|
Hans Von Bülow (general)
Hans Adolf Julius von Bülow was a General of the Artillery in the Imperial German Army. He was the Inspector-General of Artillery from 1879 to 1882. He retired when he had conflicts with Georg von Kameke, the Minister of War. Biography Hans von Bülow was born in the Kingdom of Prussia as first-born of his father, Werner Ludwig von Bülow. He had one younger sister, and one younger brother. After serving as cadet he became a second lieutenant on 5 August 1833. During the time of peace, Bülow increased his knowledge and his skills as he rose the ranks. He was promoted to First Lieutenant in 1844, Hauptmann in 1851 and Major in 1858. In 1859, he became commander of the fortress battalion of the 6th Artillery Regiment. In 1861, he became Oberstleutnant and in 1864, he got command of the 7th Field Artillery Regiment. On 18 June 1865, Bülow was promoted to Oberst. He participated in the Austro-Prussian War at the head of his regiment, which was part of the Army of the Elbe. Bü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Von Bülow (general)
Hans Adolf Julius von Bülow was a General of the Artillery in the Imperial German Army. He was the Inspector-General of Artillery from 1879 to 1882. He retired when he had conflicts with Georg von Kameke, the Minister of War. Biography Hans von Bülow was born in the Kingdom of Prussia as first-born of his father, Werner Ludwig von Bülow. He had one younger sister, and one younger brother. After serving as cadet he became a second lieutenant on 5 August 1833. During the time of peace, Bülow increased his knowledge and his skills as he rose the ranks. He was promoted to First Lieutenant in 1844, Hauptmann in 1851 and Major in 1858. In 1859, he became commander of the fortress battalion of the 6th Artillery Regiment. In 1861, he became Oberstleutnant and in 1864, he got command of the 7th Field Artillery Regiment. On 18 June 1865, Bülow was promoted to Oberst. He participated in the Austro-Prussian War at the head of his regiment, which was part of the Army of the Elbe. Bü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Elbe
The Army of the Elbe was a Prussian formation during the Austro-Prussian War. Being a wartime organization of the Prussian Army; it afterwards was demobilized. Creation Helmuth von Moltke the Elder created the Army of the Elbe for the Austro-Prussian War. It was one of three main field armies of the Prussian Army established during that war. The Army of the Elbe consisted of three division, two cavalry brigades and 144 guns. When it was created the unit were in cantonments around Torgau. Commanded by General Karl Eberhard Herwarth von Bittenfeld; the Army of the Elbe used to be the VIII Corps, reinforced by the 14th Division. Chief of Staff was Oberst Ludwig von Schlotheim. Order of Battle The Army of the Elbe had the following order of battle: Commanding General: General Karl Eberhard Herwarth von Bittenfeld Chief of Staff: Oberst Ludwig von Schlotheim Chief of Artillery: Oberst Hermann von Rozynski-Manger 14th Division * 14. Division, Hugo Eberhard zu Müns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Red Eagle
The Order of the Red Eagle (german: Roter Adlerorden) was an order of chivalry of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was awarded to both military personnel and civilians, to recognize valor in combat, excellence in military leadership, long and faithful service to the kingdom, or other achievements. As with most German (and most other European) orders, the Order of the Red Eagle could only be awarded to commissioned officers or civilians of approximately equivalent status. However, there was a medal of the order, which could be awarded to non-commissioned officers and enlisted men, lower ranking civil servants and other civilians. History The predecessor to the Order of the Red Eagle was founded on 17 November 1705, by the Margrave Georg Wilhelm of Brandenburg-Bayreuth as the '' Ordre de la Sincerité''. This soon fell into disuse but was revived in 1712 in Brandenburg-Bayreuth and again in 1734 in Brandenburg-Ansbach, where it first received the name of "Order of the Brandenburg Red Eagle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Iron Crown (Austria)
The Imperial Order of the Iron Crown (german: Kaiserlicher Orden der Eisernen Krone; it, Ordine imperiale della Corona ferrea) was one of the highest orders of merit in the Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary until 1918. It was founded in 1815 by Emperor Franz I of Austria as a re-establishment of the original Order of the Iron Crown, which previously had been an order of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy. The order had three classes and, until 1884, all classes conferred automatic hereditary ennoblement. The third class conferred the rank of ''Ritter'', the second class conferred the rank of '' Baron'', and the first class conferred the title of Privy Councillor, the style of Excellency and the right to attend court. According to the order's statutes, only a limited number of members throughout the empire were allowed at any given time. The maximum number of 1st class knights was 20, for the 2nd class it was 30 and for the 3rd class 50, limiting the total number of members to 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalleutnant
is the Germanic variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries. Austria Generalleutnant is the second highest general officer rank in the Austrian Armed Forces (''Bundesheer''), roughly equivalent to the NATO rank of OF-8. Belgium Germany ''Generalleutnant'', short ''GenLt'', ('lieutenant general') is the second highest general officer rank in the German Army (''Heer'') and the German Air Force (''Luftwaffe''). This three-star rank in other countries is lieutenant general. Rank in modern Germany The rank is rated OF-8 in NATO, and is grade B9 in the pay rules of the Federal Ministry of Defence. It is equivalent to ''Vizeadmiral'' in the German Navy (''Marine''), or to Generaloberstabsarzt, and Admiraloberstabsarzt in the '' Zentraler Sanitätsdienst der Bundeswehr''. On the shoulder straps (Heer, Luftwaffe) there are three golden pips (stars) in golden oak leaves. History German armies and air forces until 1945 =Generalleutnant of the Wehrm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Orléans (1870)
The Second Battle of Orléans was a battle of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870. It took place on December 3 and 4, 1870 and was part of the Loire Campaign. The Germans recaptured Orléans, which had been retaken by the French on November 11, 1870 after the Battle of Coulmiers, and divided the French Army of the Loire in two. Future king of Serbia, Peter, took part in the battle on the French side. The French lost 19,000 men in two days of combat, including 12,000 prisoners as well as 74 guns and four gunboats. German manpower losses amounted to 1,746, of which 353 killed or dead of wounds, 1,327 wounded and 67 missing. The Germans lost 368 horse The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...s, including 175 killed, 183 wounded and 10 missing. Citations References * vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IX Corps (German Empire)
The IX Army Corps / IX AK (german: IX. Armee-Korps) was a corps level command of the Prussian and German Armies before and during World War I. IX Corps was one of three formed in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War (the others being X Corps and XI Corps). The Corps was formed in October 1866 with headquarters in Altona. The catchment area included the newly annexed Province of Schleswig-Holstein, the Grand Duchies of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz and the Hanseatic cities of Lübeck, Hamburg and Bremen. During the Franco-Prussian War it was assigned to the 2nd Army. The Corps was assigned to the III Army Inspectorate but joined the 1st Army at the start of the First World War. It was still in existence at the end of the war. The Corps was disbanded with the demobilisation of the German Army after World War I. Franco-Prussian War During the Franco-Prussian War, the corps formed part of the 2nd Army. The 17th Division was initially part of the rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernéville
Vernéville (; german: Wernheim) is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. See also * Communes of the Moselle department The following is a list of the 725 communes of the Moselle department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Moselle (department) {{Metz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (german: link=no, Eisernes Kreuz, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, and later in the German Empire (1871–1918) and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). King Frederick William III of Prussia established it on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Queen Louise. Louise was the first person to receive this decoration (posthumously). Recommissioned Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War (EK 1870), World War I (EK 1914), and World War II (EK 1939). During the 1930s and World War II, the Nazi regime superimposed a swastika on the traditional medal. The Iron Cross was usually a military decoration only, though there were instances awarded to civilians for performing military functions, including Hanna Reitsch, who received the Iron Cross, 2nd class, and Iron Cross, 1st Class, and Melitta Schenk Gräfin von Stauffenberg, who received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
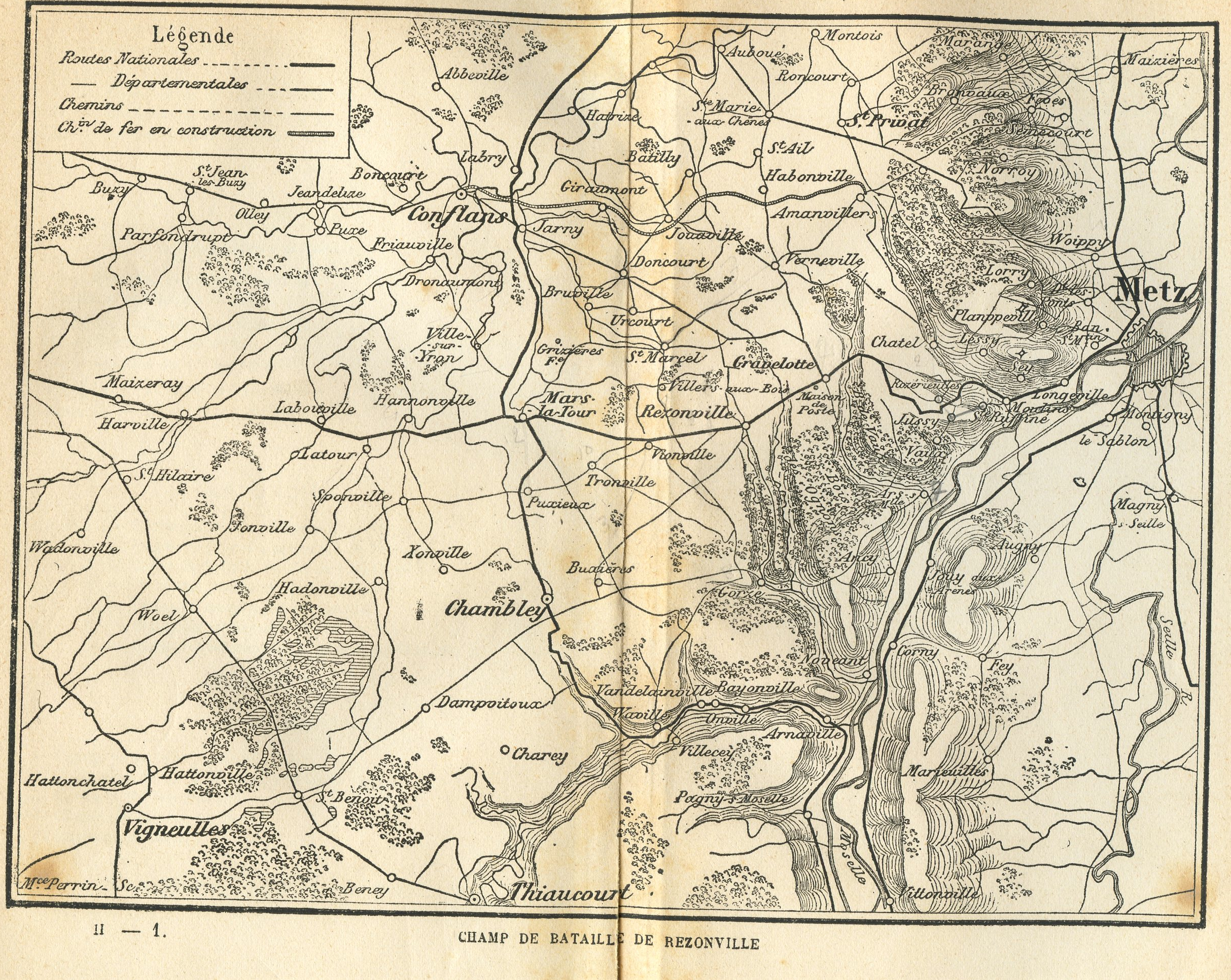
Battle Of Mars-la-Tour
The Battle of Mars-la-Tour (also known as the Battle of Vionville or Battle of Rezonville) was fought on 16 August 1870, during the Franco-Prussian War, near the village of Mars-La-Tour in northeast France. One Prussian corps, reinforced by two more later in the day, encountered the entire French Army of the Rhine in a meeting engagement and, surprisingly, forced the Army of the Rhine to retreat toward the fortress of Metz. A cavalry patrol of the 1st Squadron of the 1st Hanoverian Dragoon Regiment No. 9, led by Rittmeister Oskar von Blumenthal, discovered that Marshal François Bazaine's 160,000-man Army of the Rhine was attempting to escape from Metz to join with French forces at Verdun. This intelligence prompted General Prince Friedrich Karl, commander of the Prussian Second Army, to order at 1900 on 15 August a grossly outnumbered group of 30,000 men of the advanced III Corps under General Constantin von Alvensleben to cut off the French line of retreat at Mars-la-Tour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
III Corps (German Empire)
The III Army Corps / III AK (german: III. Armee-Korps) was a corps level command of the Prussian and then the Imperial German Armies from the 19th century to World War I. It was established in 1814 as the General Headquarters in Berlin (''Generalkommando in Berlin'') and became the III Army Corps on 3 April 1820. Its headquarters was in Berlin and its catchment area was the Province of Brandenburg. In peacetime, the Corps was assigned to the IV Army Inspectorate, joining the 1st Army at the start of the First World War. It was still in existence at the end of the war in the 7th Army, ''Heeresgruppe Deutscher Kronprinz'' on the Western Front. The Corps was disbanded with the demobilisation of the German Army after World War I. War of the Sixth Coalition In 1813 the III Corps fought at the battles of Luckau, Grossbeeren, Dennewitz, Leipzig and Arnhem. In 1814, the corps fought at Hoogstraten and Laon. Second Schleswig War Part of the Corps (10th Brigade of the 5th Divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint John (Bailiwick Of Brandenburg)
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of different ways * Hierarchy, an arrangement of items that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another * an action or inaction that must be obeyed, mandated by someone in authority People * Orders (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Order'' (album), a 2009 album by Maroon * "Order", a 2016 song from ''Brand New Maid'' by Band-Maid * ''Orders'' (1974 film), a 1974 film by Michel Brault * ''Orders'', a 2010 film by Brian Christopher * ''Orders'', a 2017 film by Eric Marsh and Andrew Stasiulis * ''Jed & Order'', a 2022 film by Jedman Business * Blanket order, purchase order to allow multiple delivery dates over a period of time * Money order or postal order, a financial instrument usually intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |