|
Dover Patrol
The Dover Patrol and later known as the Dover Patrol Force was a Royal Navy command of the First World War, notable for its involvement in the Zeebrugge Raid on 22 April 1918. The Dover Patrol formed a discrete unit of the Royal Navy based at Dover and Dunkirk for the duration of the First World War. Its primary task was to prevent enemy German shipping—chiefly submarines—from entering the English Channel ''en route'' to the Atlantic Ocean, thereby forcing the Imperial German Navy to travel via the much longer route around Scotland which was itself covered by the Northern Patrol. History In late July 1914, with war looming, 12 s arrived at Dover to join the near obsolete destroyers already at anchor in the harbour, most of them built in the late 19th century. These destroyers formed the nucleus of the fledgling Dover Patrol, which, from its early beginnings as a modest and poorly equipped command, became one of the most important Royal Navy commands of the First World War. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
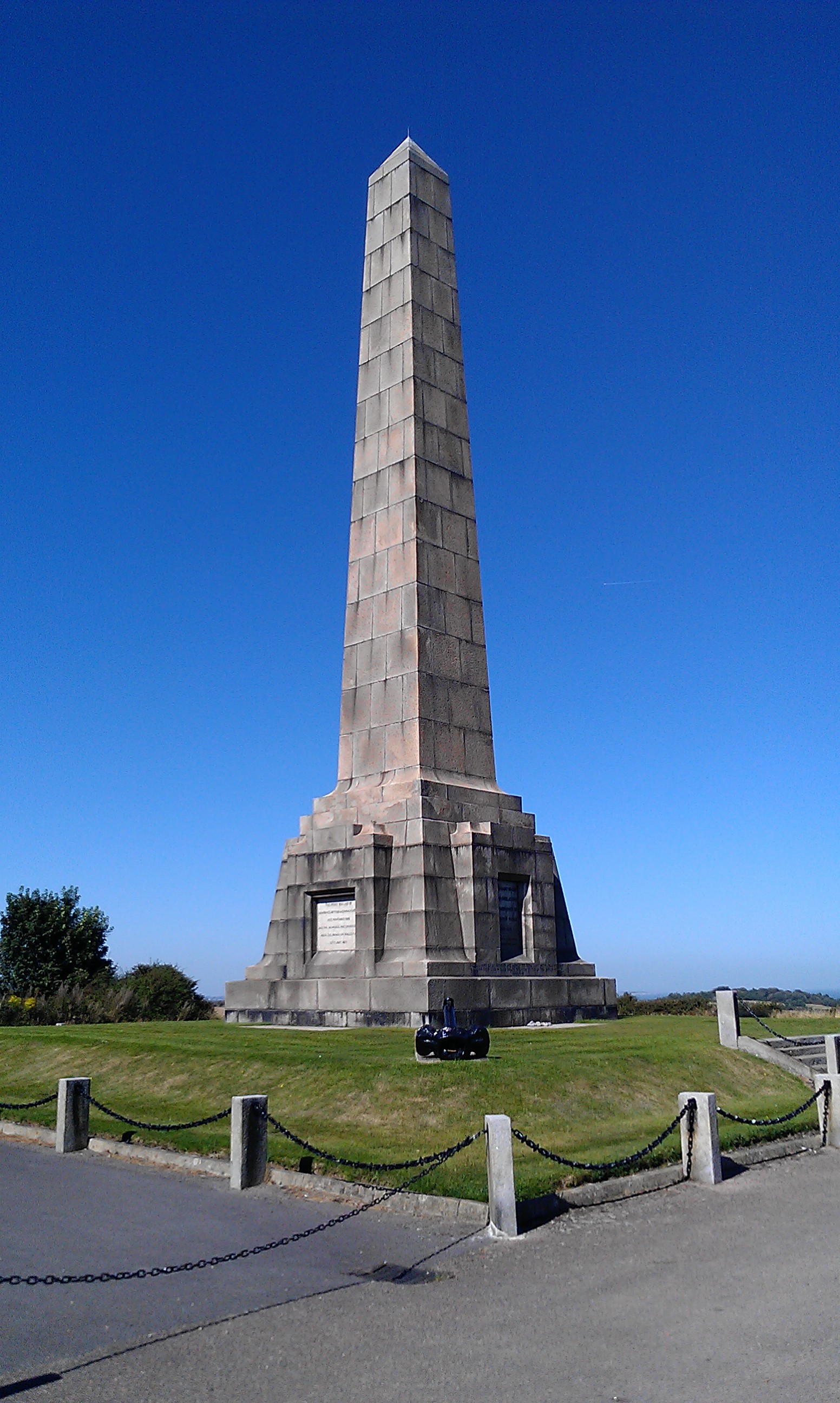
Dover Patrol Monument
The Dover Patrol Monuments are a trio of war memorials designed by Sir Aston Webb to commemorate the Royal Navy's Dover Patrol of the First World War. Two identical granite memorial obelisks, high, were erected near Dover and on the Cap Blanc-Nez near Calais in 1921 and 1922. A third was erected in Brooklyn, New York, in 1931. The UK monument became a Grade II listed building in August 1966, promoted to Grade II* in August 2015. Background The Dover Patrol was formed in July 1914, around a nucleus of the 12 Tribal class destroyers. Through the First World War, a variety of craft served in the patrol—cruisers, destroyers old and new, submarines, mine-sweepers, armed trawlers and drifters, armed yachts, motor launches and other coastal craft—as well as a variety of aircraft - flying boats, aeroplanes, and airships. From time to time, French destroyers were included in the patrol. The patrol covered the southern part of the North Sea and the eastern portion of the Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship that is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . Subsequent vessels of this type were accordingly classed as "monitors". They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dover Engineering Works
Dover ( ) is a town and major ferry port in Kent, southeast England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies southeast of Canterbury and east of Maidstone. The town is the administrative centre of the Dover District and home of the Port of Dover. Archaeological finds have revealed that the area has always been a focus for peoples entering and leaving Britain. The name derives from the River Dour that flows through it. In recent times the town has undergone transformations with a high-speed rail link to London, new retail in town with St James' area opened in 2018, and a revamped promenade and beachfront. This followed in 2019, with a new 500m Pier to the west of the Harbour, and new Marina unveiled as part of a £330m investment in the area. It has also been a point of destination for many illegal migrant crossings. The Port of Dover provides much of the town's employment, as does tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Action Of 15 February 1918
The action of 15 February 1918 was a naval engagement First World War between a (Imperial German Navy) destroyer flotilla and vessels of the Dover Patrol. The action was fought in the Strait of Dover, English Channel. Background Dover Patrol On 1 January 1918 Vice-Admiral Sir Reginald Bacon, the commander of the Dover Patrol since 13 April 1915, was sacked and replaced by Acting Vice-Admiral Sir Roger Keyes, due to differences between Bacon and a Channel Barrage Committee chaired by Keyes, to study the means of closing the Dover Strait to German U-boats and whether the existing barrage between South Calliper and the Flanders coast was capable of stopping anything. Bacon had proposed that a deep minefield be laid between the Varne Bank and Cap Gris-Nez that had been approved by the Admiralty in July 1917. The committee reported that the existing barrage was no obstacle to ships or U-boats and that its light buoys were useful to submarines navigating the straits. Dover Barrage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
U-boat
U-boats are Submarine#Military, naval submarines operated by Germany, including during the World War I, First and Second World Wars. The term is an Anglicization#Loanwords, anglicized form of the German word , a shortening of (), though the German term refers to any submarine. Austro-Hungarian Navy submarines were also known as U-boats. U-boats are most known for their unrestricted submarine warfare in both world wars, trying to Commerce raiding, disrupt merchant traffic towards the UK and force the UK out of the war. In World War I, Germany intermittently waged unrestricted submarine warfare against the United Kingdom, UK: a first campaign in 1915 was abandoned after strong protests from the US but in 1917 the Germans, facing deadlock on the continent, saw no other option than to resume the campaign in February 1917. The renewed campaign failed to achieve its goal mainly because of the introduction of Convoys in World War I, convoys. Instead the campaign ensured final defeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
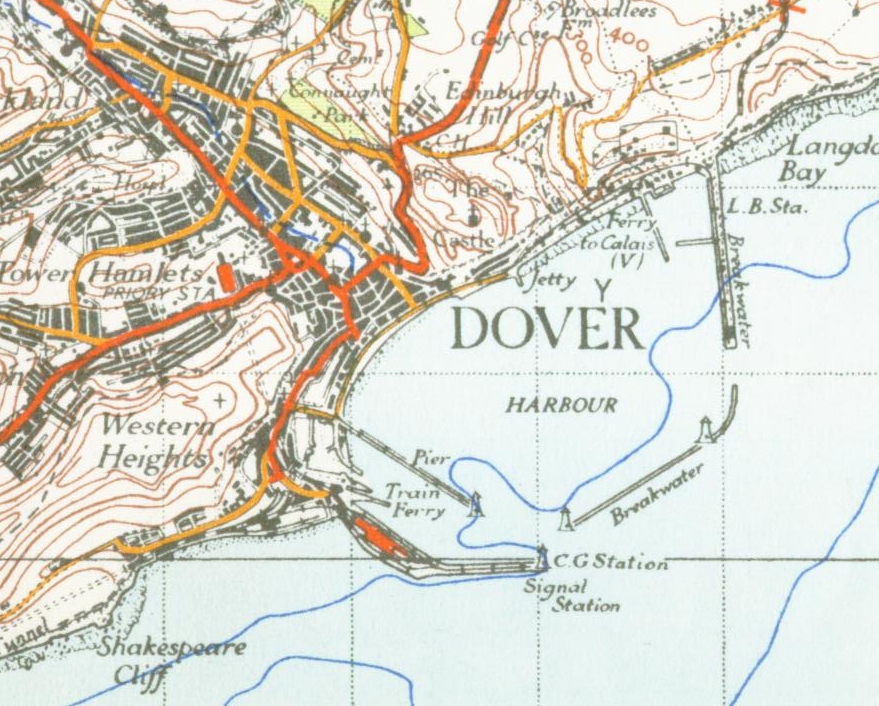
Dover Strait
The Strait of Dover or Dover Strait, historically known as the Dover Narrows, is the strait at the narrowest part of the English Channel, marking the boundary between the Channel and the North Sea, and separating Great Britain from continental Europe. The shortest distance across the strait, at approximately , is from the South Foreland, northeast of Dover in the English county of Kent, to Cap Gris Nez, a cape near to Calais in the French département of Pas-de-Calais. Between these points lies the most popular route for cross-channel swimmers. The entire strait is within the territorial waters of France and the United Kingdom, but a right of transit passage under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea allows vessels of other nations to move freely through the strait. On a clear day, it is possible to see the opposite coastline of England from France and vice versa with the naked eye, with the most famous and obvious sight being the White Cliffs of Dover from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind energy, wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Viking Age, Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Golden Age, Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
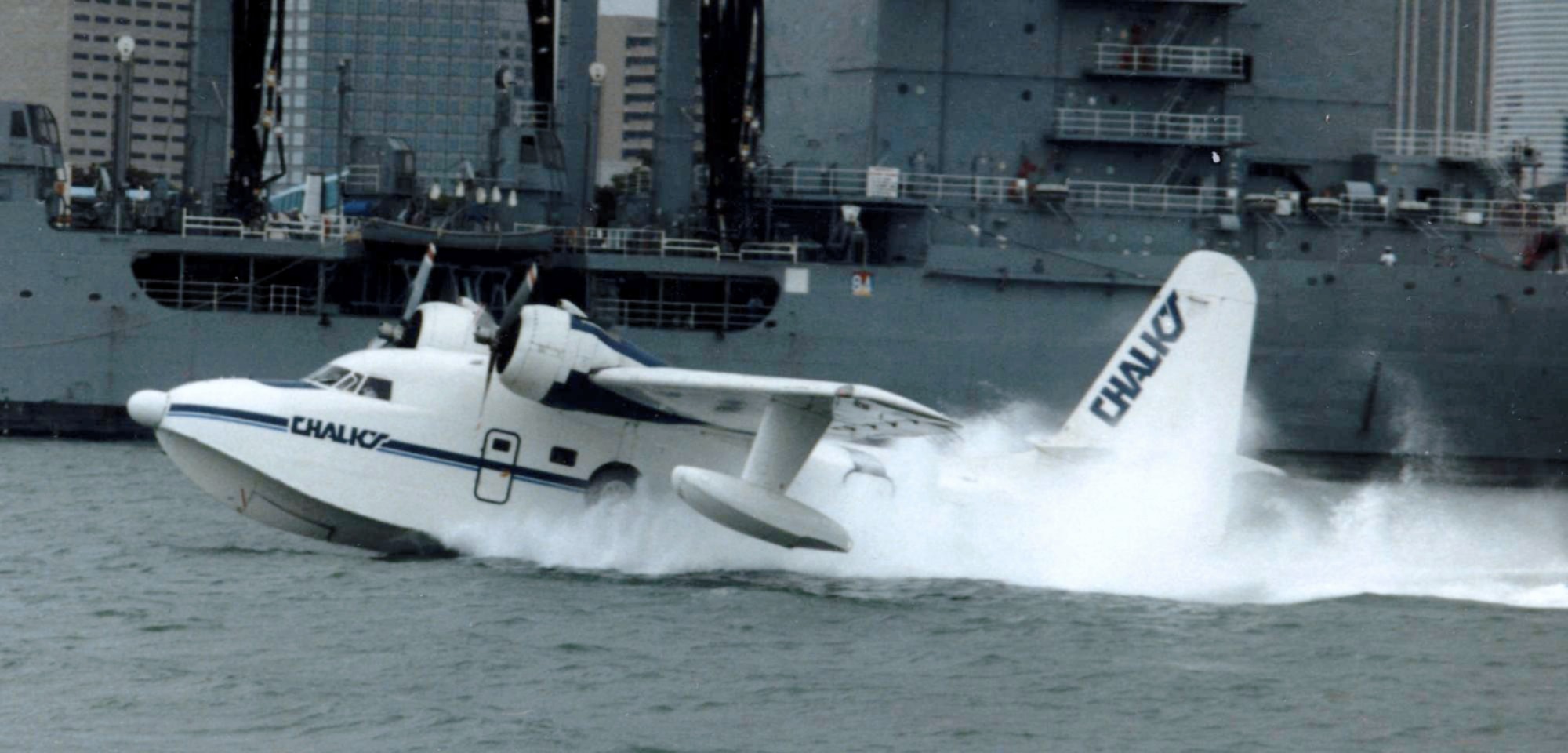
Seaplane
A seaplane is a powered fixed-wing aircraft capable of takeoff, taking off and water landing, landing (alighting) on water.Gunston, "The Cambridge Aerospace Dictionary", 2009. Seaplanes are usually divided into two categories based on their technological characteristics: floatplanes and flying boats; the latter are generally far larger and can carry far more. Seaplanes that can also take off and land on airfields are in a subclass called amphibious aircraft, or amphibians. Seaplanes were sometimes called ''hydroplanes'', but currently this term applies instead to Hydroplane (boat), motor-powered watercraft that use the technique of Planing (boat), hydrodynamic lift to skim the surface of water when running at speed. The use of seaplanes gradually tapered off after World War II, partially because of the investments in airports during the war but mainly because landplanes were less constrained by weather conditions that could result in sea states being too high to operate seaplanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or informally to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, or to medium-sized or smaller vessels (such as the midget submarine and the wet sub). Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' regardless of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and submarines were adopted by several navies. They were first used widely during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Their military uses include: attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines; aircraft carrier protection; Blockade runner, blockade running; Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
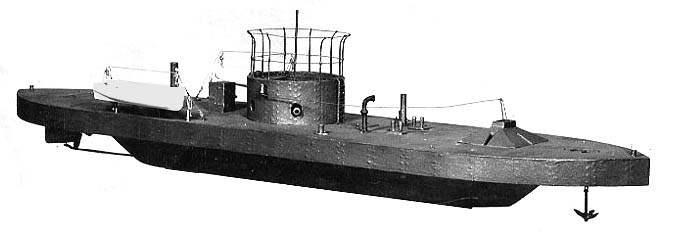
Coastal Motor Boat
Coastal Motor Boat was a small high-speed British torpedo boat used by the Royal Navy in the First World War and up to end of the Second World War. During the First World War, following a suggestion from three junior officers of the Harwich destroyer force that small motor boats carrying a torpedo might be capable of travelling over the protective minefields and attacking ships of the Imperial German Navy at anchor in their bases, the Admiralty gave tentative approval to the idea and, in the summer of 1915, produced a Staff Requirement requesting designs for a Coastal Motor Boat for service in the North Sea. These boats were expected to have a high speed, making use of the lightweight and powerful petrol engines then available. The speed of the boat when fully loaded was to be at least and sufficient fuel was to be carried to give a considerable radius of action. They were to be armed in a variety of ways, with torpedoes, depth charges or for laying mines. Secondary arma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Motor Launch (naval)
A motor launch (ML) is a small military vessel in Royal Navy service. It was designed for Harbour Defence Motor Launch, harbour defence and submarine chaser, submarine chasing. Similar vessels were used by the Royal Air Force for armed high-speed air-sea rescue. Some vessels for water police service are also known as motor launches. Motor launches were slower than motor torpedo boats and motor gun boats World War I service Although small by naval standards, it was larger than the preceding steam or diesel-engined harbour launches of 56 ft and coastal motor boats of 40 and 55 ft length. The first motor launches entered service in the First World War. These were five hundred and eighty vessels built by the US Electric Launch Company, Elco company for the Admiralty, receiving the numbers ML-1 to ML-580. They served with the Royal Navy between 1916 and the end of the war, defending the British coast from German submarines. Some of the earliest examples, including ML 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
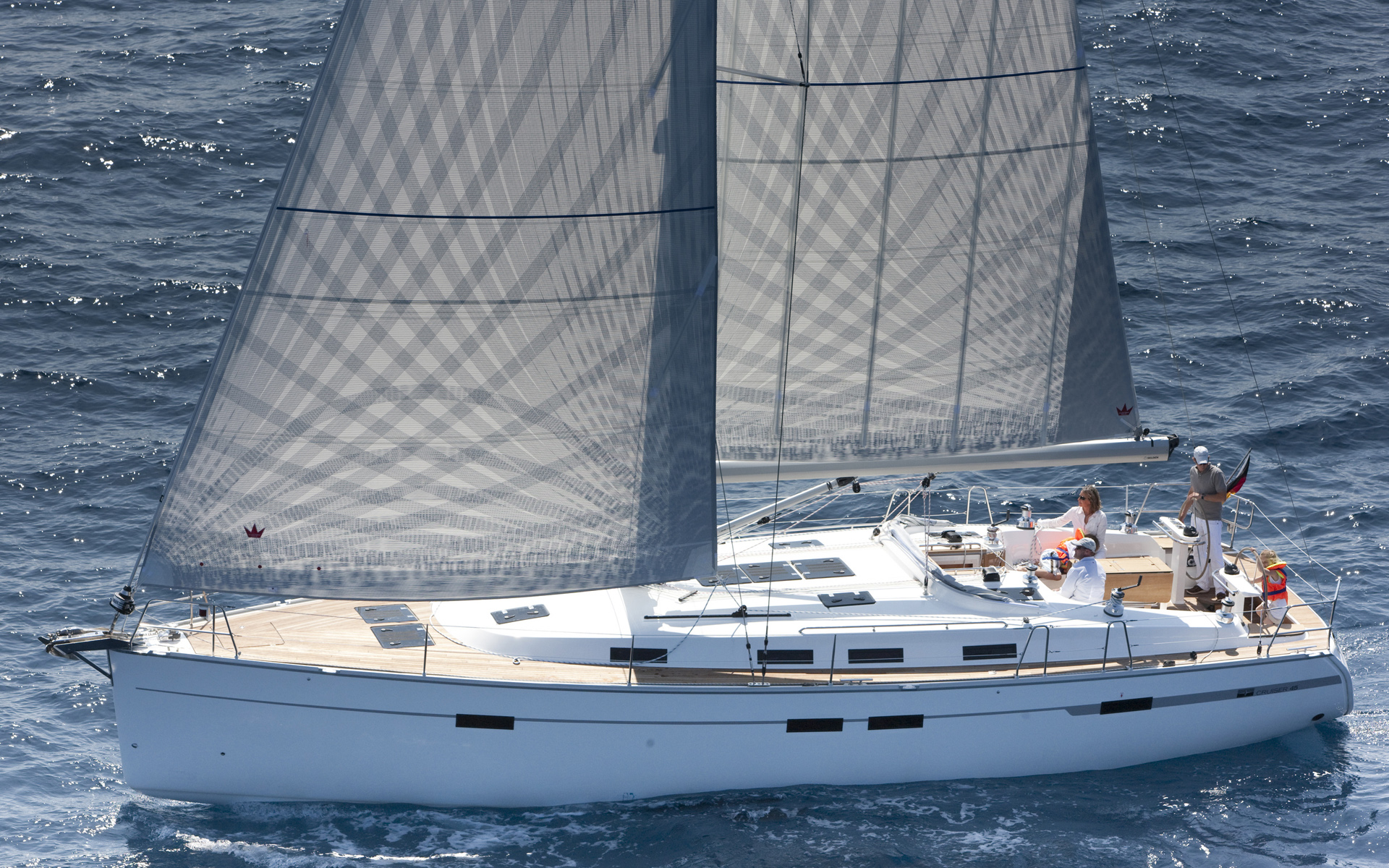
Yacht
A yacht () is a sail- or marine propulsion, motor-propelled watercraft made for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a , as opposed to a , such a pleasure vessel is likely to be at least in length and may have been judged to have good aesthetic qualities. The Commercial Yacht Code classifies yachts and over as . Such yachts typically require a hired crew and have higher construction standards. Further classifications for large yachts are : carrying no more than 12 passengers; : solely for the pleasure of the owner and guests, or by Flag#At sea, flag, the country under which it is registered. A superyacht (sometimes ) generally refers to any yacht (sail or power) longer than . Racing yachts are designed to emphasize performance over comfort. Charter yachts are run as a business for profit. As of 2020, there were more than 15,000 yachts of sufficient size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |