|
HMS Vestal (1757)
HMS ''Vestal'' was one of the four 32-gun ''Southampton''-class fifth-rate frigates of the Royal Navy. She was built at King's Yard in Harwich by John Barnard and launched in 1757. She was broken up in 1775. Service history During the Seven Years' War, on 21 February 1759, ''Vestal'', under the command of Captain Samuel Hood, was part of a squadron under the command of Rear-Admiral Charles Holmes bound for North America. ''Vestal'' was in advance of the squadron when she sighted a sail ahead, and set off in pursuit. ''Vestal'' came up to the enemy ship, the 32-gun ''Bellone'', at 2 p.m. After a fierce engagement lasting four hours, ''Bellone'' surrendered, having forty men killed, and being totally dismasted. ''Vestal'' had only her lower masts standing, and had five killed and twenty wounded. She returned to Spithead with her prize, which was bought into the Navy and renamed . The prize money for the capture of the ''Bellone'' was paid out at Portsmouth from May 1760. In J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
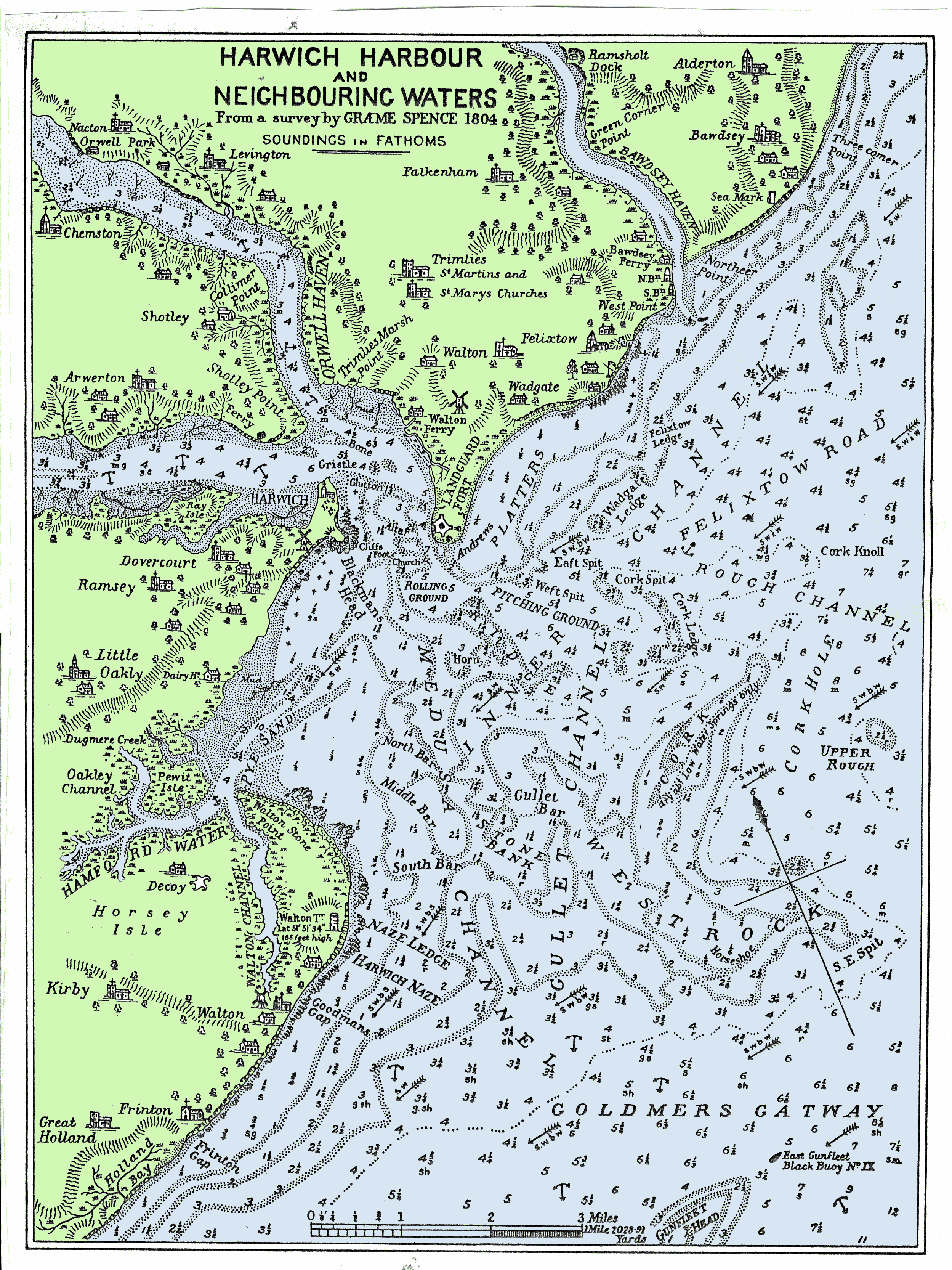
Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on-Sea to the south. It is the northernmost coastal town in Essex. Its position on the estuaries of the Stour and Orwell rivers, with its usefulness to mariners as the only safe anchorage between the Thames and the Humber, led to a long period of civil and military maritime significance. The town became a naval base in 1657 and was heavily fortified, with Harwich Redoubt, Beacon Hill Battery, and Bath Side Battery. Harwich is the likely launch point of the ''Mayflower'', which carried English Puritans to North America, and is the presumed birthplace of ''Mayflower'' captain Christopher Jones. Harwich today is contiguous with Dovercourt and the two, along with Parkeston, are often referred to collectively as ''Harwich''. History The tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Holmes (Royal Navy Officer)
Sir Charles John Holmes, KCVO (11 November 1868, Preston, Lancashire – 7 December 1936, Kensington, London) was a British painter, art historian and museum director. His writing on art combined theory with practice, and he was an expert on the painting techniques of the Old Masters, from whose example he had learned to draw and paint. Early life Holmes was the son of a clergyman, Charles Rivington Holmes, and Mary Susan Dickson. His uncle was Sir Richard Holmes, librarian at Windsor Castle. He attended Eton College from 1883 and attained a scholarship to Brasenose College, Oxford in 1887. From 1889, Holmes worked as a publisher's and printer's assistant in London, first for his cousin Francis Rivington, then at the Ballantyne Press, and finally with John Cumming Nimmo. From 1896 to 1903, he was manager of the Vale Press, supporting Charles Ricketts and Charles Shannon. Holmes also wrote an art column for the Athenaeum which he shared with Roger Fry. In 1903, Holmes marri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1757 Ships
Events January–March * January 2 – Seven Years' War: The British Army, under the command of Robert Clive, captures Calcutta, India. * January 5 – Robert-François Damiens makes an unsuccessful assassination attempt on Louis XV of France, who is slightly wounded by the knife attack. On March 28 Damiens is publicly executed by burning and dismemberment, the last person in France to suffer this punishment. * January 12 – Koca Ragıp Pasha becomes the new Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire, and administers the office for seven years until his death in 1763. * February 1 – King Louis XV of France dismisses his two most influential advisers. His Secretary of State for War, the Comte d'Argenson and the Secretary of the Navy, Jean-Baptiste de Machault d'Arnouville, are both removed from office at the urging of the King's mistress, Madame de Pompadour. * February 2 – At Versailles in France, representatives of the Russian Empire an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Warships In The Age Of Sail
''British Warships in the Age of Sail'' is a series of four books by maritime historian Rif Winfield comprising a historical reference work providing details of all recorded ships that served or were intended to serve in the (British) Royal Navy from 1603 to 1863. Similar volumes dealing with other navies during the Age of Sail have followed from the same publisher. Scope The books draw data from Admiralty official records to give details on the location of construction, dates of construction (ordering, keel laying, launch, commissioning and completion of fitting-out), principal dimensions and tonnage, complement of men and armament, machinery (for steam vessels) and fate of every ship of the Royal Navy over the period. Designed dimensions and tonnage are given for every class of vessel planned and built for the Navy, but in addition the actual dimensions measured for each individual vessel completed to those designs are separately given; this treatment has also been applied to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livorno
Livorno () is a port city on the Ligurian Sea on the western coast of Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of 158,493 residents in December 2017. It is traditionally known in English as Leghorn (pronounced , "Leghorn" in the . or ). During the , Livorno was designed as an "". Developing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Money
Prize money refers in particular to naval prize money, usually arising in naval warfare, but also in other circumstances. It was a monetary reward paid in accordance with the prize law of a belligerent state to the crew of a ship belonging to the state, either a warship of its navy or a privateer vessel commissioned by the state. Prize money was most frequently awarded for the capture of enemy ships or of cargoes belonging to an enemy in time of war, either arrested in port at the outbreak of war or captured during the war in international waters or other waters not the territorial waters of a neutral state. Goods carried in neutral ships that are classed as contraband, being shipped to enemy-controlled territory and liable to be useful to it for making war, were also liable to be taken as prizes, but non-contraband goods belonging to neutrals were not. Claims for the award of prize money were usually heard in a prize court, which had to adjudicate the claim and condemn the priz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raid On Le Havre
The Raid on Le Havre was a two-day naval bombardment of the French port of Le Havre early in July 1759 by Royal Navy forces under Rear-Admiral George Rodney during the Seven Years' War, which succeeded in its aim of destroying many of the invasion barges being gathered there for the planned French invasion of Great Britain. Background By the summer of 1759 the duc de Choiseul's invasion plans was under way with intensive naval preparations taking place along the French ports in the Atlantic and in the channel – Brest, Le Havre, Rochefort and Toulon. Troops were assembled at number of points principally at Dunkirk, Saint-Omer, Ostend, Lille and Vannes.McLynn (2011) pp 239-40 Choiseul had decided that the Le Havre was to be the main base for the Prince de Soubise's strike at England as it lay on the Seine and troop movement was far easier than any other French port. The British had received intelligence that the French had a number of flat bottomed boats were prepared at Le Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Brydges Rodney, 1st Baron Rodney
Admiral George Brydges Rodney, 1st Baron Rodney, KB ( bap. 13 February 1718 – 24 May 1792), was a British naval officer. He is best known for his commands in the American War of Independence, particularly his victory over the French at the Battle of the Saintes in 1782. It is often claimed that he was the commander to have pioneered the tactic of breaking the line. Rodney came from a distinguished but poor background, and went to sea at the age of fourteen. His first major action was the Second Battle of Cape Finisterre in 1747. He made a large amount of prize money during the 1740s, allowing him to purchase a large country estate and a seat in the House of Commons of Great Britain. During the Seven Years' War, Rodney was involved in a number of amphibious operations such as the raids on Rochefort and Le Havre and the Siege of Louisbourg. He became well known for his role in the capture of Martinique in 1762. Following the Peace of Paris, Rodney's financial situation sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spithead
Spithead is an area of the Solent and a roadstead off Gilkicker Point in Hampshire, England. It is protected from all winds except those from the southeast. It receives its name from the Spit, a sandbank stretching south from the Hampshire shore for . Spithead is long by about in average breadth. Spithead has been strongly defended since 1864 by four Solent Forts, which complement the Fortifications of Portsmouth. The Fleet Review is a British tradition that usually takes place at Spithead, where the monarch reviews the massed Royal Navy. The Spithead mutiny occurred in 1797 in the Royal Navy fleet at anchor at Spithead. It is also the location where sank in 1782 with the loss of more than 800 lives. In popular culture In the operetta ''H.M.S. Pinafore'' by Gilbert and Sullivan Gilbert and Sullivan was a Victorian era, Victorian-era theatrical partnership of the dramatist W. S. Gilbert (1836–1911) and the composer Arthur Sullivan (1842–1900), who jointly crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood
Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood (12 December 1724 – 27 January 1816) was an Admiral (Royal Navy), admiral in the Royal Navy. As a junior officer he saw action during the War of the Austrian Succession. While in temporary command of , he drove a French ship ashore in Audierne, Audierne Bay, and captured two privateers in 1757 during the Seven Years' War. He held senior command as North America and West Indies Station, Commander-in-Chief, North American Station and then as Leeward Islands Station, Commander-in-Chief, Leeward Islands Station, leading the British fleet to victory at Battle of the Mona Passage in April 1782 during the American Revolutionary War. He went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth, then First Sea Lord, First Naval Lord and, after briefly returning to the Portsmouth command, became Mediterranean Fleet, Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet during the French Revolutionary Wars. His younger brother was Admiral Alexander Hood, 1st Viscount Bridport (1726–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deptford
Deptford is an area on the south bank of the River Thames in southeast London, within the London Borough of Lewisham. It is named after a ford of the River Ravensbourne. From the mid 16th century to the late 19th it was home to Deptford Dockyard, the first of the Royal Dockyards. This was a major shipbuilding dock and attracted Peter the Great to come and study shipbuilding. Deptford and the docks are associated with the knighting of Sir Francis Drake by Queen Elizabeth I aboard the ''Golden Hind'', the legend of Sir Walter Raleigh laying down his cape for Elizabeth, Captain James Cook's third voyage aboard HMS ''Resolution'', and the mysterious apparent murder of Christopher Marlowe in a house along Deptford Strand. Though Deptford began as two small communities, one at the ford, and the other a fishing village on the Thames, Deptford's history and population has been mainly associated with the docks established by Henry VIII. The two communities grew together and flouri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |