|
Hakea
''Hakea'' ( ) is a genus of about 150 species of plants in the Family ''Proteaceae'', endemic to Australia. They are shrubs or small trees with leaves that are sometimes flat, otherwise circular in cross section in which case they are sometimes divided. The flowers are usually arranged in groups in leaf axils and resemble those of other genera, especially ''Grevillea''. Hakeas have woody fruit which distinguishes them from grevilleas which have non-woody fruit which release the seeds as they mature. Hakeas are found in every state of Australia with the highest species diversity being found in the south west of Western Australia. Description Plants in the genus ''Hakea'' are shrubs or small trees. Some species have flat leaves, whilst others have leaves which are needle-like, in which case they are sometimes divided and sometimes have a groove on the lower surface. The flowers are arranged in groups in leaf axils and are surrounded by bracts when in bud. The flowers have both male ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakea Teretifolia
''Hakea teretifolia'', commonly known as the dagger hakea, is a species of woody shrub of the family Proteaceae and is common on heathlands in coastal eastern Australia from northern New South Wales through to Victoria and Tasmania. A very prickly shrub, it is rarely cultivated but easy to grow. Description ''Hakea teretifolia'' is a prickly shrub that can reach 3 m (10 ft) in height. It has spirally arranged, thick, tough, succulent spike-tipped leaves. Flowering occurs in summer though some may be seen in winter. The small white inflorescences occur on branches and consist of 4-8 individual small flowers. These are followed by sharp pointed (dagger-shaped) seed pods from where the plant gets its common name. Taxonomy and naming Richard Salisbury initially described the species in his book ''Prodromus stirpium in horto ad Chapel Allerton vigentium'' in 1796 and gave it the name ''Banksia teretifolia''. The specific epithet (''teretifolia'') is from the Latin ''tereti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
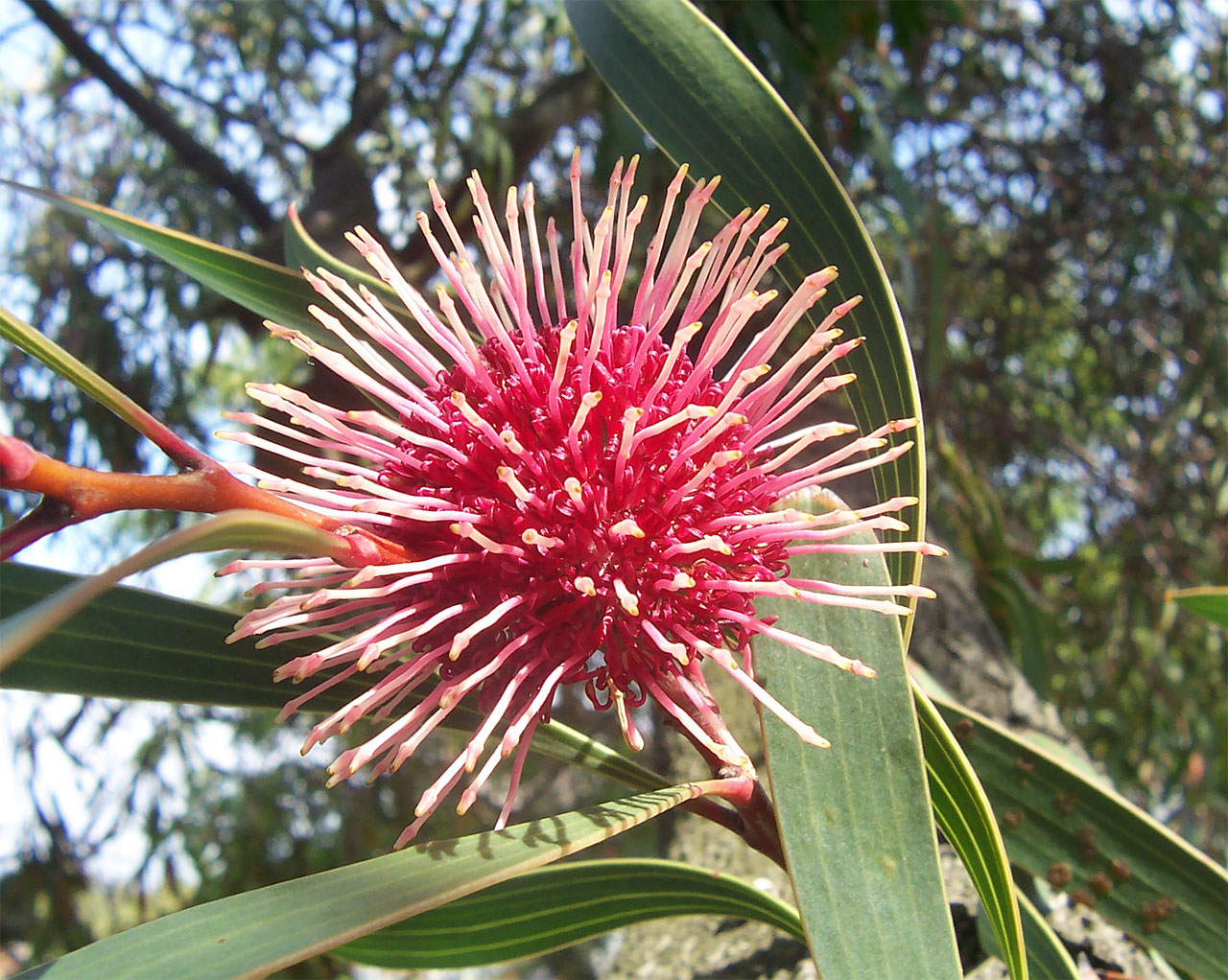
Hakea Laurina
''Hakea laurina'' is shrub or small tree commonly known as kodjet or pin-cushion hakea and is endemic to Western Australia. The Noongar name for the plant is ''kodjet'' or ''kojet''. It has red and cream conspicuous globular flowers and lance shaped leaves. Description ''Hakea laurina'' is an upright shrub or small tree with smooth grey bark, high, wide and does not form a lignotuber. The inflorescence consists of 120-190 conspicuous white, deep pink or red pin cushion shaped flowers in the leaf axils. The pedicels are long and smooth. The perianth is dark pink to red, the pistil long, cream-white or occasionally red or dark pink. The flower buds are enclosed in scale-like bracts. Flowering occurs from April to July. The leaves are simple, slightly blue green, flat, smooth, margins entire, lance or egg-shaped and taper to a blunt point at the tip. The leaves are arranged alternately along the branches, long, wide on a stem long and narrowing at the base. The fruit ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
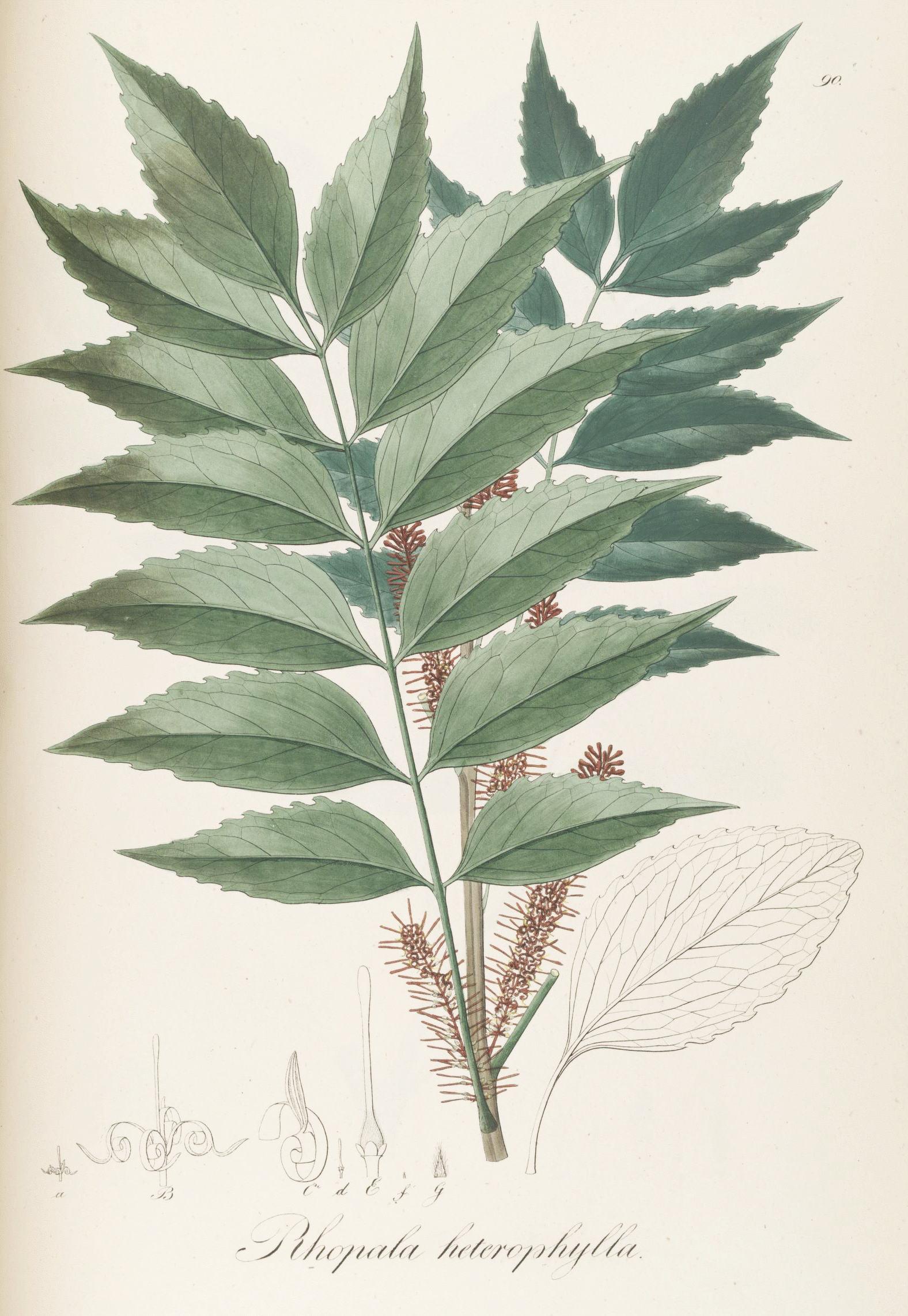
Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Proteales. Well-known genera include ''Protea'', ''Banksia'', ''Embothrium'', ''Grevillea'', ''Hakea'' and ''Macadamia''. Species such as the New South Wales waratah (''Telopea speciosissima''), king protea (''Protea cynaroides''), and various species of ''Banksia'', ''soman'', and ''Leucadendron'' are popular cut flowers. The nuts of ''Macadamia integrifolia'' are widely grown commercially and consumed, as are those of Gevuina avellana on a smaller scale. Australia and South Africa have the greatest concentrations of diversity. Etymology The name Proteaceae was adapted by Robert Brown from the name Proteae coined in 1789 for the family by Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, based on the genus ''Protea'', which in 1767 Carl Linnaeus derived from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, ''banksias'' are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of species are rare and endangered. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Schrader (botanist)
Heinrich Adolf Schrader (1 January 1767 in Alfeld near Hildesheim – 22 October 1836 in Göttingen) was a German botanist and mycologist. He studied medicine early in life. He named the Australian plant genus ''Hakea'' in 1797. In 1795 he received his medical doctorate from the University of Göttingen, where in 1803 he became an associate professor to the medical faculty and director of the botanical garden. In 1809 he attained the title of "full professor" at Göttingen, where he taught classes until his retirement. Among his better known publications are ''Nova genera plantarum'' (1797) and ''Flora germanica'' (1806). The plant genus ''Schraderanthus'' is named in his honour. Schrader was elected a corresponding member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences ( sv, Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien) is one of the Swedish Royal Academies, royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Ludwig Von Hake
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 The term ''sepalum'' was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived . Collectively the sepals are called the calyx (plural calyces), the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. The word ''calyx'' was adopted from the Latin ,Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 not to be confused with 'cup, goblet'. ''Calyx'' is derived from Greek 'bud, calyx, husk, wrapping' ( Sanskrit 'bud'), while is derived from Greek 'cup, goblet', and the words have been used interchangeably in botanical Latin. After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial. Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary (botany)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels (e.g. dicarpel or tricarpel), and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries. Fruits A fruit is the mature, ripened ovary of a flower following double fertilization in an angiosperm. Because gymnosperms do not have an ovary but reproduce through double fertilization of unprotected ovules, they produce naked seeds that do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning " pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (botany)
In botany, sessility (meaning "sitting", used in the sense of "resting on the surface") is a characteristic of plant parts (such as flowers and leaves) that have no stalk. Plant parts can also be described as subsessile, that is, not completely sessile. A sessile flower is one that lacks a pedicel (flower stalk). A flower that is not sessile is pedicellate. For example, the genus ''Trillium'' is partitioned into two subgenera, the sessile-flowered trilliums (''Trillium'' subg. ''Sessilium'') and the pedicellate-flowered trilliums. Sessile leaves lack petioles (leaf stalks). A leaf that is not sessile is petiolate. For example, the leaves of most monocotyledons lack petioles. The term sessility is also used in mycology to describe a fungal fruit body that is attached to or seated directly on the surface of the substrate, lacking a supporting stipe or pedicel Pedicle or pedicel may refer to: Human anatomy *Pedicle of vertebral arch, the segment between the transvers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_(255_30)_Tulip;_cross-section.jpg)
