|
Hadabal
Hadabal (also spelled 'Adabal) was a god worshiped in Ebla and its surroundings in the third millennium BCE. He was one of the main gods of that area, and appears frequently in Eblaite documents. His character is not well understood, though it has been proposed that he might have been an agricultural or lunar god. Like the city's tutelary god Kura and his wife Barama, he is absent from sources postdating the destruction of Ebla. Name and origin The name Hadabal was written as dNI-''da''-KUL or dNI-''da''-BAL in Eblaite cuneiform. The KUL sign being a simplified version of BAL, employed in texts later than the time of the vizier Arrukum. Alfonso Archi assumes that it belonged to a linguistic substrate, similar to these of other Eblaite gods, including Adamma, Aštabi, Ishara and Kura. The existence of a non- Semitic and non-Hurrian substrate language in ancient Syria has been first proposed by Igor M. Diakonoff, who in 1971 concluded that Ishara and Kubaba, while worshiped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamma (goddess)
Adamma was a goddess from the pantheon of Ebla, later incorporated into Hurrian religion. Origin Alfonso Archi, a researcher of Eblaite culture and religion, considers Adamma to most likely be one of the Syrian deity names with origins in a pre- Semitic and pre-Hurrian substratum, much like Hadabal, Ishara, Kura or Aštabi. Another possibility he considers is that her name was derived from the root *''ʾdm'', meaning "blood" or "red." Francesco Aspesi derives it from the Hebrew Adamah, the word for "(red) soil, earth". SEL 13 (1996) 33-40. Hittitologist Piotr Taracha also considers her to be a "Syrian substrate" deity incorporated into Hur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kura (deity)
Kura was a god worshiped in Ebla (modern Tell Mardikh in Syria) in the third millennium BCE. He was the tutelary god of the city, as well as the head of the local pantheon. While his functions are difficult to ascertain, it is well attested that he was connected to the institution of kingship. The etymology of his name is presently unknown, and it is commonly assumed that it belongs to an unknown linguistic substrate, similar to the names of some of the other Eblaite deities, such as Aštabi, Hadabal or Ishara. Kura's spouse was the goddess Barama, who like him was only worshiped in Ebla. After the destruction of the city both of them disappear from records. A number of proposals have been made regarding identification of deities attested from later periods with Kura, but most of them are not widely accepted. Name and origin The oldest attestations of Kura come from administrative texts predating the destruction of Ebla by thirty five to forty years. The name of the god is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishara
Ishara (Išḫara) was the tutelary goddess of the ancient Syrian city of Ebla. The origin of her name is unknown. Both Hurrian and West Semitic etymologies have been proposed, but they found no broad support and today it is often assumed that her name belongs to an unknown linguistic substrate. Her cult had a wide reach across the ancient Near East. In addition to Ebla, she was also worshiped in cities such as Mari, Emar, Alalakh and Ugarit. From these Syrian cities the worship of Ishara spread to Mesopotamia. The Hurrians also adopted her into their pantheon after arriving in Syria, from which she found her way to the Hittite pantheon. In various time periods and areas different functions were assigned to her. In Ebla she was the tutelary deity of the ruling family, but also a love goddess. In Mesopotamia the latter function lead to an association with Ishtar, and later Nanaya, Kanisurra and Gazbaba as well. In Hurrian religion she acquired the role of a goddess associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barama (goddess)
Barama (Eblaite: '' dba-ra-ma'') was a goddess worshiped in the Syrian city of Ebla in the third millennium BCE as the wife of its tutelary god, Kura. She is not attested from any sources postdating the destruction of the city. Character Barama was the wife of Kura, the tutelary god of Ebla. She is relatively infrequently attested in Eblaite texts. Only five mentions come from offering lists, and about twenty from other administrative documents. However, it can be assumed that she nonetheless headed the pantheon alongside her husband. The status of these two deities was reflected in their connection to the royal couple of the city. Alfonso Archi proposes that her name should be understood as "full of color," and that it is derived from the Semitic root *''brm''. A possible cognate word, ''barāmu'', "to be multicolored," is known from Akkadian texts. Walther Sallaberger notes that it has been proposed that the name referred to her colorful clothes. Archi also considers it poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarikh
Yarikh (Ugaritic: , , "moon") was a moon god worshiped in the Ancient Near East. He is best attested in sources from the Amorite city of Ugarit in the north of modern Syria, where he was one of the principal deities. His primary cult center was most likely Larugadu, located further east in the proximity of Ebla. He is also attested in other areas inhabited by Amorites, for example in Mari, but also in Mesopotamia as far east as Eshnunna. In the Ugaritic texts, Yarikh appears both in strictly religious context, in rituals and offering lists, and in narrative compositions. He is the main character in ''The Marriage of Nikkal and Yarikh'', a myth possibly based on an earlier Hurrian composition. The eponymous goddess was regarded as his wife in Ugarit, but she is not attested in documents from most other Syrian cities, and most likely only entered the Ugaritic pantheon due to the influence of Hurrian religion. Ugarit ceased to exist during the Bronze Age collapse, and while Yarikh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resheph
Resheph (also Reshef and many other variants, see below; phn, 𐤓𐤔𐤐, ''ršp''; Eblaite ''Rašap'', Egyptian ') was a deity associated with plague (or a personification of plague), either war or strong protection, and sometimes thunder in ancient Canaanite religion. The originally Eblaite and Canaanite god was then more famously adopted into ancient Egyptian religion in the late Bronze Age during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (late fifteenth century BC), also becoming associated with horses and chariots. In Biblical Hebrew, ''resheph'' is a noun interpreted as "flame, lightning" but also "burning fever, plague, pestilence". Etymology Resheph is known by a multitude of names, including Rahshaf, Rasap, Rashap, Resep, Reshef, Reshpu, Rapha, Repheth, and others that are not standardized. Ebla The name is found in third millennium BCE tablets from Ebla, as ''Rašap'' (''Ra-ša-ap''), listed as divinity of the cities of Atanni, Gunu, Tunip, and Shechem. Ras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saggar (god)
Saggar (also Šaggar, Sanugaru, Šanugaru) was a god worshiped in ancient Syria, especially in the proximity of Ebla and Emar, later incorporated into the Hurrian and Hittite pantheons. His name was also the ancient name of the Sinjar Mountains. It is assumed that he was at least in part a lunar deity. Character Information about the character and development of Saggar is incomplete and difficult to interpret. The name itself is not spelled consistently, especially in sources from the second millennium BCE, and in particular the first consonant often varies between ''s'' and ''š''. The meaning of the name is unknown, and it has been proposed that it comes from a linguistic substrate unrelated to other languages of the Ancient Near East. Two primary aspects of Saggar seemed to be those of a deified mountain range and of a lunar god. Deified mountain range The name Saggar was applied to a mountain range presumably associated with the god, located in the north of modern Iraq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin (mythology)
Nanna, Sīn or Suen ( akk, ), and in Aramaic ''syn'', ''syn’'', or even ''shr'' 'moon', or Nannar ( sux, ) was the god of the moon in the Mesopotamian religions of Sumer, Akkad, Assyria, Babylonia and Aram. He was also associated with cattle, perhaps due to the perceived similarity between bull horns and the crescent moon. He was always described as a major deity, though only a few sources, mostly these from the reign of Nabonidus, consider him to be the head of the Mesopotamian pantheon. The two chief seats of his worship were Ur in the south of Mesopotamia and Harran in the north, though he was also worshiped in numerous other cities, especially in the proximity of Ur and in the Diyala area. In Ur, he was connected to royal power, and many Mesopotamian kings visited his temple in this city. According to Mesopotamian mythology, his parents were Enlil and Ninlil, while his wife was Ningal, worshiped with him in his major cult centers. Their children included maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
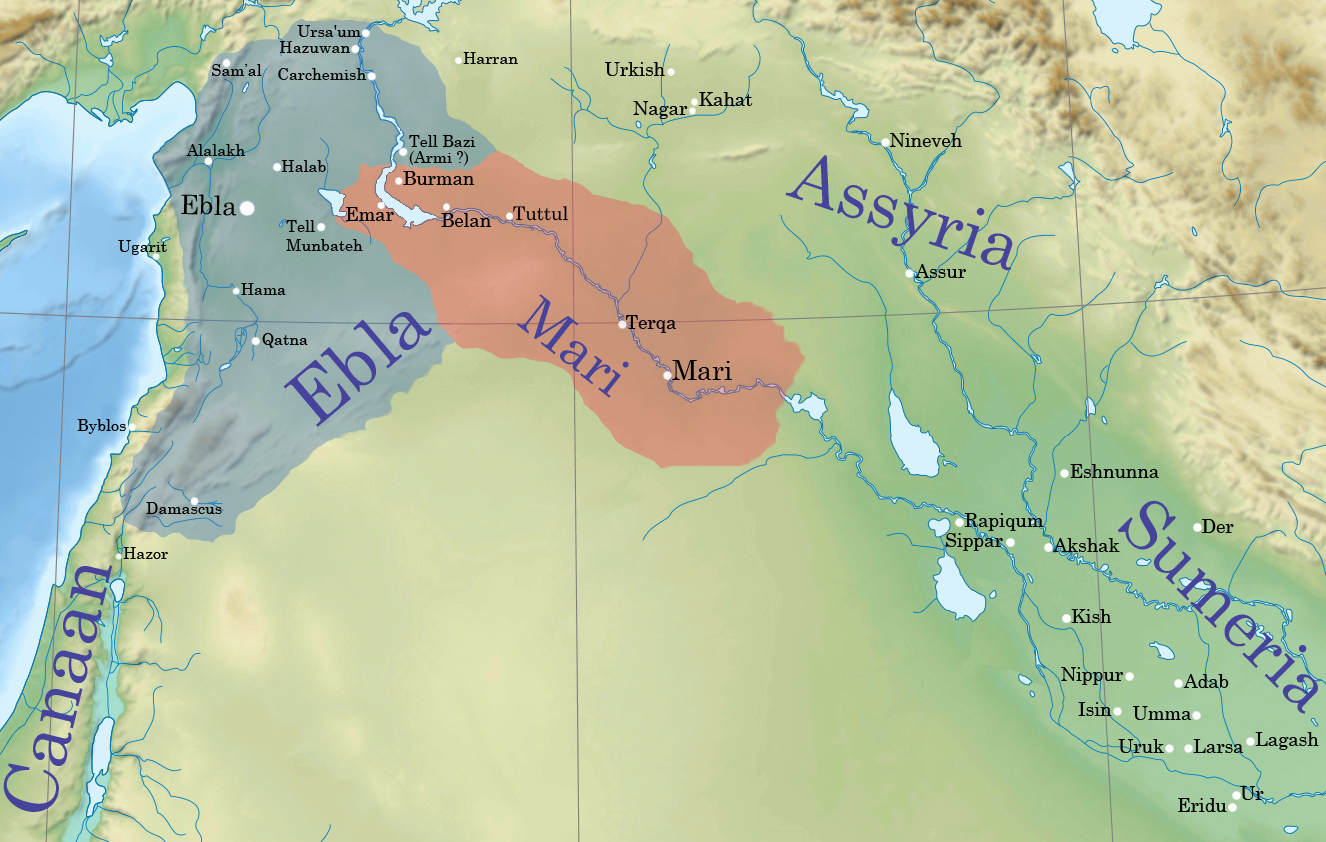
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakrub-El
Yakrub-El or Ikrub-El was a Mesopotamian god worshiped in Terqa in the kingdom of Mari in the early Old Babylonian period. Since his name is structured as if it were a theophoric personal name, is commonly assumed that he was a deified hero or ancestral figure in origin. He is absent from the sources postdating the destruction of Mari. Name and character Yakrub-El's name is structured like a theophoric name, and can be translated as "the god blesses." While Icihiro Nakata in an early study of this deity concluded that it should be understood as a reference a deity identical with Ugaritic El, Alfonso Archi argues that the elements ''el'' and ''il'' in Akkadian, Eblaite and Amorite names do not designate a specific deity, and considers the emergence of the god El to be an Ugaritic religious innovation. Variants of the name Yakrub-El already occur in the oldest Akkadian documents as given names. A single ordinary person bearing the name Yakrub-El is attested even in the corpus of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ar, تل حريري) was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was purposely built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The governors became independent with the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadad
Hadad ( uga, ), Haddad, Adad (Akkadian: 𒀭𒅎 '' DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur ( Sumerian) was the storm and rain god in the Canaanite and ancient Mesopotamian religions. He was attested in Ebla as "Hadda" in c. 2500 BCE. From the Levant, Hadad was introduced to Mesopotamia by the Amorites, where he became known as the Akkadian (Assyrian-Babylonian) god Adad. Adad and Iškur are usually written with the logogram —the same symbol used for the Hurrian god Teshub. Hadad was also called Pidar, Rapiu, Baal-Zephon, or often simply Baʿal (Lord), but this title was also used for other gods. The bull was the symbolic animal of Hadad. He appeared bearded, often holding a club and thunderbolt while wearing a bull-horned headdress. Hadad was equated with the Greek god Zeus, the Roman god Jupiter (and in the cult-center near Doliche in Asia Minor he was addressed as Jupiter Dolichenus), as well as the Hittite storm-god Teshub. The Baal Cycle, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |