|
Haplogroup Q-L804 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-L804 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-L804 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Currently Q-L804 is Q1b1a1b below Q1b-M346. Q-L472 > Q-L56 > Q-L53 > Q-L54 > Q-M1107 > Q-M930 ** Q-L804 formed 15200 ybp, TMRCA 3200 yBP *** Q-Y9052 formed 3200 ybp, TMRCA 3200 yBP **** Q-Y9294 formed 3200 ybp, TMRCA 2800 ybp ***** Q-YP5210 ***** Q-Y9048 *** Q-A13540 formed 3200 ybp, TMRCA 2900 yBP **** Q-JN15 formed 2900 ybp, TMRCA 1650 yBP ***** Q-Y16137 **** Q-Y7582 formed 2900 ybp, TMRCA 1650 yBP ***** Q-Y38488 ***** Q-Y12445 ***** Q-Y15622 Family Tree DNA Y-DNA haplotree for haplogroup Q-L804 * Q (M242) > Q-MEH2 > Q-M346 > Q-L53 > Q-L54 > Q-CTS3814 > Q-CTS11969 ** Q-L804 *** Q-BY387 **** Q-PH2487 **** Q-Y38488 *** Q-JN14 **** Q-Y16137 **** Q-BY66620 *** Q-BY459 **** Q-Y9291 The subtree Q-BY387 is found on Iceland, Scotland and England. The Q-JN14 is widely distributed in North-west Europe, but most kits are from Norway. The subtree Q-BY459 is by FT DNA m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
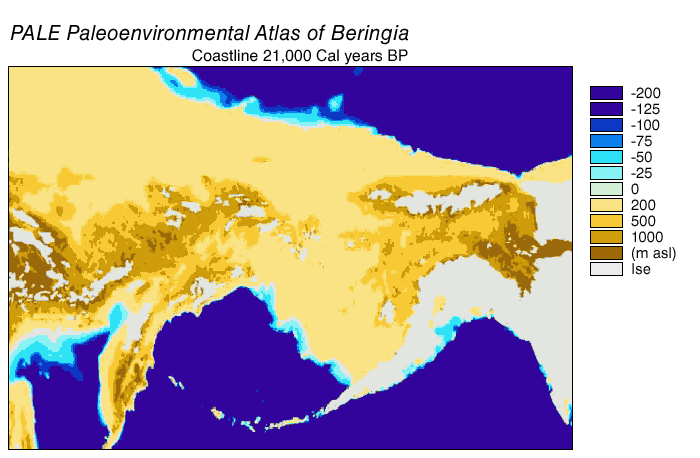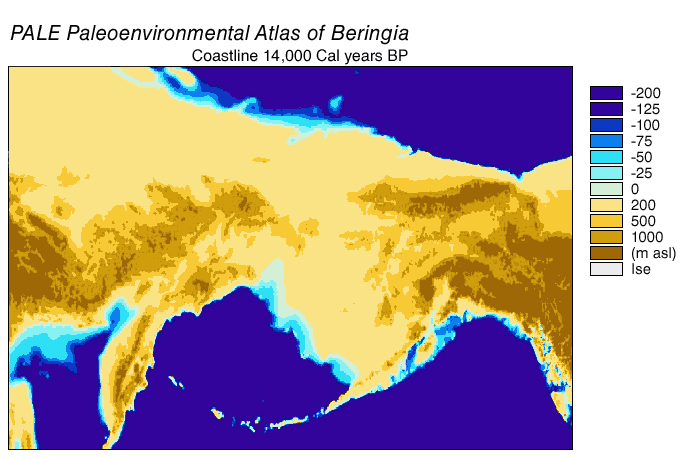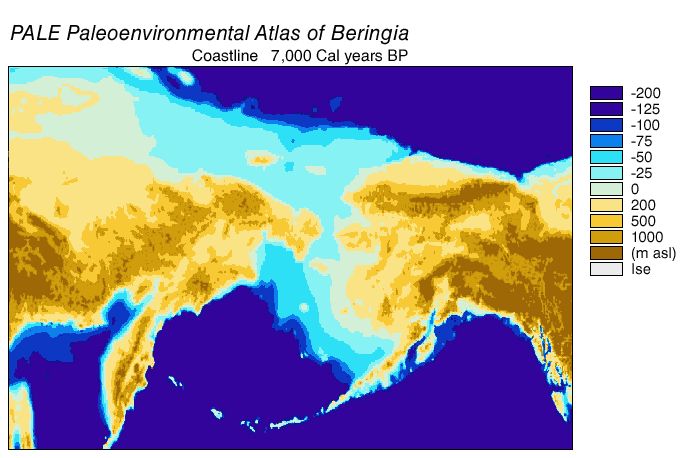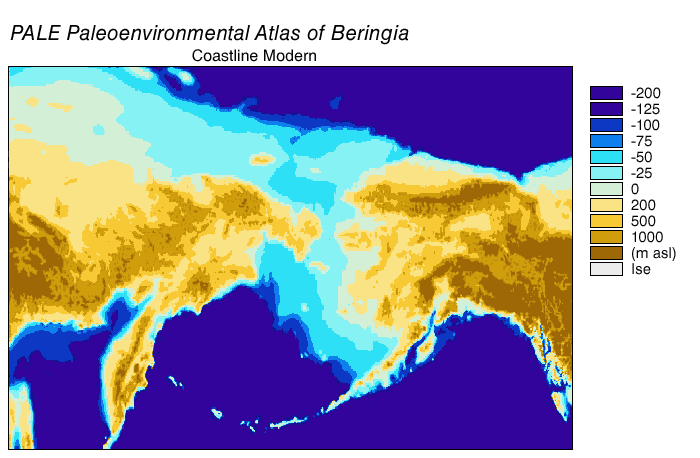
Beringia
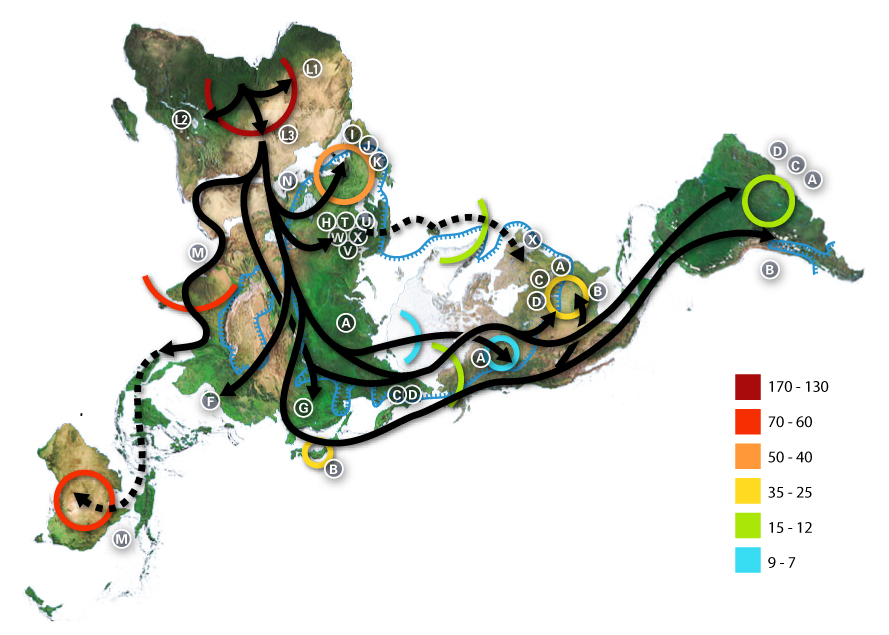
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi and Kamchatka Peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and the Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At certain times in prehistory, it formed a land bridge that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling approximately . Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Islands of St. Paul and St. George, St. Lawrence Island, St. Matthew Island, and King Island. The term ''Berin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M242 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q or Q-M242 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It has one primary subclade, Haplogroup Q1 (L232/S432), which includes numerous subclades that have been sampled and identified in males among modern populations. Q-M242 is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among Native Americans and several peoples of Central Asia and Northern Siberia. Origins Haplogroup Q-M242 is one of the two branches of P1-M45, the other being R-M207. P1, as well as R* and Q* were observed among Ancient North Eurasians, a deeply European hunter-gatherer related population. Q-M242 is believed to have arisen around the Altai Mountains area (or South Central Siberia), approximately 17,000 to 31,700 years ago. However, the matter remains unclear due to limited sample sizes and changing definitions of Haplogroup Q: early definitions used a combination of the SNPs M242, P36.2, and MEH2 as defining mutations. Technical specification of mutation The polymorphism, “M242”, is a C→T transition resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-P89
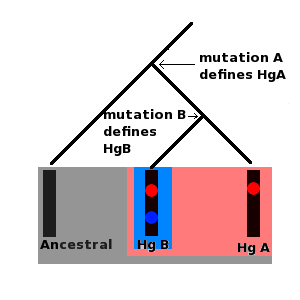
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-NWT01 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-NWT01 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q-MEH2. Haplogroup Q-NWT01 is defined by the presence of the NWT01 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-NWT01 has descendants in the Northwest Territories of modern Canada. It was in these populations that it was discovered. The Americas Q-NWT01 is present in pre-Columbian populations in the Canadian Northwest. It also has been found in a specimen of the Saqqaq culture of prehistoric Greenland.YFull Haplogroup YTree v6.03.05 at 20 July 2018. Accessed July 20, 2018.Monika Karmin, Lauri Saag, Mário Vicente, ''et al.'' (2015), "A recent bottleneck of Y chromosome diversity coincides with a global change in culture." ''Genome Research'' 25:1–8. Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; ISSN 1088-9051/15; www.genome.org. ...
|
Haplogroup Q-M346 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M346 is a subclade of Y-DNA Haplogroup Q. Haplogroup Q-M346 is defined by the presence of the M346 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Origin and distribution Q-M346 was discovered in Central Asia and announced in Sengupta 2006. A latter paper suggested that its ancestral state was isolated to India, but this has since been refuted by its presence in West Asia, Europe and the Americas. Asia Q-M346 has a wide distribution across much of Asia. The Americas In the Americas, the founding paternal lineages include those who are Q-M346 but do not belong to the Q-M3 lineage. Associated SNPs Q-M346 is marked by the presence of the M346 SNP. Since the discovery of M346 several additional SNPs have been found to also be associated with Q-M346. These SNP's include: L56 and L57. These SNPs appear to be "parallel" to M346. Subgroups This is Thomas Krahn at the Genomic Research Center's Draft treProposed Treefor haplogroup Q-M346. The first three levels of subclad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346. In 1996 the research group at Stanford University headed by Dr. Peter Underhill first discovered the SNP that was to become known as M3. At the time, it was called DYS191. Later studies completed the genetic bridge by determining that Q-M3 was related to Q-M242-bearing populations who traveled through Central Asia to East Asia. Origin and distribution Haplogroup Q-M3 is one of the Y-Chromosome haplogroups linked to the indigenous peoples of the Americas (over 90% of indigenous people in Meso & South America). Today, such lineages also include other Q-M242 branches ( Q-M346, Q-L54, Q-P89.1, Q-NWT01, and Q-Z780), haplogroup C-M130 branches ( C-M217 and C-P39), and R-M207, which are almost exclusively found in the North America. Haplogroup Q-M3 is defined by the presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M25 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M25, also known as Q1a1b is a subclade or branch of human Y-DNA haplogroup Q-F1096 (Q1a1), which is, in turn, a subclade of Q-MEH2 ( Q1a). In human genetics, each Y-DNA haplogroup constitutes a biological paternal lineages back to a shared common male ancestor. Distribution Q-M25 has descendants in modern populations across all of Eurasia. Only one detailed study on the Y-DNA on Turkmens from Turkmenistan has taken place. Haplogroup Q is found in minority Turkmen tribes living in Afghanistan at percentages of about 32%,J D Cristofaro et al., 2013, "Afghan Hindu Kush: Where Eurasian Sub-Continent Gene Flows Converge", http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0076748 and another study found that 42.6% of Iranian Turkmens have haplogroup Q-M25 (also known as Q1a1b). The Americas Q-M25 has not been detected in pre-Columbian populations in the Americas. Asia Q-M25 has been detected in the Northeast of East Asia, in South Asia, and across Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-M120 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q-M120, also known as Q1a1a1, is a Y-DNA haplogroup. It is the only primary branch of haplogroup Q1a1a (F746/NWT01). The lineage is most common amongst modern populations in north-east Eurasia. Distribution Q-M120 has descendants in modern populations across eastern Eurasia. The Americas One of the 1K Genomes samples, HG01944, from Peruvians in Lima, Peru belongs to Q-M120. Q-M120 is the other branch under Q-F746. It is best known as an East Asian branch of Q. This is intriguing; if it is not a result of post-colonial admixture, it will mark a fourth or fifth Q lineage in the Americas. The branch of Q-M120 including this sample has a calculated TMRCA of 5,000 to 7,000 years, meaning that it may be the result of a later pre-Columbian immigration from North or East Asia. Asia Q-M120 is present in Eastern Asia and may trace its origin to East Asia. It has been found at low frequency in samples of Han Chinese, Dungans, Hmong Daw in Laos,Cai X, Qin Z, Wen B, Xu S, Wan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L53 (Y-DNA)
Q-L53 is a subclade of haplogroup Q-M346. Q-L53 is defined by the presence of the L53 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP). Distribution Q-L53 has descendants across much of Eurasia and in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is the parent of the major Haplogroup Q-L54 branch. Associated SNPs Q-L53 is currently defined by the L53 SNP as well as the L55, L213, L331, L475, and L476 SNPs. Subgroups This is Thomas Krahn at the Genomic Research Center's Draft treProposed Treefor haplogroup Q-L53. It shows the first two branch points. * Q-L53 L53, L55, L213, L331, L475, L476 ** Q-L54 L54 *** Q-M3 M3, L341.2 *** Q-Z780 Z780 *** Q-L456 L456 *** Q-L568 L568, L569, L570, L571 *** Q-L330 L330, L334 *** Q-L804 L804, L805 See also *Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L940 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L717 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q-L330 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |