|
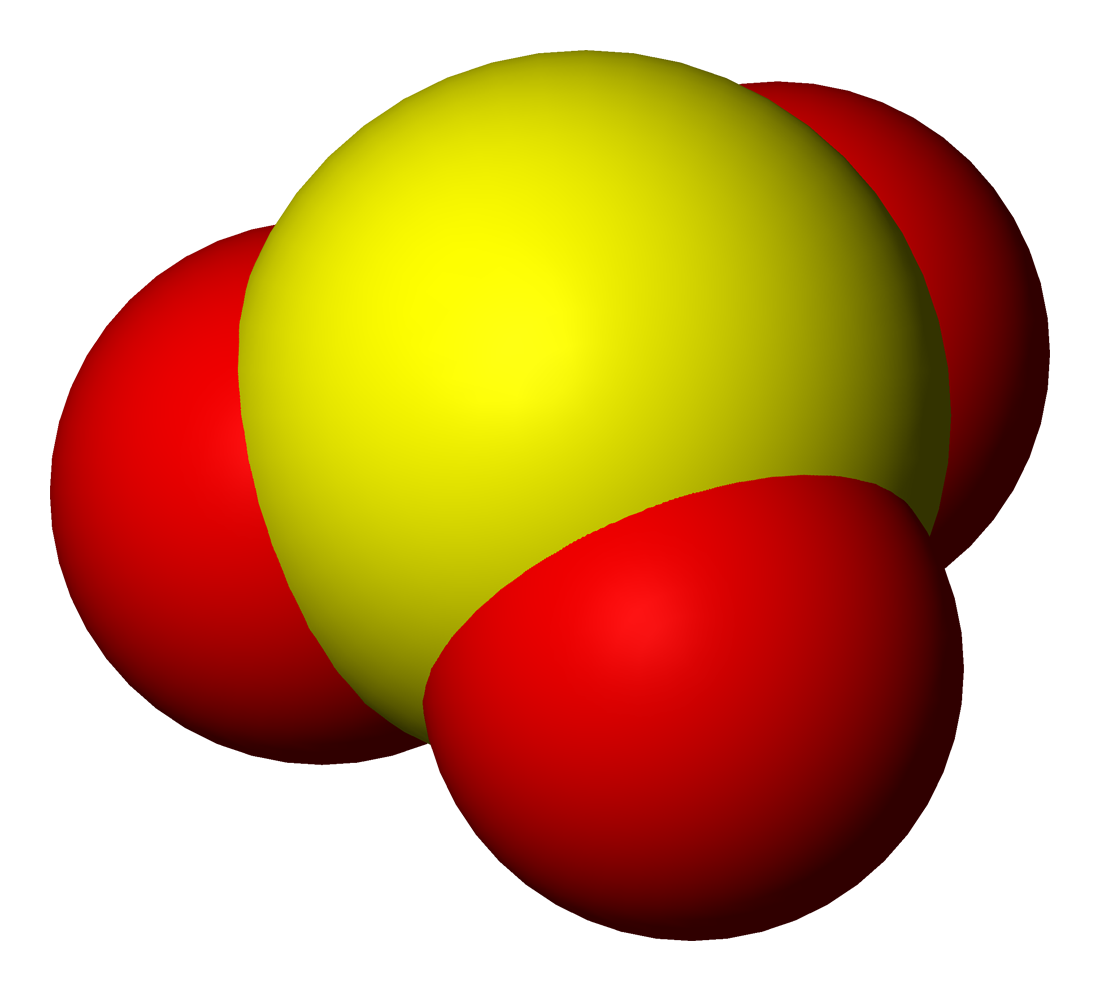
Hypomanganate
In chemistry, hypomanganate, also called manganate(V) or tetraoxidomanganate(3−), is a trivalent anion ( negative ion) composed of manganese and oxygen, with formula . Hypomanganates are usually bright blue.D. Reinen, W. Rauw, U. Kesper, M. Atanasov, H. U Güdel, M. Hazenkamp, and U. Oetliker (1997): "Colour, luminescence and bonding properties of tetrahedrally coordinated chromium(IV), manganese(V) and iron(VI) in various oxide ceramics" ''Journal of Alloys and Compounds'', volume 246, issue 1-2, pages 193-208. Potassium hypomanganate is the best known salt, but sodium hypomanganate , barium hypomanganate , and the mixed potassium-barium salt is also known. The anion can replace phosphate in synthetic variants of the minerals apatiteK. Dardenne, D. Vivien, and D. Huguenin (1999): "Color of Mn(V)-substituted apatites A10((B, Mn)O4)6F2, A = Ba, Sr, Ca; B= P, V". ''Journal of Solid State Chem.istry, volume 146, issue 2, pages 464-472. Grisafe, D.A. and Hummel, F.A. (1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hypomanganate
Potassium hypomanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula . Also known as potassium manganate(V), this bright blue solid is a rare example of a salt with the hypomanganate or manganate(V) anion, where the manganese atom is in the +5 oxidation state. Preparative routes *by two-electron reduction of potassium permanganate with excess potassium sulfite;.. : *by the single-electron reduction of potassium manganate with hydrogen peroxide in 10 M potassium hydroxide solution;. : *by the single-electron reduction of potassium manganate with mandelate in 3–10 M potassium hydroxide solution; : *by disproportionation when manganese dioxide Manganese dioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . This blackish or brown solid occurs naturally as the mineral pyrolusite, which is the main ore of manganese and a component of manganese nodules. The principal use for is for dry-cell ... is dissolved in a concentrated solution of potassium hydroxide; : The compound is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganate
In inorganic nomenclature, a manganate is any negatively charged molecular entity with manganese as the central atom.. However, the name is usually used to refer to the tetraoxidomanganate(2−) anion, MnO, also known as manganate(VI) because it contains manganese in the +6 oxidation state. Manganates are the only known manganese(VI) compounds.. Other manganates include hypomanganate or manganate(V), , permanganate or manganate(VII), , and the dimanganate or dimanganate(III) . A manganate(IV) anion has been prepared by radiolysis of dilute solutions of permanganate.. It is mononuclear in dilute solution, and shows a strong absorption in the ultraviolet and a weaker absorption at 650 nm. Structure The manganate(VI) ion is tetrahedral, similar to sulfate or chromate: indeed, manganates are often isostructural with sulfates and chromates, a fact first noted by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1831.. The manganese–oxygen distance is 165.9 pm, about 3 pm longer than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth ( botany), the formation of igneous rocks ( geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded ( ecology), the properties of the soil on the moon ( cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyanion
An oxyanion, or oxoanion, is an ion with the generic formula (where A represents a chemical element and O represents an oxygen atom). Oxyanions are formed by a large majority of the chemical elements. The formulae of simple oxyanions are determined by the octet rule. The corresponding oxyacid of an oxyanion is the compound . The structures of condensed oxyanions can be rationalized in terms of AO''n'' polyhedral units with sharing of corners or edges between polyhedra. The oxyanions (specifically, phosphate and polyphosphate esters) adenosine monophosphate ( AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are important in biology. Monomeric oxyanions The formula of monomeric oxyanions, , is dictated by the oxidation state of the element A and its position in the periodic table. Elements of the first row are limited to a maximum coordination number of 4. However, none of the first row elements has a monomeric oxyanion with that coordination number. Instead, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandelic Acid
Mandelic acid is an aromatic alpha hydroxy acid with the molecular formula C6H5CH(OH)CO2H. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful precursor to various drugs. The molecule is chiral. The racemic mixture is known as ''paramandelic acid''. Isolation, synthesis, occurrence Mandelic acid was discovered in 1831 by the German pharmacist Ferdinand Ludwig Winckler (1801–1868) while heating amygdalin, an extract of bitter almonds, with diluted hydrochloric acid. The name is derived from the German "Mandel" for "almond". Mandelic acid is usually prepared by the acid-catalysed hydrolysis of mandelonitrile, which is the cyanohydrin of benzaldehyde. Mandelonitrile can also be prepared by reacting benzaldehyde with sodium bisulfite to give the corresponding adduct, forming mandelonitrile with sodium cyanide, which is hydrolyzed: : Alternatively, it can be prepared by base hydrolysis of phenylchloroacetic acid as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid (sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are widely used. Sulfites are substances that naturally occur in some foods and the human body. They are also used as regulated food additives. When in food or drink, sulfites are often lumped together with sulfur dioxide.SeREGULATION (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL/ref> Structure The structure of the sulfite anion can be described with three equivalent resonance structures. In each resonance structure, the sulfur atom is double-bonded to one oxygen atom with a formal charge of zero (neutral), and sulfur is singly bonded to the other two oxygen atoms, which each carry a formal charge of −1, together accounting for the −2 charge on the anion. There is also a non-bonded lone pair on the sulfur, so the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet–visible Spectroscopy
UV spectroscopy or UV–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely used in diverse applied and fundamental applications. The only requirement is that the sample absorb in the UV-Vis region, i.e. be a chromophore. Absorption spectroscopy is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy. Parameters of interest, besides the wavelength of measurement, are absorbance (A) or transmittance (%T) or reflectance (%R), and its change with time. Optical transitions Most molecules and ions absorb energy in the ultraviolet or visible range, i.e., they are chromophores. The absorbed photon excites an electron in the chromophore to higher energy molecular orbitals, giving rise to an excited state. For organic chromophores, four possible types of transitio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted ) is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction :HA A^- + H^+ known as dissociation in the context of acid–base reactions. The chemical species HA is an acid that dissociates into , the conjugate base of the acid and a hydrogen ion, . The system is said to be in equilibrium when the concentrations of its components will not change over time, because both forward and backward reactions are occurring at the same rate. The dissociation constant is defined by :K_\text = \mathrm, or :\mathrmK_\ce = - \log_ K_\text = \log_\frac where quantities in square brackets represent the concentrations of the species at equilibrium. Theoretical background The acid dissociation constant for an acid is a direct consequence of the underlying thermodynamics of the dissociation reaction; the p'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liter
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3). A cubic decimetre (or litre) occupies a volume of (see figure) and is thus equal to one-thousandth of a cubic metre. The original French metric system used the litre as a base unit. The word ''litre'' is derived from an older French unit, the '' litron'', whose name came from Byzantine Greek—where it was a unit of weight, not volume—via Late Medieval Latin, and which equalled approximately 0.831 litres. The litre was also used in several subsequent versions of the metric system and is accepted for use with the SI,Bureau International des Poids et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (unit)
The mole, symbol mol, is the unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units (SI). The quantity amount of substance is a measure of how many elementary entities of a given substance are in an object or sample. The mole is defined as containing exactly elementary entities. Depending on what the substance is, an elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an ion pair, or a subatomic particle such as an electron. For example, 10 moles of water (a chemical compound) and 10 moles of mercury (a chemical element), contain equal amounts of substance and the mercury contains exactly one atom for each molecule of the water, despite the two having different volumes and different masses. The number of elementary entities in one mole is known as the Avogadro number, which is the approximate number of nucleons ( protons or neutrons) in one gram of ordinary matter. The previous definition of a mole was simply the number of elementary entities equal to that of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |