|
Hōkai-ji (Kamakura)
is a Buddhist temple in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. Often called , or "bush-clover temple", because those flowers are numerous in its garden, its existence is directly linked to a famous tragedy that on July 4, 1333 wiped out almost the entire Hōjō clan, ruler of Japan for 135 years. The temple was founded expressly to enshrine the souls of the 870 members (men, women and children) of the clan who, in accordance with the samurai code of honor, committed suicide on that day at their family temple (''bodaiji'') of Tōshō-ji to escape defeat.Shirai (261:1976) Together with ancient Sugimoto-dera, Hōkai-ji is the only temple of the Tendai denomination in Kamakura. Formerly a of the great Kan'ei-ji (one of the two Tokugawa family temples), after its destruction it became a branch of Enryaku-ji. History The temple of Tōshō-ji was built in 1237 by Hōjō Yasutoki in memory of his mother and, according to the ''Taiheiki'', from its foundation until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Hall (Japanese Buddhism)
Main hall is the building within a Japanese Buddhist temple compound ('' garan'') which enshrines the main object of veneration.Kōjien Japanese dictionary Because the various denominations deliberately use different terms, this single English term translates several Japanese words, among them ''butsuden'', ''butsu-dō'', ''kondō'', ''konpon-chūdō'', and ''hondō''. ''Hondō'' is its exact Japanese equivalent, while the others are more specialized words used by particular sects or for edifices having a particular structure. Kondō (Asuka and Nara periods) The term started to be used during the Asuka and Nara periods. A ''kondō'' is the centerpiece of an ancient Buddhist temple's ''garan'' in Japan. The origin of the name is uncertain, but it may derive from the perceived preciousness of its content, or from the fact that the interior was lined with gold. This is the name used by the oldest temples in the country.Iwanami Nihonshi Jiten A ''kondō'', for example Hōryū-ji's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enryaku-ji
is a Tendai monastery located on Mount Hiei in Ōtsu, overlooking Kyoto. It was first founded in 788 during the early Heian period (794–1185) by Saichō was a Japanese Buddhist monk credited with founding the Tendai school of Buddhism based on the Chinese Tiantai school he was exposed to during his trip to Tang China beginning in 804. He founded the temple and headquarters of Tendai at Enryaku-j ... (767–822), also known as Dengyō Daishi, who introduced the Tendai sect of Mahayana Buddhism to Japan from China. The temple complex has undergone several reconstruction efforts since then, with the most significant (that of the main hall) taking place in 1642 under Tokugawa Iemitsu. Enryaku-ji is the headquarters of the Tendai sect and one of the most significant monasteries in Japanese history. As such, it is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto (Kyoto, Uji and Otsu Cities)". The founders of Jōdo-shū, Jōdo Shinshū, Sōtō, Sōt� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikken
The was a titular post held by a member of the Hōjō clan, officially a regent of the shogunate, from 1199 to 1333, during the Kamakura period, and so he was head of the ''bakufu'' (shogunate). It was part of the era referred to as . During roughly the first half of that period, the ''shikken'' was the ''de facto'' military dictator of Japan (not including the independent Northern Fujiwara). The title of ''shikken'' was modified, as second in command to the ''Tokusō'' in 1256, but by the Muromachi period (1333–1573) the position, though not abolished, did not even figure in the top ranks. The position ceased to exist after the Muromachi period. Etymology The word ''shikken'' is the on'yomi reading of the combination of the two kanji characters and , each meaning "to hold (something in the hand, or a service or ceremony); to administer", "power, authority" respectively. Therefore the word literally means "to hold power/authority". ''Shikken'' as supreme ruler (1199–1256) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hōjō Yoshitoki
was the second Hōjō ''shikken'' (regent) of the Kamakura shogunate and head of the Hōjō clan. He was the second son of Hōjō Tokimasa. He was ''shikken'' from the abdication of his father Tokimasa in 1205 until his death in 1224. Early years (1163–1183) Hōjō Yoshitoki was born in 1163, who was the second son of Hōjō Tokimasa and his wife, who was a daughter of Itō Sukechika. At the time of his birth, he had an older brother, Hōjō Munetoki, and an older sister, Hōjō Masako. Later on in the decade, he would have another brother, Hōjō Tokifusa, and a sister whose name remains unknown, but their birth dates are not known. The Hōjō clan was at that time in control of Izu, and Yoshitoki, being a Hōjō, was also a descendant of the Taira clan and also of the imperial family. At that time, the Taira, under Taira no Kiyomori, had consolidated their power in Kyoto, the capital, and expelled the Minamoto clan, their rival. Minamoto no Yoshitomo, the head of the cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongen
A , literally "incarnation", was believed to be the manifestation of a buddha in the form of an indigenous kami, an entity who had come to guide the people to salvation, during the era of shinbutsu-shūgō in premodern Japan.Encyclopedia of Shinto''Gongen''accessed on October 5, 2008Tamura (2000:87) The words and are synonyms for gongen. is the term for belief in the existence of gongen. The gongen concept is the cornerstone of the honji suijaku theory, according to which Buddhist deities choose to appear to the Japanese as native kami in order to save them, which is based on the Mahayana Buddhist notion of upaya, "expedient means". History It is sometimes assumed that the word ''gongen'' derives from Tokugawa Ieyasu's posthumous name (Tōshō Daigongen). However, the term was created and started being used in the middle of the Heian period in an effort to harmonize Buddhism and indigenous religious practice in what is called shinbutsu-shūgō or "syncretism of kami and bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokusō
was the title (post) held by the head of the mainline Hōjō clan, who also monopolized the position of ''shikken'' (regents to the shogunate) of the Kamakura shogunate in Japan during the period of Regent Rule (1199–1333). It’s important not to confuse a regent of the shogunate with a regent of the Emperor (the latter are called ''Sesshō'' and ''Kampaku''). ''Shikkens'' were the first regents to the shogunate. The ''tokusō'' from 1256 to 1333 was the military dictator of Japan as de facto head of the ''bakufu'' (shogunate); despite the actual shōgun being merely a puppet. This implies that all other positions in Japan—the Emperor, the Imperial Court, ''Sesshō'' and ''Kampaku'', and the ''shikken'' (regent of the shōgun)—had also been reduced to figureheads.「執権 (一)」(『国史大辞典 6』( 吉川弘文館、 1985年) ) Origin The name ''tokusō'' is said to have come from , the Buddhist name of Hōjō Yoshitoki, but Hōjō Tokimasa is usually reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komachi (Kanagawa)
is a locality (a ) in Kamakura, Kanagawa prefecture, Japan, defined as the part of town north of the Ebisubashi bridge on the Namerigawa The is a river that goes from the Asaina Pass in northern Kamakura, Kanagawa to the beach in Yuigahama, for a total length of about 8 km. Although Yuigahama is in fact the name of the entire 3.2 km beach that goes from Inamuragasaki to ....Kamakura Shōkō Kaigijo (2008:60-61) The part of town south of the same bridge is called . Notes References * Kamakura, Kanagawa {{kanagawa-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakura period, shoguns were themselves figureheads, with real power in hands of the Shikken of the Hōjō clan. The office of shogun was in practice hereditary, though over the course of the history of Japan several different clans held the position. The title was originally held by military commanders during Heian period in the eighth and ninth centuries. When Minamoto no Yoritomo gained political ascendency over Japan in 1185, the title was revived to regularize his position, making him the first shogun in the usually understood sense. The shogun's officials were collectively referred to as the ; they were the ones who carried out the actual duties of administration, while the Imperial court retained only nominal authority.Beasley, William G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
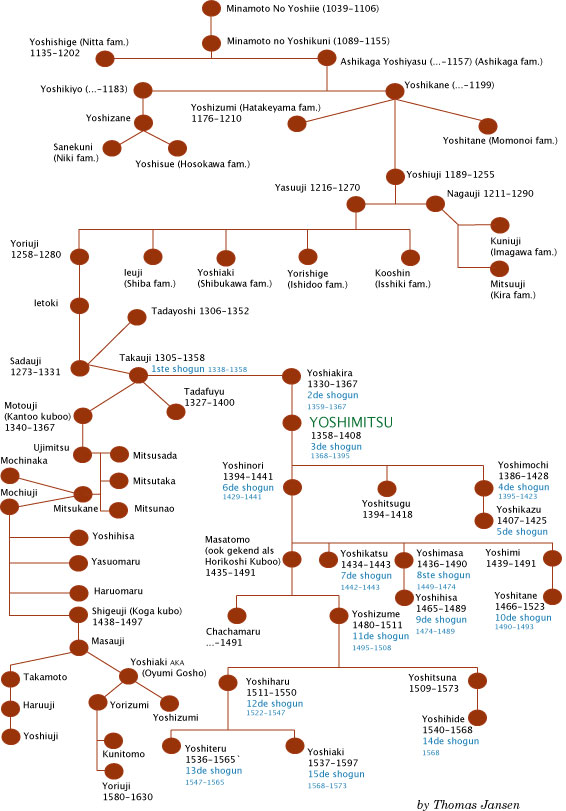
Ashikaga Clan
The was a prominent Japanese samurai clan which established the Muromachi shogunate and ruled Japan from roughly 1333 to 1573. The Ashikaga were descended from a branch of the Minamoto clan, deriving originally from the town of Ashikaga in Shimotsuke Province (modern-day Tochigi Prefecture). For about a century the clan was divided in two rival branches, the Kantō Ashikaga, who ruled from Kamakura, and the Kyōto Ashikaga, rulers of Japan. The rivalry ended with the defeat of the first in 1439. The clan had many notable branch clans, including the Hosokawa, Imagawa, Hatakeyama (after 1205), Kira , Shiba, and Hachisuka clans. After the head family of the Minamoto clan died out during the early Kamakura period, the Ashikaga came to style themselves as the head of the Minamoto, co-opting the prestige which came with that name. Another Ashikaga clan, not related by blood, and derived instead from the Fujiwara clan, also existed. History Emperor Go-Daigo 後醍醐天皇 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
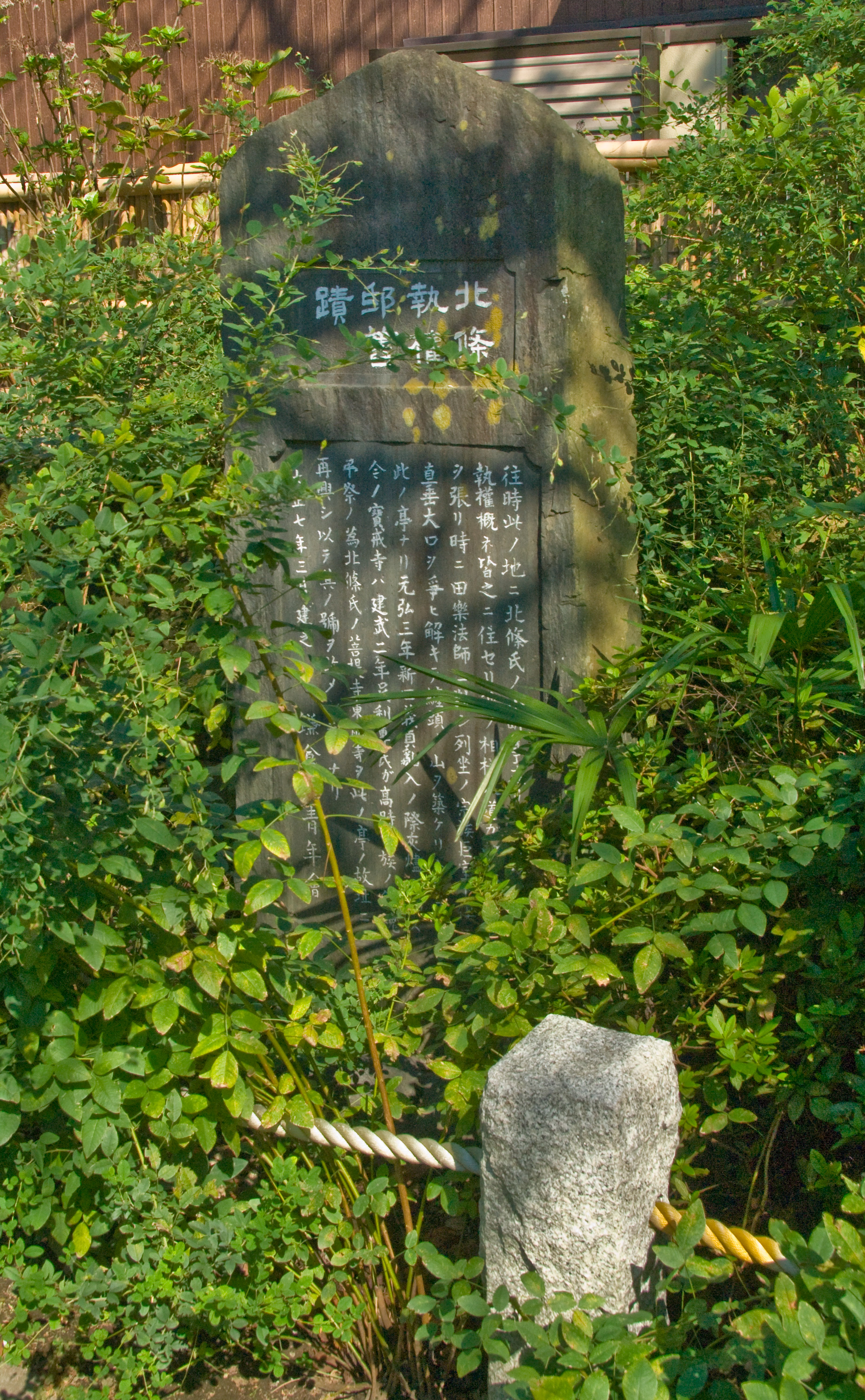
Stele Houkai-ji Kamakura
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), when derived from Latin, is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected in the ancient world as a monument. The surface of the stele often has text, ornamentation, or both. These may be inscribed, carved in relief, or painted. Stelae were created for many reasons. Grave stelae were used for funerary or commemorative purposes. Stelae as slabs of stone would also be used as ancient Greek and Roman government notices or as boundary markers to mark borders or property lines. Stelae were occasionally erected as memorials to battles. For example, along with other memorials, there are more than half-a-dozen steles erected on the battlefield of Waterloo at the locations of notable actions by participants in battle. A traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitta Yoshisada
was a samurai lord of the Nanboku-chō period Japan. He was the head of the Nitta clan in the early fourteenth century, and supported the Southern Court of Emperor Go-Daigo in the Nanboku-chō period. He famously marched on Kamakura, besieging and capturing it from the Hōjō clan in 1333. Later he fought the Takauji brothers on the Emperor's behalf in a see-saw campaign which saw the capital change hands several times. After a peaceful compromise was agreed, Yoshisada was entrusted with two royal princes. At the siege of Kanegasaki (1337), both princes were killed, along with Yoshisada's son, although Yoshisada was able to escape. He committed seppuku when his horse was killed at the siege of Kuromaru. Early life Yoshisada was born in 1301, the eldest son of Nitta Tomouji. He succeeded his father and became the lord of Nitta Manor in Kōzuke Province in 1317. At this time, he also became the head of the Nitta clan. Yoshisada courted a daughter of a court noble, Kōtō-Naish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikken
The was a titular post held by a member of the Hōjō clan, officially a regent of the shogunate, from 1199 to 1333, during the Kamakura period, and so he was head of the ''bakufu'' (shogunate). It was part of the era referred to as . During roughly the first half of that period, the ''shikken'' was the ''de facto'' military dictator of Japan (not including the independent Northern Fujiwara). The title of ''shikken'' was modified, as second in command to the ''Tokusō'' in 1256, but by the Muromachi period (1333–1573) the position, though not abolished, did not even figure in the top ranks. The position ceased to exist after the Muromachi period. Etymology The word ''shikken'' is the on'yomi reading of the combination of the two kanji characters and , each meaning "to hold (something in the hand, or a service or ceremony); to administer", "power, authority" respectively. Therefore the word literally means "to hold power/authority". ''Shikken'' as supreme ruler (1199–1256) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |