|
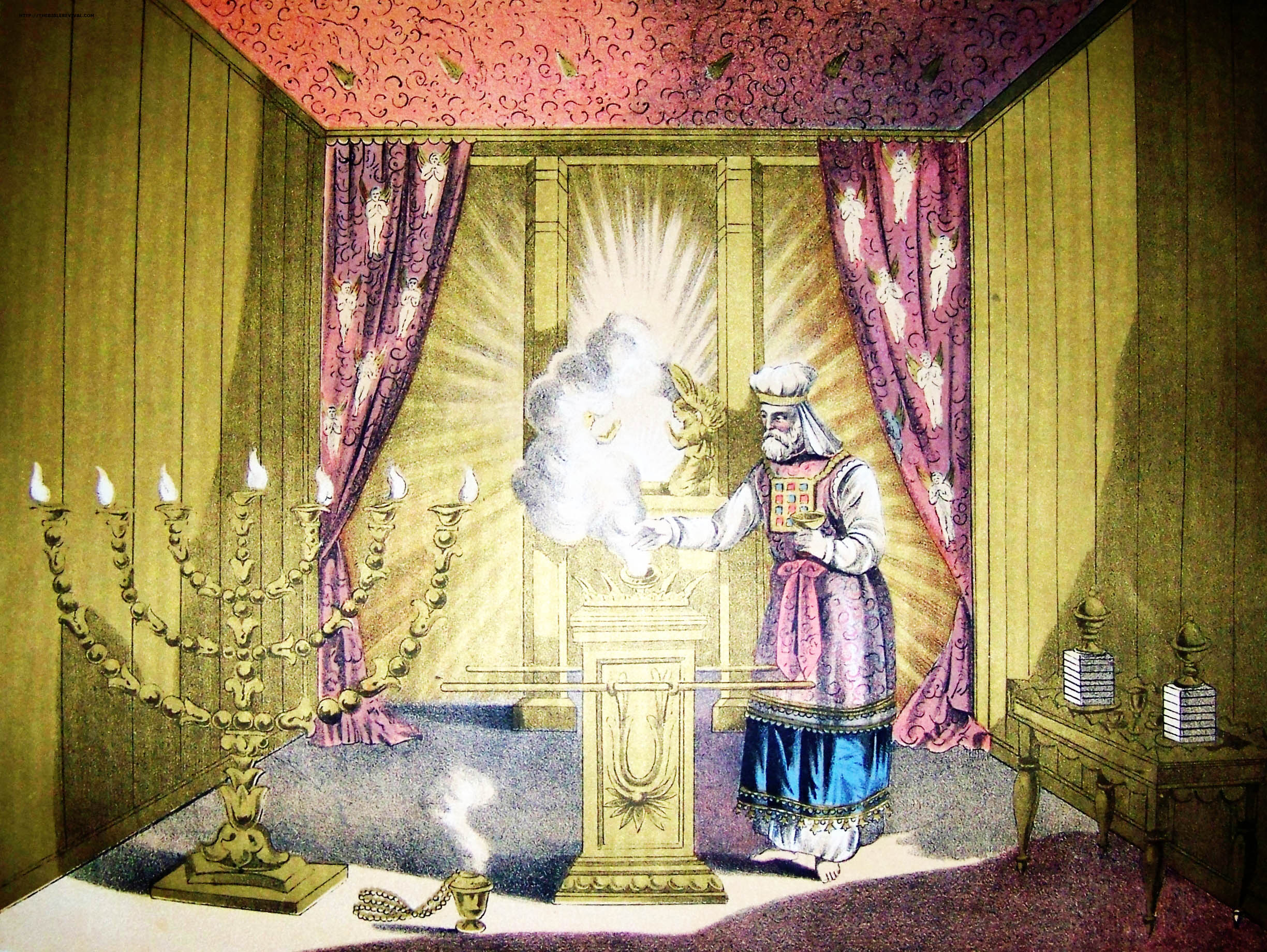
Hanina Segan Ha-Kohanim
Hanina [Hananyah] Segan ha-Kohanim ( he, ר' חנינא (חנניה) סגן הכהנים, lit. ''"R. Hanina (Hananiah) [the] Segan (Deputy) Ha-Kohanim (High priest)"'') was of the first Generation of the Jewish Tannaim, Tanna sages. He was the father of Rabbi Simeon ben ha-Segan. He lived during the destruction of Second Temple of Jerusalem, and had testified, following that event, on what he had seen occur during the destruction. The book "Yihusei Tanna'im ve-Amora'im" cites that he was killed along with Shimon ben Gamliel and Ishmael ben Elisha ha-Kohen. It is said that he was one of the Ten Martyrs, and was killed on the 25th of Sivan. Hanina earned his title due to the role he fulfilled - as Deputy to the Kohen Gadol (High priest) in the Holy Temple of Jerusalem. Ha-Segan was a position with the responsibility of overseeing the actions of the work of the Kohen, Temple priest staff, as well as a stand-in position, ready to take the role of High priest in case he will be foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tannaim
''Tannaim'' ( Amoraic Hebrew: תנאים , singular , ''Tanna'' "repeaters", "teachers") were the rabbinic sages whose views are recorded in the Mishnah, from approximately 10–220 CE. The period of the ''Tannaim'', also referred to as the Mishnaic period, lasted about 210 years. It came after the period of the ''Zugot'' ("pairs"), and was immediately followed by the period of the '' Amoraim'' ("interpreters"). The root ''tanna'' () is the Talmudic Aramaic equivalent for the Hebrew root ''shanah'' (), which also is the root-word of ''Mishnah''. The verb ''shanah'' () literally means "to repeat hat one was taught and is used to mean "to learn". The Mishnaic period is commonly divided up into five periods according to generations. There are approximately 120 known ''Tannaim''. The ''Tannaim'' lived in several areas of the Land of Israel. The spiritual center of Judaism at that time was Jerusalem, but after the destruction of the city and the Second Temple, Yohanan ben Zakkai an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orach Chayim
Orach Chayim, (''manner/way of life'') is a section of Rabbi Jacob ben Asher's compilation of Halakha (Jewish law), Arba'ah Turim. This section addresses aspects of Jewish law pertinent to the Hebrew calendar (be it the daily, weekly, monthly, or annual calendar). Rabbi Yosef Karo modeled the framework of the ''Shulkhan Arukh'' (שולחן ערוך), his own compilation of practical Jewish law, after the ''Arba'ah Turim.'' Many later commentators used this framework, as well. Thus, ''Orach Chayim'' in common usage may refer to another area of halakha, separate from Rabbi Jacob ben Asher's compilation. Orach Chayim deals with, but is not limited to: *Washing the hands in the morning, *Tefillin *Tzitzit (ritual fringes), *Prayer, *Sabbath, *Festivals, *Torah reading in synagogue. Commentaries on the Shulchan Aruch - Orach Chayim * Taz (Turei Zohov) - by Rabbi David HaLevi Segal * Magen Avraham - by Rabbi Avraham Gombiner * Biur HaGra - by the Vilna Gaon * Pri Megadim - by Rabbi Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segan
The Aramaic term ''segan'' (סגן) or ''segan hakohanim'' ( he, סגן הכהנים) is a title used in the Talmud to refer to the priest serving as the deputy to the High Priest of Israel. Hebrew Bible The form ''segan'' is Aramaic (סְגַן), appearing 5 times in the Hebrew Bible in the Aramaic sections of the Book of Daniel to refer to officers of the Babylonian government. The Hebrew form ''sagan'' (סָגָן) occurs a further 17 times in Nehemiah and elsewhere, again to refer to officials of the Babylonian rulers. Talmud According to the Talmud the deputy was appointed to the position of the ''segan ha-kohanim'' with the responsibility of overseeing the actions of the work of the Temple's priests' staff, as well as a stand-in position, ready to take the role of High Priest in case he will be found unfit to serve the holy work on the temple, and thus, the Segan was only second to the High Priest, as Rabbi Hanina Segan ha-Kohanim (40 – 80 CE) attests: Many times the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemara
The Gemara (also transliterated Gemarah, or in Yiddish Gemo(r)re; from Aramaic , from the Semitic root ג-מ-ר ''gamar'', to finish or complete) is the component of the Talmud comprising rabbinical analysis of and commentary on the Mishnah written in 63 books. At first, Gemara was only transmitted orally and was forbidden to be written down, however after the Mishnah was published by Judah the Prince (c. 200 CE), the work was studied exhaustively by generation after generation of rabbis in Babylonia and the Land of Israel. Their discussions were written down in a series of books that became the Gemara, which when combined with the Mishnah constituted the Talmud. There are two versions of the Gemara. The Jerusalem Talmud (Talmud Yerushalmi), also known as the Palestinian Talmud, was compiled by Jewish scholars of the Land of Israel, primarily of the academies of Tiberias and Caesarea, and was published between about 350–400 CE. The Talmud Bavli (Babylonian Talmud) was pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohen
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally believed and halakhically required to be of direct patrilineal descent from the biblical Aaron (also ''Aharon''), brother of Moses. During the existence of the Temple in Jerusalem, ''kohanim'' performed the daily and holiday (Yom Tov) duties of korban, sacrificial offerings. Today, ''kohanim'' retain a lesser though distinct status within Rabbinic and Karaite Judaism and are bound by additional restrictions according to Orthodox Judaism. In the Samaritan community, the kohanim have remained the primary religious leaders. Ethiopian Jewish religious leaders are sometimes called ''kahen'', a form of the same word, but the position is not hereditary and their duties are more like those of rabbis than kohanim in most Jewish communities. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ha-Segan
The Aramaic term ''segan'' (סגן) or ''segan hakohanim'' ( he, סגן הכהנים) is a title used in the Talmud to refer to the priest serving as the deputy to the High Priest of Israel. Hebrew Bible The form ''segan'' is Aramaic (סְגַן), appearing 5 times in the Hebrew Bible in the Aramaic sections of the Book of Daniel to refer to officers of the Babylonian government. The Hebrew form ''sagan'' (סָגָן) occurs a further 17 times in Nehemiah and elsewhere, again to refer to officials of the Babylonian rulers. Talmud According to the Talmud the deputy was appointed to the position of the ''segan ha-kohanim'' with the responsibility of overseeing the actions of the work of the Temple's priests' staff, as well as a stand-in position, ready to take the role of High Priest in case he will be found unfit to serve the holy work on the temple, and thus, the Segan was only second to the High Priest, as Rabbi Hanina Segan ha-Kohanim (40 – 80 CE) attests: Many times the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post-Babylonian captivity, Exilic times until Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Roman Empire, Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Yahwism, Israelite religion, including during the time of the History of ancient Israel and Judah, kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a List of Jewish states and dynasties, Jewish kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shulchan Aruch
The ''Shulchan Aruch'' ( he, שֻׁלְחָן עָרוּך , literally: "Set Table"), sometimes dubbed in English as the Code of Jewish Law, is the most widely consulted of the various legal codes in Judaism. It was authored in Safed (today in Israel) by Joseph Karo in 1563 and published in Venice two years later. Together with its commentaries, it is the most widely accepted compilation of Jewish law ever written. The ''halachic'' rulings in the ''Shulchan Aruch'' generally follow Sephardic law and customs, whereas Ashkenazi Jews generally follow the halachic rulings of Moses Isserles, whose glosses to the ''Shulchan Aruch'' note where the Sephardic and Ashkenazi customs differ. These glosses are widely referred to as the ''mappah'' (literally: the "tablecloth") to the ''Shulchan Aruch's'' "Set Table". Almost all published editions of the ''Shulchan Aruch'' include this gloss, and the term "Shulchan Aruch" has come to denote ''both'' Karo's work as well as Isserles', with Karo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ha-Segan
The Aramaic term ''segan'' (סגן) or ''segan hakohanim'' ( he, סגן הכהנים) is a title used in the Talmud to refer to the priest serving as the deputy to the High Priest of Israel. Hebrew Bible The form ''segan'' is Aramaic (סְגַן), appearing 5 times in the Hebrew Bible in the Aramaic sections of the Book of Daniel to refer to officers of the Babylonian government. The Hebrew form ''sagan'' (סָגָן) occurs a further 17 times in Nehemiah and elsewhere, again to refer to officials of the Babylonian rulers. Talmud According to the Talmud the deputy was appointed to the position of the ''segan ha-kohanim'' with the responsibility of overseeing the actions of the work of the Temple's priests' staff, as well as a stand-in position, ready to take the role of High Priest in case he will be found unfit to serve the holy work on the temple, and thus, the Segan was only second to the High Priest, as Rabbi Hanina Segan ha-Kohanim (40 – 80 CE) attests: Many times the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arba'ah Turim
''Arba'ah Turim'' ( he, אַרְבָּעָה טוּרִים), often called simply the ''Tur'', is an important Halakhic code composed by Yaakov ben Asher (Cologne, 1270 – Toledo, Spain c. 1340, also referred to as ''Ba'al Ha-Turim''). The four-part structure of the ''Tur'' and its division into chapters (''simanim'') were adopted by the later code Shulchan Aruch. This was the first book to be printed in Southeast Europe and the Near East. Meaning of the name The title of the work in Hebrew means "four rows", in allusion to the jewels on the High Priest's breastplate. Each of the four divisions of the work is a "Tur", so a particular passage may be cited as "Tur Orach Chayim, siman 22", meaning "Orach Chayim division, chapter 22". This was later misunderstood as meaning "Tur, Orach Chayim, chapter 22" (to distinguish it from the corresponding passage in the Shulchan Aruch), so that "Tur" came to be used as the title of the whole work. Arrangement and contents The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivan
''Sivan'' (Hebrew: סִיוָן, Standard ''Sīvan'', Tiberian ''Sīwān''; from Akkadian ''simānu'', meaning "Season; time") is the ninth month of the civil year and the third month of the ecclesiastical year on the Hebrew calendar. It is a month of 30 days. ''Sivan'' usually falls in May–June on the Gregorian calendar. Along with all other current, post-biblical Jewish month names, Sivan was adopted during the Babylonian captivity. In the Babylonian calendar it was named Araḫ Simanu. Holidays in Sivan * 6–7 Sivan – Shavuot Sivan in Jewish history * 1 Sivan (1096) – Worms Jews massacred as part of the Rhineland massacres by the First Crusade during morning prayers after taking refuge in a local castle. (see " Iyar in Jewish History" for Iyar 8.) * 4 Sivan ( BCE) – Birth of David. * 6 Sivan (c. ?) - Birth of the Seventh Antediluvian Patriarch/Hero Enoch. * 6 Sivan (c. 1313 BCE) – The Torah was given to Moses at Mount Sinai and thus observed as the holiday of Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |