|
Hanameel The Egyptian
Ananelus (also known as Hanameel) was a Jewish High priest in the 1st century BCE. Though of priestly descent, he was not a member of the Hasmonean dynasty. The Mishnah (Parah 3:5) identifies him as Hanameel the Egyptian, while Josephus ("Ant." xv. 2, § 4) identifies him as being from Babylon. He was appointed by Herod to fill the office of high priest made vacant by the death of Antigonus (37 BCE). Ananelus's incumbency was of short duration. Prudence compelled Herod to remove him, and to fill his place with the Hasmonean Aristobulus (36 BCE). The youthful Hasmonean, however, was too popular with the patriotic party; though he was a brother of Mariamne, Herod's beloved wife, he was treacherously drowned at Herod's instigation (35 BCE), and Ananelus was restored to the high position. How long he continued in office historians do not state; but it could not have been for many years, since after the execution of Mariamne (29 BCE) Herod remarried, and appointed his second father- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
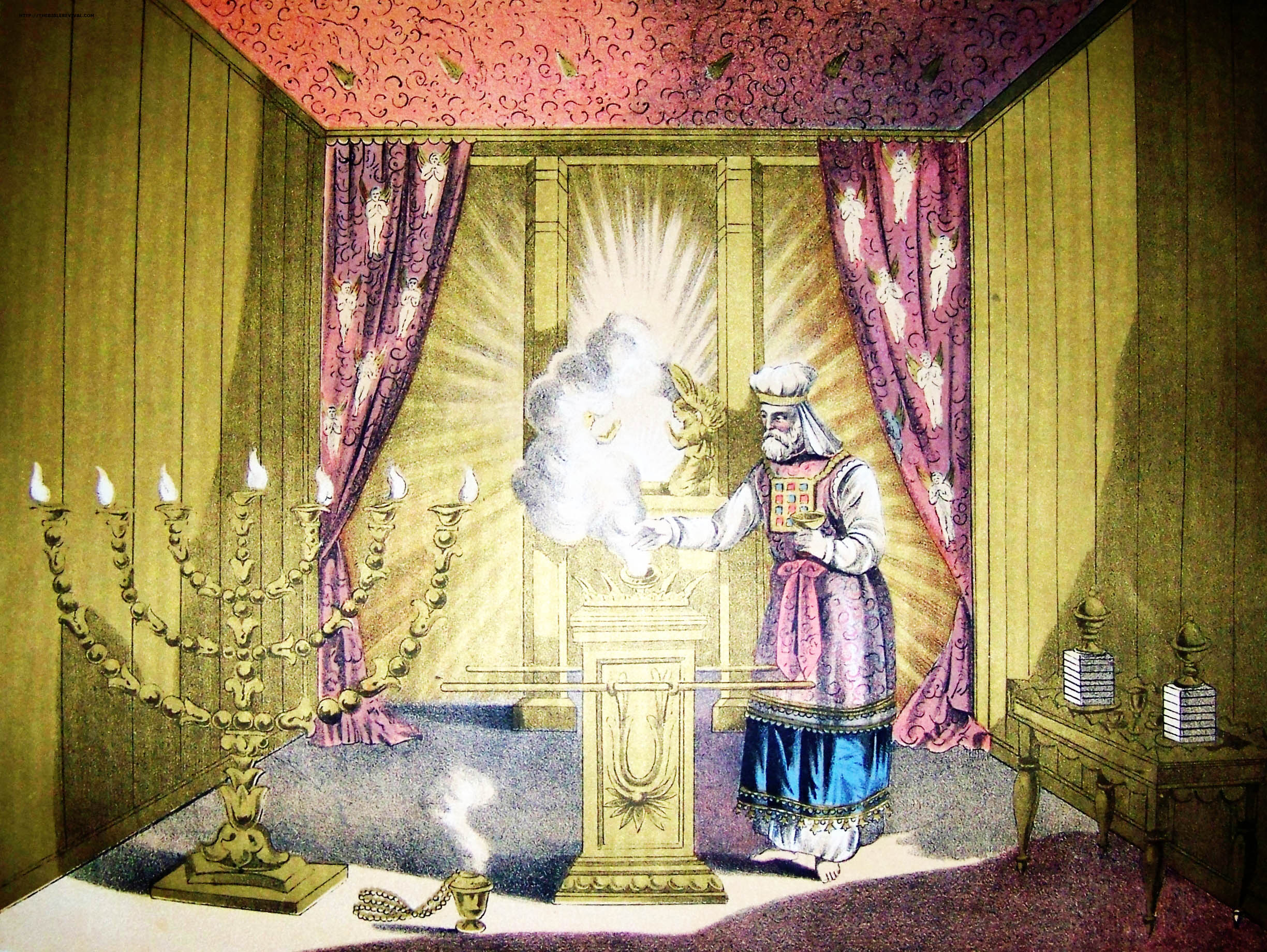
Kohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post-Babylonian captivity, Exilic times until Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE), the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Roman Empire, Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Yahwism, Israelite religion, including during the time of the History of ancient Israel and Judah, kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a List of Jewish states and dynasties, Jewish kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kohen
Kohen ( he, , ''kōhēn'', , "priest", pl. , ''kōhănīm'', , "priests") is the Hebrew word for "priest", used in reference to the Aaronic priesthood, also called Aaronites or Aaronides. Levitical priests or ''kohanim'' are traditionally believed and halakhically required to be of direct patrilineal descent from the biblical Aaron (also ''Aharon''), brother of Moses. During the existence of the Temple in Jerusalem, ''kohanim'' performed the daily and holiday (Yom Tov) duties of korban, sacrificial offerings. Today, ''kohanim'' retain a lesser though distinct status within Rabbinic and Karaite Judaism and are bound by additional restrictions according to Orthodox Judaism. In the Samaritan community, the kohanim have remained the primary religious leaders. Ethiopian Jewish religious leaders are sometimes called ''kahen'', a form of the same word, but the position is not hereditary and their duties are more like those of rabbis than kohanim in most Jewish communities. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasmonean Dynasty
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, and from roughly 110 BCE, with the empire disintegrating, Judea gained further autonomy and expanded into the neighboring regions of Perea, Samaria, Idumea, Galilee, and Iturea. Some modern scholars regard the Hasmonean realm as an independent Israel. The Hasmonean rulers took the Greek title '' basileus'' ("king" or "emperor"). Forces of the Roman Republic conquered the Hasmonean kingdom in 63 BCE and made it into a client state; Herod the Great displaced the last reigning Hasmonean client-ruler in 37 BCE. Simon Thassi established the dynasty in 141 BCE, two decades after his brother Judas Maccabeus ( ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') had defeated the Seleucid army during the Maccabean Revolt of 167 to 141 BCE. According to 1 Maccabees, 2 Maccabee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah. It is also the first major work of rabbinic literature. The Mishnah was redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit Shearim or Sepphoris at the beginning of the 3rd century CE in a time when, according to the Talmud, the persecution of the Jews and the passage of time raised the possibility that the details of the oral traditions of the Pharisees from the Second Temple period (516 BCE – 70 CE) would be forgotten. Most of the Mishnah is written in Mishnaic Hebrew, but some parts are in Aramaic. The Mishnah consists of six orders (', singular ' ), each containing 7–12 tractates (', singular ' ; lit. "web"), 63 in total, and further subdivided into chapters and paragraphs. The word ''Mishnah'' can also indicate a single paragraph of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for ''The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly descent and a mother who claimed royal ancestry. He initially fought against the Romans during the First Jewish–Roman War as head of Jewish forces in Galilee, until surrendering in 67 AD to Roman forces led by Vespasian after the six-week siege of Yodfat. Josephus claimed the Jewish Messianic prophecies that initiated the First Jewish–Roman War made reference to Vespasian becoming Emperor of Rome. In response, Vespasian decided to keep Josephus as a slave and presumably interpreter. After Vespasian became Emperor in 69 AD, he granted Josephus his freedom, at which time Josephus assumed the emperor's family name of Flavius.Simon Claude Mimouni, ''Le Judaïsme ancien du VIe siècle avant notre ère au IIIe siècle de notre ère : Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon
''Bābili(m)'' * sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠 * arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel'' * syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel'' * grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn'' * he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel'' * peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru'' * elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babili'' *Kassite: ''Karanduniash'', ''Karduniash'' , image = Street in Babylon.jpg , image_size=250px , alt = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon , caption = A partial view of the ruins of Babylon , map_type = Near East#West Asia#Iraq , relief = yes , map_alt = Babylon lies in the center of Iraq , coordinates = , location = Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq , region = Mesopotamia , type = Settlement , part_of = Babylonia , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = Sumerian, Akkadian, Amorite, Kassite, Assyrian, Chaldean, Achaemenid, Hellenistic, Parthian, Sasanian, Muslim , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = Hormuzd Rassam, Robe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herod The Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renovation of the Second Temple in Jerusalem and the expansion of the Temple Mount towards its north, the enclosure around the Cave of the Patriarchs in Hebron, the construction of the port at Caesarea Maritima, the fortress at Masada, and Herodium. Vital details of his life are recorded in the works of the 1st century CE Roman–Jewish historian Josephus. Herod also appears in the Christian Gospel of Matthew as the ruler of Judea who orders the Massacre of the Innocents at the time of the birth of Jesus, although most Herod biographers do not believe that this event occurred. Despite his successes, including singlehandedly forging a new aristocracy from practically nothing, he has still been criticised by various historians. His reign pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigonus II Mattathias
Antigonus II Mattathias ( grc-gre, Αντίγονος ''Antígonos''; he, , ''Matīṯyāhū''), also known as Antigonus the Hasmonean (died 37 BCE) was the last Hasmonean king of Judea. A puppet king installed by the Parthians, he was the son of King Aristobulus II of Judea. In 37 BCE Herod handed him over to the Romans for execution, after Antigonus's three-year reign during which he led the Jews' fierce struggle for independence against the Romans. Rome Antigonus was the second son of Aristobulus II, and together with his father, were carried off to Rome as prisoners by Pompey in 63 BCE. Antigonus eventually escaped and returned to Judaea in 57 BCE. Despite an unsuccessful attempt to oppose the Roman forces there, the senate released him, yet he refused to surrender his dynastic rights. After the death of his older brother Alexander, Antigonus claimed that his uncle Hyrcanus II was a puppet of the Idumaean Antipater and attempted to overthrow him with the help and consent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristobulus III Of Judea
Aristobulus III (53–36 BCE) was the last scion of the Hasmonean royal house, brother of Herod the Great's wife Mariamne, and grandson of Hyrcanus II and Aristobulus II. He was a favourite of the people on account of his noble descent and handsome presence, and thus became an object of fear to Herod, who at first sought to ignore him entirely by debarring him from the high priesthood. But his mother Alexandra, through intercession with Cleopatra and Mark Antony, compelled Herod to remove Ananelus from the office of High Priest and appoint Aristobulus instead. To secure himself against danger from Aristobulus, Herod instituted a system of espionage against him and his mother. This surveillance proved so onerous that they sought to gain their freedom by taking refuge with Cleopatra. As told by the Roman Jewish historian Josephus, their plans were betrayed and the disclosure had the effect of greatly increasing Herod's suspicions against his brother-in-law. As Herod dared not resort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Son Of Boethus
Simon son of Boethus (also known as Simon son of Boëthus, Simeon ben Boethus or Shimon ben Boethus) () was a Jewish High priest (ca. 23 – 4 BCE) in the 1st century BCE and father-in-law of Herod the Great. According to Josephus, he was also known by the name Cantheras (). His family is believed to have been connected to the school of the Boethusians, and a family whose origins are from Alexandria in Egypt. He succeeded Jesus, son of Fabus and was removed by Herod when his daughter, Mariamne II was implicated in the plot of Antipater against her husband in 4 BCE. As a result, Herod divorced her and removed her father (Simon Boethus) as high priest.Josephus, ''Antiquities of the Jews''Book XVII Chapter 4:2 Simon's grandson Herod II was removed from the line of succession in Herod's last will. See also * Simon son of Joseph Simon of Peraea or Simon son of Joseph was a former slave of Herod the Great who rebelled and was killed by the Romans some time after Herod's death in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Ben Fabus
Jesus, son of Fabus, also known as Jesus, son of Phabet, Jesus son of Phiabi or Joshua ben Fabus (), was a Jewish High priest (c. 30 – 23 BCE) in the 1st century BCE. He succeeded Ananelus and was removed by Herod when he appointed his father-in-law, Simon ben Boethus Simon son of Boethus (also known as Simon son of Boëthus, Simeon ben Boethus or Shimon ben Boethus) () was a Jewish High priest (ca. 23 – 4 BCE) in the 1st century BCE and father-in-law of Herod the Great. According to Josephus, he was also ..., to the high-priesthood. References {{Judaism-bio-stub 1st-century BCE High Priests of Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_-_Copie.png)