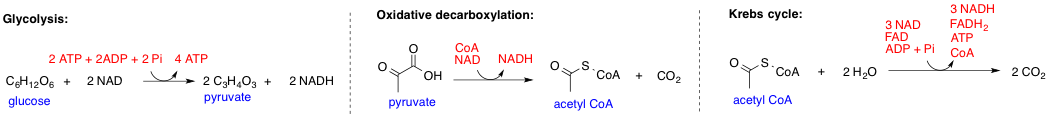|
Hydrocarbon-degrading Bacteria
Microbial biodegradation is the use of bioremediation and biotransformation methods to harness the naturally occurring ability of microbial xenobiotic metabolism to degrade, transform or accumulate environmental pollutants, including hydrocarbons (e.g. oil), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), heterocyclic compounds (such as pyridine or quinoline), pharmaceutical substances, radionuclides and metals. Interest in the microbial biodegradation of pollutants has intensified in recent years, and recent major methodological breakthroughs have enabled detailed genomic, metagenomic, proteomic, bioinformatic and other high-throughput analyses of environmentally relevant microorganisms, providing new insights into biodegradative pathways and the ability of organisms to adapt to changing environmental conditions. Biological processes play a major role in the removal of contaminants and take advantage of the catabolic versatility of microorganisms to degrade or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioremediation
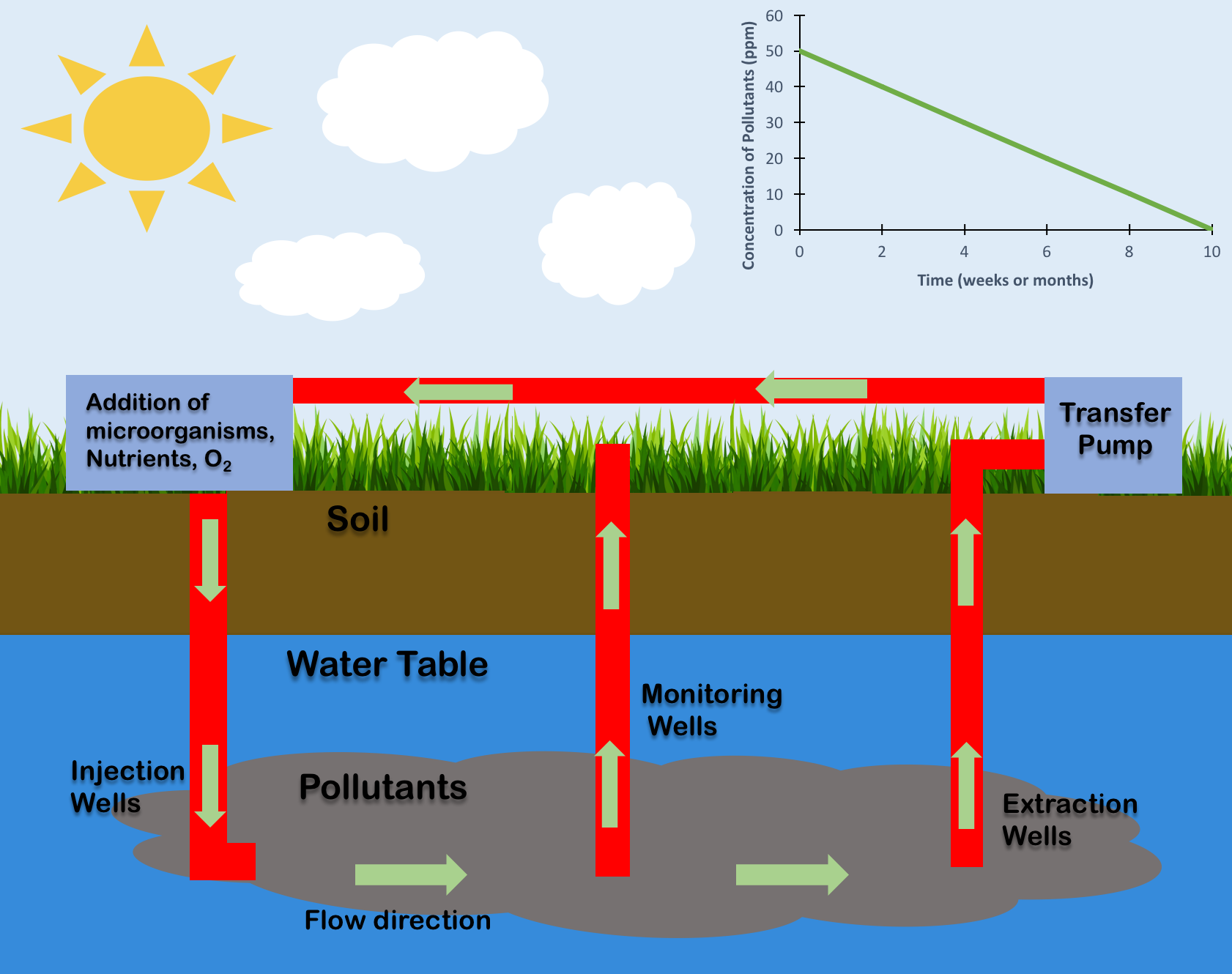
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia Xenovorans
''Paraburkholderia xenovorans'' is a species of bacteria. Genomics The genome of ''Paraburkholderia xenovorans'' (LB400) is one of the largest bacterial genomes completely sequenced to date. The recent genomic studies of this organism have helped expand understanding of bacterial catabolism, noncatabolic physiological adaptation to organic compounds, and the evolution of large bacterial genomes. The metabolic pathways from phylogenetically diverse isolates are very similar with respect to overall organization. As originally noted in pseudomonads, a large number of "peripheral aromatic" pathways funnel a range of natural and xenobiotic compounds into a restricted number of "central aromatic" pathways. These pathways are genetically organized in genus-specific fashions. Comparative genomic studies reveal that some pathways are more widespread than initially thought. Functional genomic studies have established that even organisms harboring high numbers of homologous enzymes seem to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table (halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig (in 1825) and Antoine Jérôme Balard (in 1826), its name was derived from the Ancient Greek (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell. Elemental bromine is very reactive and thus does not occur as a native element in nature but it occurs in colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, analogous to table salt. In fact, bromine and all the halogens are so reactive that they form bonds in pairs—never in single atoms. While it is rather rare in the Earth's crust, the high solubility of the bromide ion (Br) has caused its accumulation in the oceans. Commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorinated
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens (F2, Cl2, Br2, I2). Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride. Organic chemistry Several pathways exist for the halogenation of organic compounds, including free radical halogenation, ketone halogenation, electrophilic halogenation, and halogen addition reaction. The nature of the substrate determines the pathway. The facility of halogenation is influenced by the halogen. Fluorine and chlorine are more electrophilic and are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. Deep waters of the ocean are a common anoxic environment. First observation In his letter of 14 June 1680 to The Royal Society, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described an experiment he carried out by filling two identical glass tubes about halfway with crushed pepper powder, to which some clean rain water was added. Van Leeuwenhoek sealed one of the glass tubes using a flame an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Enzymes
Homology may refer to: Sciences Biology *Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor *Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences *Homologous chromosomes, chromosomes in a biological cell that pair up (synapse) during meiosis *Homologous recombination, genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between molecules of DNA *Homologous desensitization, a receptor decreases its response to a signalling molecule when that agonist is in high concentration *Homology modeling, a method of protein structure prediction Chemistry *Homology (chemistry), the relationship between compounds in a homologous series *Homologous series, a series of organic compounds having different quantities of a repeated unit *Homologous temperature, the temperature of a material as a fraction of its absolute melting point *Homologation reaction, a chemical reaction which produces the next lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenobiotic
A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual. Natural compounds can also become xenobiotics if they are taken up by another organism, such as the uptake of natural human hormones by fish found downstream of sewage treatment plant outfalls, or the chemical defenses produced by some organisms as protection against predators. The term xenobiotics, however, is very often used in the context of pollutants such as dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls and their effect on the biota, because xenobiotics are understood as substances foreign to an entire biological system, i.e. artificial substances, which did not exist in nature before their synthesis by humans. The term xenobiotic is derived from the Greek words ξένος (xenos) = foreigner, stranger and βίος (bios) = life, plus the Greek suffix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadaceae
The Pseudomonadaceae are a family of bacteria which includes the genera ''Azomonas'', ''Azorhizophilus'', ''Azotobacter'', '' Mesophilobacter'', ''Pseudomonas'' (the type genus), and '' Rugamonas''. The family Azotobacteraceae was recently reclassified into this family. History Pseudomonad literally means false unit, being derived from the Greek ''pseudo'' (ψευδο – false) and ''monas'' (μονος – a single unit). The term "monad" was used in the early history of microbiology to denote single-celled organisms. Because of their widespread occurrence in nature, the pseudomonads were observed early in the history of microbiology. The generic name ''Pseudomonas'' created for these organisms was defined in rather vague terms in 1894 as a genus of Gram-negative, rod-shaped, and polar-flagellated bacteria. Soon afterwards, a large number of species was assigned to the genus. Pseudomonads were isolated from many natural niches. New methodology and the inclusion of approaches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function. Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell. For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane. In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |