|
HMS Alexander (1778)
HMS ''Alexander'' was a 74-gun third-rate of the Royal Navy. She was launched at Deptford Dockyard on 8 October 1778. During her career she was captured by the French, and later recaptured by the British. She fought at the Nile in 1798, and was broken up in 1819. She was named after Alexander the Great. British service and capture On 13 March 1780, ''Alexander'' and HMS ''Courageaux'' captured the 40-gun French privateer ''Monsieur'' after a long chase and some exchange of fire. The Royal Navy took the privateer into service as HMS ''Monsieur''. In 1794, whilst returning to England in the company of HMS ''Canada'' after escorting a convoy to Spain, ''Alexander'', under the command of Rear-Admiral Richard Rodney Bligh, fell in with a French squadron of five 74-gun ships, and three frigates, led by Joseph-Marie Nielly.Gossett (1986), p.6. In the action of 6 November 1794 ''Alexander'' was overrun by the '' Droits de l'Homme'', but escaped when she damaged the ''Droits de l' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cleveley The Younger, Launch Of HMS Alexander At Deptford In 1778
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
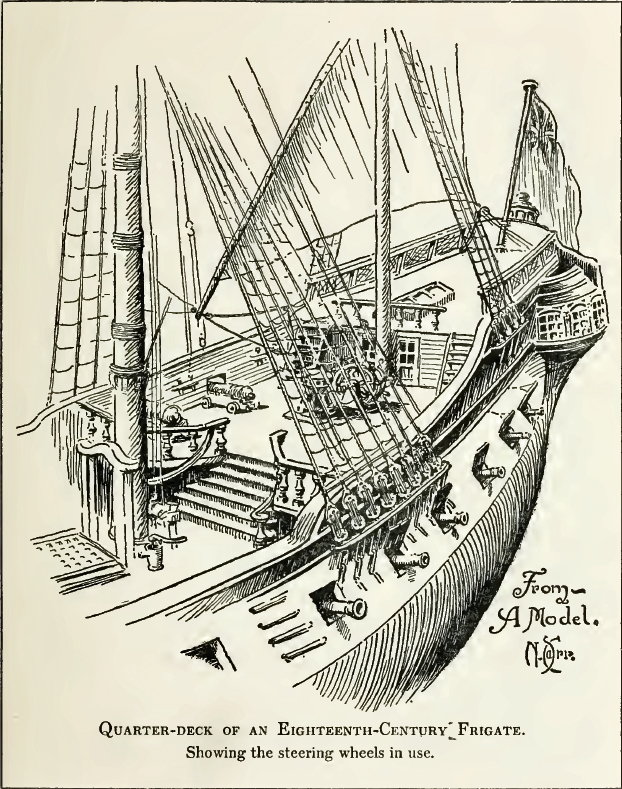
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
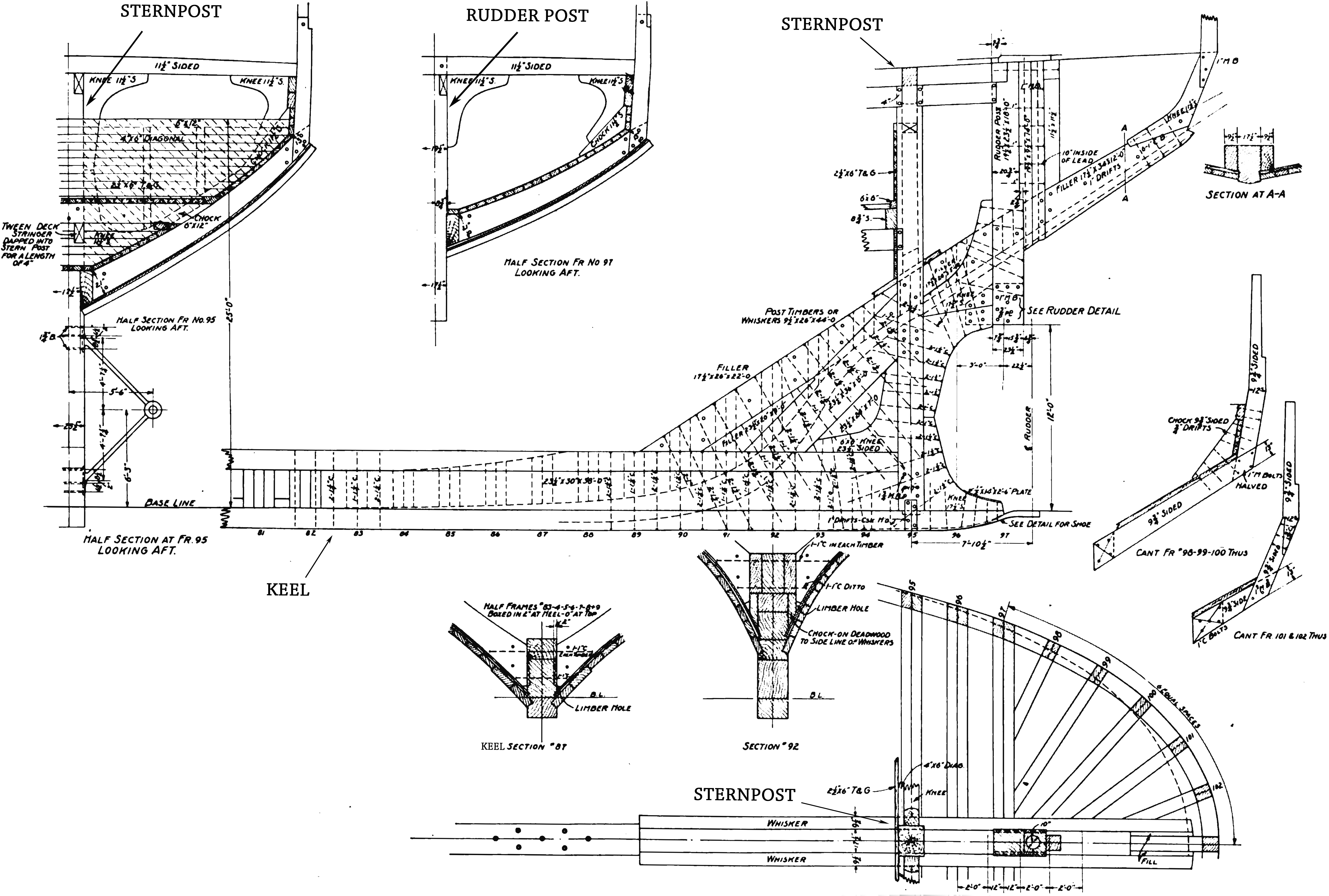
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Belleisle (1795)
''Lion'' was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the French Navy, which later served in the Royal Navy. She was named ''Lion'' on 23 April 1790 and built at Rochefort from August 1791 until June 1794. She was renamed ''Marat'' on 28 September 1793 (7 months before being launched) and then ''Formidable'' on 25 May 1795, with the changing fortunes of the French Revolution. She took part in the action of 6 November 1794, managing to rake . Capture in the Battle of Groix Fighting under captain Linois on 23 June 1795 at the Battle of Groix, she was captured by near the French port of Lorient. She was taken into service in the Royal Navy, but because the Navy already had a , she was renamed ''Belleisle'', apparently in the mistaken belief that she had been captured off Belle Île, rather than the Île de Groix. Battle of Trafalgar 1805 Captained by William Hargood, she was the second ship in the British lee column at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, and as such was engag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Droits De L'Homme (1794)
''Droits de l'Homme'' () was a Seventy-four (ship), 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy during the French Revolutionary Wars. Launched in 1794, the ship saw service in the Atlantic against the British Royal Navy. She was part of the fleet that sailed in December 1796 on the disastrous Expédition d'Irlande. After unsuccessful attempts to land troops on Ireland, the ''Droits de l'Homme'' headed back to her home port of Brest, France, Brest with the soldiers still on board. Two British frigates were waiting to intercept stragglers from the fleet, and engaged ''Droits de l'Homme'' in the action of 13 January 1797. Heavily damaged by the British ships and unable to manoeuvre in rough seas, the ship struck a sandbar and was wrecked. Hundreds of people died in the disaster. Construction and naming The ship was built at Port-Liberté (now Lorient) and launched on ''10 Prairial de l'An II'' (29 May 1794). Her name refers to the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Of 6 November 1794
The action of 6 November 1794 (Known in French as the ''Combat du 16 Brumaire an III'') was a naval engagement during the French Revolutionary Wars. Two British ships of the line, HMS ''Alexander'' and HMS ''Canada'' were intercepted while returning to Britain through the Celtic Sea by a large French squadron. The French squadron had sailed from Brest in search of an inward bound British convoy in October, but instead encountered the two British ships returning from escorting an outward-bound convoy. There had been no warning of the French approach as the British force assigned to watch Brest was absent at Plymouth due to the policy of operating a distant blockade. The British ships separated and attempted to escape, but the French commander ''Contre-amiral'' Joseph-Marie Nielly simply split his forces in response, and although ''Canada'' was eventually able to outrun pursuit, ''Alexander'' was slower and was caught by several French ships in succession. The first two oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Marie Nielly
Joseph-Marie Nielly (1751 – 1833) was a French naval officer and admiral. Nielly was born and died in Brest. He began his career aged seven aboard the ''Formidable'', and was wounded at the Battle of Quiberon Bay, on 20 November 1759. He sailed in the Caribbean until 1769, when he joined the merchant navy. In 1774, aged 23, he received his first command of a merchantman. In 1778, he joined the French Navy as ''lieutenant de frégate''. During the Naval operations in the American Revolutionary War, he commanded the 20-gun ''Guyane'', escorting convoys. On 17 August 1778, she fought against two ships of the line, two frigates and one cutter, yet managed to escaped. After war ended, he sailed again as a merchant, and joined the Navy again in 1787 after a reform of the status of officers from the ranks and files, as a ''sous-lieutenant de vaisseau''. In 1789 and 1790, and commanded the cutter ''Pilote des Indes'', escorting the fishing fleet from Granville. He later served on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Rodney Bligh
Admiral Sir Richard Rodney Bligh, GCB ( bap. 8 November 1737 – 30 April 1821) was an officer of the Royal Navy. He saw service during the American War of Independence, as well as the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, eventually rising to the rank of admiral. He served as Commander-in-Chief, Jamaica Station and Commander-in-Chief, Leith. Family and early life Bligh was born into a naval family, probably in 1737, since he was baptised on 8 November 1737 at Holy Trinity Church, Gosport. His godfather was Captain George Brydges Rodney, later to win fame during the American War of Independence, rising to the rank of admiral. Bligh's father was Richard Bligh, a lieutenant in the navy, while William Bligh was a third cousin.. The younger Richard also embarked on a naval career, joining in 1750 aboard Rodney's ship, the 44-gun . By 1756 he had risen to midshipman and was serving aboard the 90-gun HMS ''Ramillies'', then flying the flag of Admiral Sir John Byng. Bli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Canada (1765)
HMS ''Canada'' was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 17 September 1765 at Woolwich Dockyard. On 2 May 1781, ''Canada'' engaged and captured the Spanish ship , of 34 guns.Ships of the Old Navy, ''Canada''. In 1782, ''Canada'' was under the command of William Cornwallis, when she took part in the Battle of St. Kitts. Later that year she participated in the Battle of the Saintes. She took part in the action of 6 November 1794 under Charles Powell Hamilton and managed to avoid capture. Napoleonic Wars In 1807, ''Canada'' was in the Caribbean in a squadron under the command of Rear-Admiral Alexander Cochrane. The squadron, which included , , and , captured ''Telemaco'', ''Carvalho'' and ''Master'' on 17 April 1807. Following the concern in Britain that neutral Denmark was entering an alliance with Napoleon, in December 1807 ''Canada'' sailed in Cochrane's squadron in the expedition to occupy the Danish West Indies. The expedition captured th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Monsieur (1780)
HMS ''Monsieur'' was the former 40-gun French privateer ''Monsieur'', built at Le Havre between July 1778 and 1779, then armed at Granville. The Royal Navy captured her in 1780 and subsequently put her into service as a 36-gun Fifth Rate. This frigate was sold in 1783. Privateer From August 1779 to March 1780, Nicholas Guidelou was her captain. On her first cruise, in the space of four months, he captured 28 prizes off the English and Irish coasts. Only three of his prizes were retaken, and he brought into port 543 prisoners and 120 cannon. King Louis XVI honoured Guidelou with a sword and a letter of thanks.Cartwright (1911), p.319. On 28 March 1779, ''Monsieur'' captured the Scots letter of marque ''Leveller'', off the harbour of Cork. Two days later, five leagues off Cape Clear, ''Monsieur'' captured the ''Polly'', sailing for Liverpool. After ''Polly'' was ransomed for 1250 guineas, the privateer let her continue her journey. The next day, 1 April, another French privat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Courageux (1753)
''Courageux'' was a 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, launched in 1753. She was captured by the Royal Navy in 1761 and taken into service as HMS ''Courageux''. In 1778 she joined the Channel Fleet, and she was later part of the squadron commanded by Commodore Charles Fielding that controversially captured a Dutch convoy on 31 December 1779, in what became known as the Affair of Fielding and Bylandt. On 4 January 1781, ''Courageux'' recaptured in a close-range action west of Ushant that lasted more than an hour. That April, ''Courageux'' joined the convoy under George Darby which successfully relieved the Great Siege of Gibraltar. At the start of the French Revolutionary Wars, ''Courageux'' took part in the blockade and subsequent occupation of Toulon in 1793. That September, she was sent with a squadron under Robert Linzee to support an insurrection in Corsica and took part in an unsuccessful attack on San Fiorenzo. When Toulon was evacuated, ''Courageux'' was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |