as the type species. Species * ''Harpidium gavilaniae'' * '' Harpidium longisporum'' * '' Harpidium nashii'' * '' Harpidium rutilans'' The taxon In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ... ''Harpidium glaucophanum'' is now known as '' Rhizoplaca glaucophana''. References Pezizomycotina Ascomycota genera Lichen genera Taxa described in 1855 Taxa named by Gustav Wilhelm Körber {{Ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euopsis Pulvinata
''Euopsis'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Harpidiaceae. The genus contains two species. The genus was circumscribed by Finnish botanist William Nylander William Andrew Michael Junior Nylander Altelius (born 1 May 1996) is a Canadian-born Swedish professional ice hockey right winger for the Toronto Maple Leafs of the National Hockey League (NHL). Nylander was selected by the Maple Leafs in the ... in 1881. Species *'' Euopsis granatina'' *'' Euopsis pulvinata'' References Pezizomycotina Ascomycota families Taxa described in 1881 Taxa named by William Nylander (botanist) Lichen genera {{Ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euopsis Granatina
''Euopsis'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Harpidiaceae. The genus contains two species. The genus was circumscribed by Finnish botanist William Nylander in 1881. Species *'' Euopsis granatina'' *''Euopsis pulvinata ''Euopsis'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Harpidiaceae. The genus contains two species. The genus was circumscribed by Finnish botanist William Nylander William Andrew Michael Junior Nylander Altelius (born 1 May 1996) i ...'' References Pezizomycotina Ascomycota families Taxa described in 1881 Taxa named by William Nylander (botanist) Lichen genera {{Ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pezizomycotina
Pezizomycotina make up most of the Ascomycota fungi and include most lichenized fungi too. Pezizomycotina contains the filamentous ascomycetes and is a subdivision of the Ascomycota (fungi that form their spores in a sac-like ''ascus''). It is more or less synonymous with the older taxon Euascomycota. These fungi reproduce by fission rather than budding and this subdivision includes almost all the ascus fungi that have fruiting bodies visible to the naked eye (exception: genus ''Neolecta'', which belongs to the Taphrinomycotina). See the taxobox for a list of the classes that make up the Pezizomycotina. The old class Loculoascomycetes (consisting of all the bitunicate Ascomycota) has been replaced by the two classes Eurotiomycetes and Dothideomycetes. The rest of the Pezizomycotina also include the previously defined hymenial groups Discomycetes (now Leotiomycetes) and Pyrenomycetes (Sordariomycetes). Some important groups in Pezizomycotina include: Pezizomycetes (the opercula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genbank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. It is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; a part of the National Institutes of Health in the United States) as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC). GenBank and its collaborators receive sequences produced in laboratories throughout the world from more than 500,000 formally described species. The database started in 1982 by Walter Goad and Los Alamos National Laboratory. GenBank has become an important database for research in biological fields and has grown in recent years at an exponential rate by doubling roughly every 18 months. Release 250.0, published in June 2022, contained over 17 trillion nucleotide bases in more than 2,45 billion sequences. GenBank is built by direct submissions from individual laboratories, as well as from bulk submis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycobiont
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( |
DNA Sequence
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with modern D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSU RRNA
Small subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid (SSU rRNA) is the smaller of the two major RNA components of the ribosome. Associated with a number of ribosomal proteins, the SSU rRNA forms the small subunit of the ribosome. It is encoded by SSU- rDNA. Characteristics Use in phylogenetics SSU rRNA sequences are widely used for determining evolutionary relationships among organisms, since they are of ancient origin and are found in all known forms of life. See also *LSU rRNA Large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid (LSU rRNA) is the largest of the two major RNA components of the ribosome. Associated with a number of ribosomal proteins, the LSU rRNA forms the large subunit of the ribosome. The LSU rRNA acts as a rib ...: the large subunit ribosomal ribonucleic acid. References {{Ribosome subunits Ribosomal RNA Protein biosynthesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustose Lichen
Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the Substrate (biology), substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction. The basic structure of crustose lichens consists of a cortex (botany), cortex layer, an algal layer, and a medulla. The upper cortex layer is differentiated and is usually pigmented. The algal layer lies beneath the cortex. The medulla fastens the lichen to the substrate and is made up of Fungus, fungal hyphae. The surface of crustose lichens is characterized by branching cracks that periodically close in response to climatic variations such as alternate wetting and drying regimes. Subtypes * Powdery – considered as the simplest subtype due to the absence of an organized thallus. :The thallus appears powdery. :E.g. Genera ''Lepraria'', ''Vezdaea'' * Endolithic – grows inside the rock, usually in interstitial spaces between mineral grains. The :upper cortex is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)