|
HMS Canada (1765)
HMS ''Canada'' was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 17 September 1765 at Woolwich Dockyard. On 2 May 1781, ''Canada'' engaged and captured the Spanish ship , of 34 guns.Ships of the Old Navy, ''Canada''. In 1782, ''Canada'' was under the command of William Cornwallis, when she took part in the Battle of St. Kitts. Later that year she participated in the Battle of the Saintes. She took part in the action of 6 November 1794 under Charles Powell Hamilton and managed to avoid capture. Napoleonic Wars In 1807, ''Canada'' was in the Caribbean in a squadron under the command of Rear-Admiral Alexander Cochrane. The squadron, which included , , and , captured ''Telemaco'', ''Carvalho'' and ''Master'' on 17 April 1807. Following the concern in Britain that neutral Denmark was entering an alliance with Napoleon, in December 1807 ''Canada'' sailed in Cochrane's squadron in the expedition to occupy the Danish West Indies. The expedition captured th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Powell Hamilton
Admiral Charles Powell Hamilton (26 December 1747 – 12 March 1825) was an officer of the Royal Navy, who saw service during the American War of Independence, and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, eventually rising to the rank of admiral. Family and early life Hamilton was born on 26 December 1747, the third and youngest son of Lord Anne Hamilton, who was the third and youngest son of James Hamilton, 4th Duke of Hamilton.; his middle name was from his mother, Anna Charlotta Maria Powell. He joined the navy and saw some service during the American War of Independence. After the Action of 13 May 1779 in which he commanded HMS ''Fortune'', he was promoted to the rank of post-captain on 18 May 1779 and to command of the frigate HMS ''Apollo''. War with the French With the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1793 Hamilton was assigned to command the 74-gun third rate . In November 1794 the ''Canada'' and the , the latter under Captain Richard Rodney Bligh, had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1765 Ships
Events January–March * January 23 – Prince Joseph of Austria marries Princess Maria Josepha of Bavaria in Vienna. * January 29 – One week before his death, Mir Jafar, who had been enthroned as the Nawab of Bengal and ruler of the Bengali people with the support and protection of the British East India Company, abdicates in favor of his 18-year-old son, Najmuddin Ali Khan. * February 8 – **Frederick the Great, the King of Prussia, issues a decree abolishing the historic punishments against unmarried women in Germany for "sex crimes", particularly the ''Hurenstrafen'' (literally "whore shaming") practices of public humiliation. **Isaac Barré, a member of the British House of Commons for Wycombe and a veteran of the French and Indian War in the British American colonies, coins the term "Sons of Liberty" in a rebuttal to Charles Townshend's derisive description of the American colonists during the introduction of the proposed Stamp Act. MP Barré ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line Of The Royal Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison Ship
A prison ship, often more accurately described as a prison hulk, is a current or former seagoing vessel that has been modified to become a place of substantive detention for convicts, prisoners of war or civilian internees. While many nations have deployed prison ships over time, the practice was most widespread in 18th- and 19th-century Britain, as the government sought to address the issues of overcrowded civilian jails on land and an influx of enemy detainees from the War of Jenkins' Ear, the Seven Years' War and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. History The terminology "hulk" comes from the Royal Navy meaning a ship incapable of full service either through damage or from initial non-completion. In England in 1776, during the reign of King George III, due to a shortage of prison space in London, the concept of "prison hulks" moored in the Thames, was introduced to meet the need for prison space. The first such ship came into use on 15 July 1776 under command o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
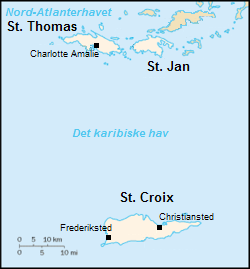
Saint Croix, U
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or Sikh g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Thomas, U
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or Sikh g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies ( da, Dansk Vestindien) or Danish Antilles or Danish Virgin Islands were a Danish colonization of the Americas, Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, Saint Thomas with ; Saint John, U.S. Virgin Islands, Saint John ( da, St. Jan) with ; and Saint Croix with . The islands have belonged to the United States since they were Treaty of the Danish West Indies, purchased in 1917. Water Island, U.S. Virgin Islands, Water Island was part of the Danish West Indies until 1905, when the Danish state sold it to the East Asiatic Company, a private shipping company. The Danish West India Company, Danish West India-Guinea Company annexed uninhabited St. Thomas in 1672; annexed St. John in 1718; and bought St. Croix from France (King Louis XIV) on June 28, 1733. When the Danish West India-Guinea Company went bankruptcy, bankrupt in 1754, Frederik V of Denmark, King Frederik V of Denmark–Norway assumed direct cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of The Danish West Indies (1807)
The second British Invasion of the Danish West Indies took place in December 1807 when a British fleet captured the Danish islands of St Thomas on 22 December and Santa Cruz on 25 December. The Danes did not resist and the invasion was bloodless. This British occupation of the Danish West Indies lasted until 20 November 1815, when Britain returned the islands to Denmark. Background During the later stages of the French Revolutionary Wars (1793-1802), Denmark–Norway, Prussia, and Sweden established the Second League of Armed Neutrality (1800-1801), intending to protect their trade in the Baltic from the British. However, Britain attacked Denmark with the First Battle of Copenhagen in April 1801. Slightly in advance of that, a British fleet arrived at St Thomas at the end of March. The Danes accepted the Articles of Capitulation the British proposed and the British occupied the islands without a shot being fired. The British occupation lasted until April 1802, when the British r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway (Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, and other possessions), the Duchy of Schleswig, and the Duchy of Holstein.Feldbæk 1998:21f, 125, 159ff, 281ff The state also claimed sovereignty over three historical peoples: Frisians, Gutes and Wends.Feldbæk 1998:21 Denmark–Norway had several colonies, namely the Danish Gold Coast, the Nicobar Islands, Serampore, Tharangambadi, and the Danish West Indies.Feldbæk 1998:23 The union was also known as the Dano-Norwegian Realm (''Det dansk-norske rige''), Twin Realms (''Tvillingerigerne'') or the Oldenburg Monarchy (''Oldenburg-monarkiet'') The state's inhabitants were mainly Danes, Norwegians and Germans, and also included Faroese, Icelanders and Inuit in the Norwegian overseas possessions, a Sami minori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |