|
Hüsnüşah Hatun
Hüsnüşah Hatun ( ota, حسنی شاہ خاتون "''Beauty of the Sah''", died 1513), called also Hüsnişah Hatun, was a consort of Sultan Bayezid II of the Ottoman Empire. Family Hüsnüşah Hatun was the daughter of Nasuh Bey, the maternal grandson of Ibrahim II Bey, ruler of the Karamanids, and the governor of İçil. She had two brothers named Pir Ahmed Bey, and Abdülkerim Bey. Marriage Hüsnüşah entered Bayezid's harem when he was still a prince, and the governor of Amasya sanjak. She gave birth to two children, a son, Şehzade Şehinşah in 1474, and a daughter, Sultanzade Sultan. According to Turkish tradition, all princes were expected to work as provincial governors as a part of their training. In 1481 Şehinşah, was sent to Manisa sanjak, and then in 1485 to Karaman, and Hüsnüşah accompanied him. She built and endowed a mosque in 1490, and Kurşunlu Han in 1497 at Manisa. She also made several endowments in memory of her ancestors. After Şehzade Şehi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayezid II
Bayezid II ( ota, بايزيد ثانى, Bāyezīd-i s̱ānī, 3 December 1447 – 26 May 1512, Turkish: ''II. Bayezid'') was the eldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512. During his reign, Bayezid II consolidated the Ottoman Empire and thwarted a Safavid rebellion soon before abdicating his throne to his son, Selim I. He evacuated Sephardi Jews from Spain after the proclamation of the Alhambra Decree, and resettled them throughout Ottoman lands, especially in Salonica. Early life Bayezid II was the son of Mehmed II (1432–1481) and Gülbahar Hatun, she is generally accepted as the real mother of Bayezid II. There are sources that claim that Bayezid was the son of Sittişah Hatun. This would make Ayşe Gülbahar Hatun a first cousin of Bayezid II. However, the marriage of Sittisah Hatun took place two years after Bayezid was born and the whole arrangement was not to Mehmed's liking. Born in Demotika, Bayezid II was educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
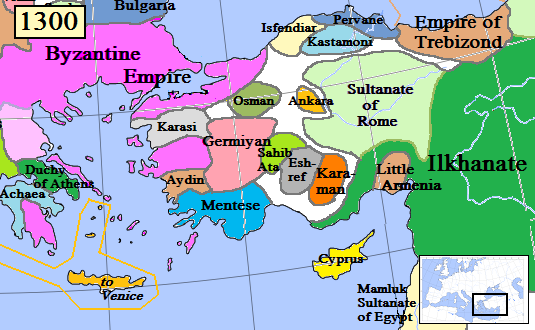
Karaman Province
Karaman Province ( tr, ) is a province of south-central Turkey. It has an area of . A 2010 estimate puts the population at 232,633 people. According to the 2000 census, the population was 243,210. The population density is 27.54 people/km. The traffic code is 70. The capital is the city of Karaman. Karaman was the location of the Karamanid Beylik, which came to an end in 1486. Districts and Towns Karaman Province is divided into 6 districts: Ayrancı, Başyayla, Ermenek, Kazımkarabekir, Sarıveliler, and the capital, Karaman. Towns include Yeşildere, Sudurağı, Akçaşehir, and Taşkale. Place of interest * Binbirkilise, a region around Mount Karadağ north of Karaman with Byzantine church ruins. See also * Görmeli, a village on the hillside of the Taurus Mountains near Ermenek * Mount Karadağ, an extinct volcano north of Karaman city * List of populated places in Karaman Province Gallery File:Karaman Karadağ in distance 2242.jpg, Mount Karadağ seen from Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15th-century Consorts Of Ottoman Sultans
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian dates from 1 January 1401 ( MCDI) to 31 December 1500 ( MD). In Europe, the 15th century includes parts of the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the " European miracle" of the following centuries. The architectural perspective, and the modern fields which are known today as banking and accounting were founded in Italy. The Hundred Years' War ended with a decisive French victory over the English in the Battle of Castillon. Financial troubles in England following the conflict resulted in the Wars of the Roses, a series of dynastic wars for the throne of England. The conflicts ended with the defeat of Richard III by Henry VII at the Battle of Bosworth Field, establishing the Tudor dynasty in the later part of the century. Constantinople, known as the capital of the world an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed II
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Sultan Mehmed, links=no), was an Ottoman sultan who ruled from August 1444 to September 1446, and then later from February 1451 to May 1481. In Mehmed II's first reign, he defeated the crusade led by John Hunyadi after the Hungarian incursions into his country broke the conditions of the truce Peace of Szeged. When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he strengthened the Ottoman navy and made preparations to attack Constantinople. At the age of 21, he conquered Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and brought an end to the Byzantine Empire. After the conquest Mehmed claimed the title Caesar of the Roman Empire ( ota, قیصر روم, Qayser-i Rûm, links=no), based on the fact that Constantinople had been the seat and capital of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Şirin Hatun
Şirin Hatun ( ota, شیریں خاتون; meaning "sweet") was a consort of Sultan Bayezid II of the Ottoman Empire. Life Şirin married Bayezid when he was still a prince, and the governor of Amasya. She gave birth to Bayezid's eldest son, Şehzade Abdullah in 1463, followed by a daughter, Aynışah Hatun. According to Turkish tradition, all princes were expected to work as provincial governors as a part of their training. In 1467–68, Şirin accompanied Abdullah, when was sent to Manisa, and then to Trabzon in early 1470s. In 1480, the two returned to Manisa, and following the 1481 succession struggle to Karaman. The Sultan had granted her the village of Emakin in Mihaliç. She endowed two schools, one in Bursa, and the another in Mihaliç. She also built two mosques, one in Eynesil, and the other known as "Hatuniye Mosque" located inside Trabzon Castle in 1470. For her endowments, she allocated the villages of Kabacaağaç and Kadi in Şile, as well as four existing mills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite lasting only eight years, his reign is notable for the enormous expansion of the Empire, particularly his conquest between 1516 and 1517 of the entire Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt, which included all of the Levant, Hejaz, Tihamah and Egypt itself. On the eve of his death in 1520, the Ottoman Empire spanned about , having grown by seventy percent during Selim's reign. Selim's conquest of the Middle Eastern heartlands of the Muslim world, and particularly his assumption of the role of guardian of the pilgrimage routes to Mecca and Medina, established the Ottoman Empire as the pre-eminent Muslim state. His conquests dramatically shifted the empire's geographical and cultural center of gravity away from the Balkans and toward the Middle East. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manisa
Manisa (), historically known as Magnesia, is a city in Turkey's Aegean Region and the administrative seat of Manisa Province. Modern Manisa is a booming center of industry and services, advantaged by its closeness to the international port city and the regional metropolitan center of İzmir and by its fertile hinterland rich in quantity and variety of agricultural production. In fact, İzmir's proximity also adds a particular dimension to all aspects of life's pace in Manisa in the form of a dense traffic of daily commuters between the two cities, separated as they are by a half-hour drive served by a fine six-lane highway nevertheless requiring attention at all times due to its curves and the rapid ascent (sea-level to more than 500 meters at Sabuncubeli Pass) across Mount Sipylus's mythic scenery. The historic part of Manisa spreads out from a forested valley in the immediate slopes of Sipylus mountainside, along Çaybaşı Stream which flows next to Niobe's "Weeping Rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
İçil
İçil was the name of a sanjak (a former administrative unit until 1921) in Turkey Nomenclature During the Ottoman Empire, İçil was a sanjak (an administrative unit smaller than vilayet and larger than kaza) in south Turkey. It roughly corresponded to Cilicia Trachaea of the antiquity. İçil literally means "inner territory". Although it borders the Mediterranean Sea, the Toros Mountains, which are mostly impassable (except for the Sertavul Pass), may be the reason of the name, was first documented in the 12th century by Sejukid Turks. They used the name only for the Göksu River valley. But soon it became the name of a wider territory. According to an official map drawn by Vital Cuinet the east border of İçil was Alata River and the west border was an unidentified river just to the east of Alanya (may be Dim River). The northern border followed the summit line of the mountains. Kazas According to salname (annual) of Adana Vilayet, there were six kazas (districts, now calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karamanids
The Karamanids ( tr, Karamanoğulları or ), also known as the Emirate of Karaman and Beylik of Karaman ( tr, Karamanoğulları Beyliği), was one of the Anatolian beyliks, centered in South-Central Anatolia around the present-day Karaman Province. From the middle 1300s until its fall in 1487, the Karamanid dynasty was one of the most powerful beyliks in Anatolia. History The Karamanids traced their ancestry from Hodja Sad al-Din and his son Nure Sufi Bey, who emigrated from Arran (roughly encompassing modern-day Azerbaijan) to Sivas because of the Mongol invasion in 1230. The Karamanids were members of the Salur tribe of Oghuz Turks. According to Muhsin Yazıcıoğlu and others, they were members of the Afshar tribe,Cahen, Claude, ''Pre-Ottoman Turkey: A General Survey of the Material and Spiritual Culture and History c. 1071–1330'', trans. J. Jones-Williams (New York: Taplinger, 1968), pp. 281–2. which participated in the revolt led by Baba Ishak and afterwards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrahim II Of Karaman
Ibrahim II (died 1464) was a bey of Karaman. Background During the post-Seljuk era in the second half of the 13th century, numerous Turkoman principalities, which are collectively known as the Anatolian beyliks, emerged in Anatolia. Initially the Karamanids, centered on the modern provinces of Karaman and Konya, were the most important power in Anatolia. But towards the end of the 14th century the Ottomans began to dominate most of Anatolia, reducing Karamanid influence and prestige. Thus the campaign of Timur to Anatolia and the ensuing Ottoman Interregnum gave the Karamanids a chance for revival. However the Karamanids also experienced a period of interregnum during Ottoman interregnum, so they were unable to end Ottoman domination in Anatolia. Ibrahim Bey and the Ottomans Ibrahim Bey was Mehmet Bey's son. He fought against his uncle Ali Bey, and with Ottoman support he ascended to throne in 1424. Nevertheless, their help did not ensure his fidelity to the Ottomans. He secre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |