|
HMS Brilliant (1891)
HMS ''Brilliant'' was an of the British Royal Navy which served from 1893 to 1918 in various colonial posts and off the British Isles as a hastily converted minelayer during the First World War. Operational history ''Brilliant'' was commissioned at Portsmouth on 1 October 1901 by Captain Hugh Pigot Williams, for service with the Cruiser Squadron. In May 1902 she was taken into Portsmouth for a refit, and on 16 August that year she took part in the fleet review held at Spithead for the coronation of King Edward VII. The following month she visited the Aegean Sea with other ships of her squadron for combined manoeuvres with the Mediterranean Fleet, returning to Portsmouth in October. Late that year she was ordered back to Gibraltar for temporary service in the Mediterranean to protect British interests in Morocco. First World War On 23 October 1914, ''Brilliant'', together with sister ship , and several sloops and destroyers, shelled German troops on the Belgian coast. On 28 O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheerness Dockyard
Sheerness Dockyard also known as the Sheerness Station was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the Sheerness peninsula, at the mouth of the River Medway in Kent. It was opened in the 1660s and closed in 1960. Location In the Age of Sail, the Royal Navy would often establish shore facilities close to safe anchorages where the fleet would be based in home waters. This was the case when, around 1567, a Royal Dockyard was established at Chatham, Kent, on the bank of the River Medway. At that time, HM Ships would often lay at anchor either within the river, on Chatham Reach or Gillingham Reach, or beyond it, around The Nore. Chatham Dockyard had its disadvantages, however. The vagaries of wind and tide, coupled with the restricted depth of the river, meant that vessels entering the river, for repairs or to replenish supplies at Chatham, could be delayed for considerable lengths of time. What was an inconvenience at times of peace became a serious impediment at times of war; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronation Of King Edward VII And Queen Alexandra
The coronation of Edward VII and his wife, Alexandra, as King and Queen of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and as Emperor and Empress of India took place at Westminster Abbey, London, on 9 August 1902. Originally scheduled for 26 June of that year, the ceremony had been postponed at very short notice, because the King had been taken ill with an abdominal abscess that required immediate surgery. In contrast to the previous coronation some 64 years previously, Edward's had been carefully planned as a spectacle reflecting the influence and culture of the British Empire, then at the height of its power, but also as a meaningful religious occasion. Preparations The 1838 coronation of Queen Victoria, Edward VII's mother and predecessor, had been an unrehearsed and somewhat lacklustre event in the Abbey, though the newly extended street procession and celebrations around the country had been a great popular success. The success of Victoria's Golden and Diamond Jubilee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lerwick
Lerwick (; non, Leirvik; nrn, Larvik) is the main town and port of the Shetland archipelago, Scotland. Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick had a population of about 7,000 residents in 2010. Centred off the north coast of the Scottish mainland and on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland, Lerwick lies north-by-northeast of Aberdeen; west of the similarly sheltered port of Bergen in Norway; and south east of Tórshavn in the Faroe Islands. One of the UK's coastal weather stations is situated there, with the local climate having small seasonal variation due to the maritime influence. Being located further north than Saint Petersburg and the three mainland Nordic capitals, Lerwick's nights in the middle of summer only get dark twilight and winters have below six hours of complete daylight. History Lerwick is a name with roots in Old Norse and its local descendant, Norn, which was spoken in Shetland until the mid-19th century. The name "Lerwick" means ''bay of clay''. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shields
South Shields () is a coastal town in South Tyneside, Tyne and Wear, England. It is on the south bank of the mouth of the River Tyne. Historically, it was known in Roman times as Arbeia, and as Caer Urfa by Early Middle Ages. According to the 2011 census, the town had a population of 75,337. It is the fourth largest settlement in Tyne and Wear; after Newcastle upon Tyne, Sunderland and Gateshead. The town became part of Tyne and Wear in 1974. It is within the historic county boundaries of County Durham. History The first evidence of a settlement within what is now the town of South Shields dates from pre-historic times. Stone Age arrow heads and an Iron Age round house have been discovered on the site of Arbeia Roman Fort. The Roman garrison built a fort here around AD 160 and expanded it around AD 208 to help supply their soldiers along Hadrian's Wall as they campaigned north beyond the Antonine Wall. Divisions living at the fort included Tigris bargemen (from Persia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallsend
Wallsend is a town in North Tyneside, England, at the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall. It has a population of 43,842 and lies east of Newcastle upon Tyne. History Roman Wallsend In Roman times, this was the site of the fort of Segedunum. This fort protected the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall, which did not terminate at the western wall of the fort, but continued from its south-eastern corner down to the shore of the River Tyne. As David Breeze writes, "In the early nineteenth century, as recorded by Bruce, John Buddle the Younger had often seen the Wall foundations extending far into the river when swimming there as a boy." Pre-Conquest The withdrawal of the Romans from the Wall immediately brought the Picts from the north and shortly afterwards the Angles, sailing from near the mouth of the River Elbe with frequent raids both from sea and from land. Ida the Saxon laid waste to the whole of the north in 547 and Wallsend doubtless suffered in the general devastation. It was not un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarrow
Jarrow ( or ) is a town in South Tyneside in the county of Tyne and Wear, England. It is east of Newcastle upon Tyne. It is situated on the south bank of the River Tyne, about from the east coast. It is home to the southern portal of the Tyne Tunnel. In 2011, Jarrow had a population of 43,431. Jarrow is part of the historic County Palatine of Durham. In the eighth century, the monastery of Saint Paul in Jarrow (now Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey) was the home of Bede, The Venerable Bede, who is regarded as the greatest Anglo-Saxon scholar and the father of English history. From the middle of the 19th century until 1935, Jarrow was a centre for shipbuilding, and was the starting point of the Jarrow March against unemployment in 1936. History and naming Foundation The town's name is recorded around AD 750 as ''Gyruum'', representing Old English language, Old English ''[æt] Gyrwum''="[at] the marsh dwellers", from Anglo-Saxon ''gyr''="mud", "marsh". Later spellings are Jaruum in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover Patrol
The Dover Patrol and later known as the Dover Patrol Force was a Royal Navy command of the First World War, notable for its involvement in the Zeebrugge Raid on 22 April 1918. The Dover Patrol formed a discrete unit of the Royal Navy based at Dover and Dunkirk for the duration of the First World War. Its primary task was to prevent enemy German shipping—chiefly submarines—from entering the English Channel ''en route'' to the Atlantic Ocean, thereby obliging the Imperial German Navy to travel via the much longer route around Scotland which was itself covered by the Northern Patrol. History In late July 1914, with war looming, 12 Tribal-class destroyers arrived at Dover to join the near obsolete destroyers already at anchor in the harbour, most of them built in the late 19th century. These destroyers formed the nucleus of the fledgling Dover Patrol, which, from its early beginnings as a modest and poorly equipped command, became one of the most important Royal Navy commands of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace Hood
Rear Admiral Sir Horace Lambert Alexander Hood, (2 October 1870 – 31 May 1916) was a Royal Navy admiral of the First World War, whose lengthy and distinguished service saw him engaged in operations around the world, frequently participating in land campaigns as part of a shore brigade. His early death at the Battle of Jutland in the destruction of his flagship was met with mourning and accolades from across Britain. Hood was a youthful, vigorous and active officer whose service in Africa won him the Distinguished Service Order and who was posthumously appointed a Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath in recognition of his courageous and ultimately fatal service in the Battle of Jutland, during which his ship was constantly engaged from its arrival at the action and caused fatal damage to a German light cruiser. He has been described as "the beau ideal of a naval officer, spirited in manner, lively of mind, enterprising, courageous, handsome, and youthful in appearance … ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Great Britain, Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many illegal migrant crossings during the English Channel migrant crossings (2018-present) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM U-12 (Germany)
SM ''U-12'' was a German submarine, built in 1911 and sunk off Scotland in 1915. It was the first submarine to launch a plane at sea. ''U-12'' was a Type U 9 U-boat built for the Imperial German Navy. Her construction was ordered on 15 July 1908 and her keel was laid down by Kaiserliche Werft in Danzig. She was launched on 6 May 1910 and commissioned on 13 August 1911. The German Empire was the first nation to experiment with submarine aircraft carriers. Oberleutnant zur See Friedrich von Arnauld de la Perière of the Naval Air Service and ''U-12s Kapitanleutnant Walther Forstmann theorised that they could increase the range of their seaplanes by carrying the aircraft out to sea on the deck of submarine and launching the seaplanes after the sub partially submerged, allowing the plane to float off. Service history On 15 January 1915 ''U-12'' left Zeebrugge transporting a Friedrichshafen FF.29 seaplane on its deck. Once beyond the safety of the breakwater, the captain real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Downs (ship Anchorage)
The Downs is a roadstead (area of sheltered, favourable sea) in the southern North Sea near the English Channel off the east Kent coast, between the North and the South Foreland in southern England. In 1639 the Battle of the Downs took place here, when the Dutch navy destroyed a Spanish fleet which had sought refuge in neutral English waters. From the Elizabethan era onwards, the presence of the Downs helped to make Deal one of the premier ports in England, and in the 19th century, it was equipped with its own telegraph and timeball tower to enable ships to set their marine chronometers. The anchorage has depths down to 12 fathoms (22 m). Even during southerly gales some shelter was afforded, though under this condition wrecks were not infrequent. Storms from any direction could also drive ships onto the shore or onto the sands, which—in spite of providing the sheltered water—were constantly shifting, and not always adequately marked. The Downs served in the age of sail as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



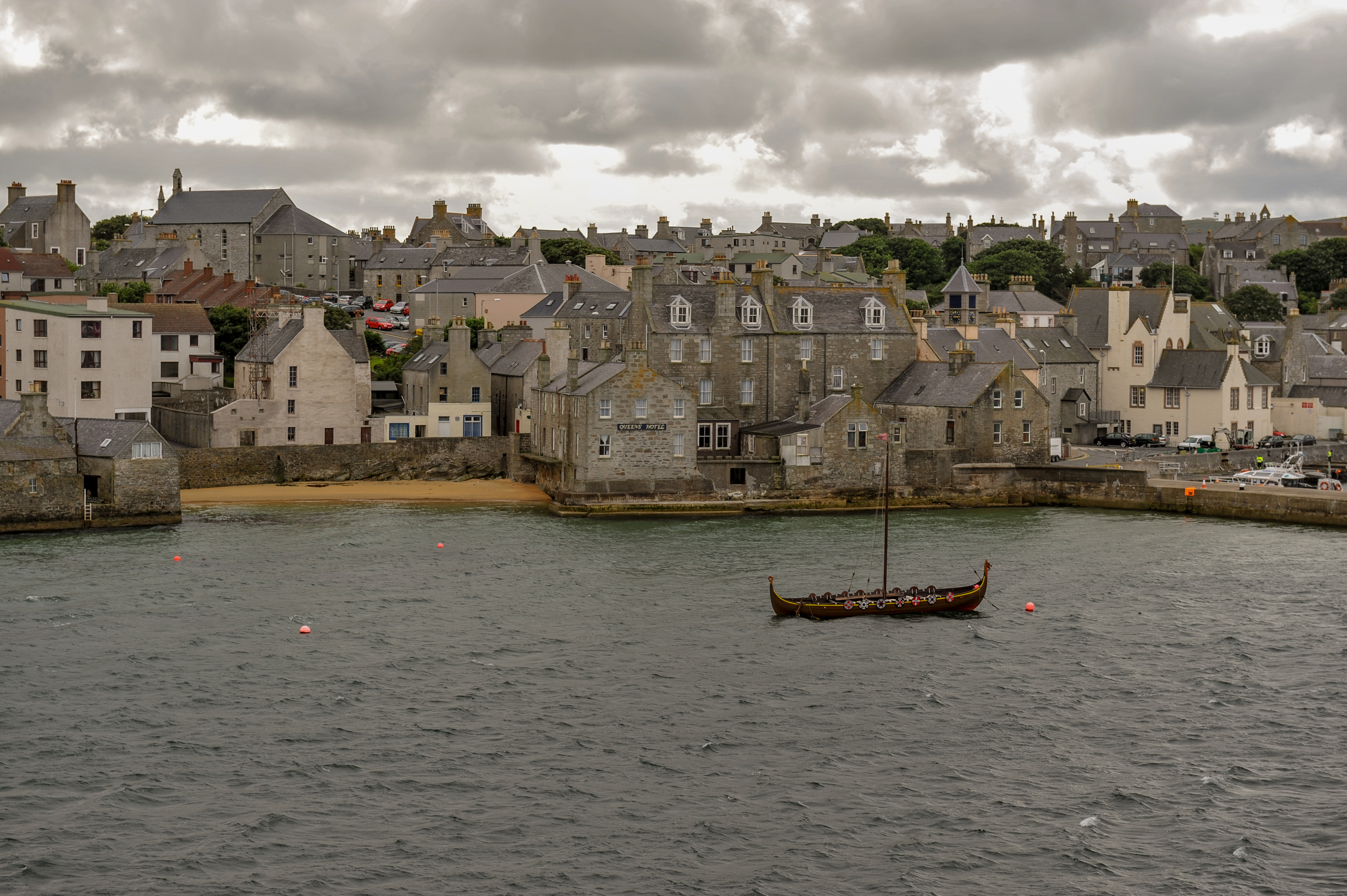



_British_Battleship.jpg)
