|
Hydristor
Hydristor is a joining of the words 'hydraulic' and 'transistor'. The device invented by Tom Kasmer in 1996 and is based on the dual pressure balanced hydraulic vane pump invented by Harry F. Vickers in 1925. Vane pump details The Vickers design included an elliptic chamber which confined the radial motion of the vanes nested in the rotor slots. As the rotor and vanes turn, each vane is first pushed radially inward followed by a maximum radial extension and that happens twice per revolution. The displacement of the fixed device is calculated by determining the difference in vane extension between minimum and maximum, times the axial length of the vanes and rotor. This multiplies to an area subject to the hydraulic pressure in the device whether used as a motor or a pump. Then an average of the minimum and maximum extensions establishes a 'radius of motion' for the pressurized equivalent pressure/force area. of each vane which passes one of the 4 axial sealing areas. What happens i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydristor2
Hydristor is a joining of the words 'hydraulic' and 'transistor'. The device invented by Tom Kasmer in 1996 and is based on the dual pressure balanced hydraulic vane pump invented by Harry F. Vickers in 1925. Vane pump details The Vickers design included an elliptic chamber which confined the radial motion of the vanes nested in the rotor slots. As the rotor and vanes turn, each vane is first pushed radially inward followed by a maximum radial extension and that happens twice per revolution. The displacement of the fixed device is calculated by determining the difference in vane extension between minimum and maximum, times the axial length of the vanes and rotor. This multiplies to an area subject to the hydraulic pressure in the device whether used as a motor or a pump. Then an average of the minimum and maximum extensions establishes a 'radius of motion' for the pressurized equivalent pressure/force area. of each vane which passes one of the 4 axial sealing areas. What happens i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Bicycle
A hydraulic bicycle is a chainless bicycle that transfers power to the pedals by means of a liquid passing through tubes from hydraulic pump to hydraulic motor and back. Advantages include: * Shifting, through valves and displacement, provides either continuously variable gearing or more steps than traditional bicycles. * Shifts smoothly under full power. * Drive transmits power while pedaling forward and backward. Thus racers can power bicycle through turns by alternating short forward and backward pedal strokes. No slack or backlash occurs, in either direction. Ability to coast is maintained. * Mechanism is clean and operates silently. * Fewer moving parts (about 10 vs over 70), all of which are continuously bathed in clean lubricating fluid. * Sealed systems require less maintenance than open chain system. * Front-wheel drive and two-wheel drive systems can be implemented. (See Two-wheel drive) * Drive can double as a hydraulic brake, eliminating the weight, cost, and maintenanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Longevity
Car longevity is of interest to many car owners and includes several things: maximum service life in either mileage or time (duration), relationship of components to this lifespan, identification of factors that might afford control in extending the lifespan. Barring an accidental end to the lifespan, a car would have a life constrained by the earliest part to fail. Some have argued that rust and other factors related to the body of a car are the prime limits to extended longevity. Background An automobile is a highly engineered collection of complex components, each of which has its own lifespan and longevity characteristics. The MTBF (mean time between failures) of some components is expected to be smaller than the life of the car, as the replacement of these is considered part of regular maintenance. Other components, which typically experience less wear, are expected to have a longer life; however, a large longevity may very well require replacement of several of these, raising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanisms (engineering)
Mechanism may refer to: *Mechanism (engineering), rigid bodies connected by joints in order to accomplish a desired force and/or motion transmission *Mechanism (biology), explaining how a feature is created *Mechanism (philosophy), a theory that all natural phenomena can be explained by physical causes *Mechanism (sociology), a theory that all social phenomena can be explained by the existence of a deterministic mechanism * "The Mechanism", song by Disclosure * ''The Mechanism'' (TV series), a Netflix TV series See also *Machine *Machine (mechanical) *Linkage (mechanical) *Mechanism design, the art of designing rules of a game to achieve a specific outcome *Mechanism of action, the means by which a drug exerts its biological effects *Defence mechanism, unconscious mechanisms aimed at reducing anxiety *Reaction mechanism, the sequence of reactions by which overall chemical change occurs *Antikythera mechanism, an ancient Greek analog computer *Theory of operation A theory of op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulics
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and cover concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. Free surface hydraulics is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers, canals, lakes, estuar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids. The basic principle with hybrid vehicles is that the different motors work better at different speeds; the electric motor is more efficient at producing torque, or turning power, and the combustion engine is better for maintaining high speed than a typical electric motor. Switching from one to the other at the proper time while speeding up yields a win-win in terms of energy efficiency, such that it translates into greater fuel efficiency. Vehicle types Two-wheeled and cycle-type vehicles Mopeds, electric bicycles, and even electric kick scooters are a simple form of a hybrid, powered by an internal combustion engine or electric motor and the rider's muscles. Early prototype motorcycles in the late 19th century used the same principle. * In a parall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids. The basic principle with hybrid vehicles is that the different motors work better at different speeds; the electric motor is more efficient at producing torque, or turning power, and the combustion engine is better for maintaining high speed than a typical electric motor. Switching from one to the other at the proper time while speeding up yields a win-win in terms of energy efficiency, such that it translates into greater fuel efficiency. Vehicle types Two-wheeled and cycle-type vehicles Mopeds, electric bicycles, and even electric kick scooters are a simple form of a hybrid, powered by an internal combustion engine or electric motor and the rider's muscles. Early prototype motorcycles in the late 19th century used the same principle. * In a parall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery. Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide short-term energy storage, while others can endure for much longer. Bulk energy storage is currently dominated by hydroelectric dams, both conventional as well as pumped. Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Common examples of energy storage are the rechargeable battery, which stores chemical energy readily convertible to electricity to operate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
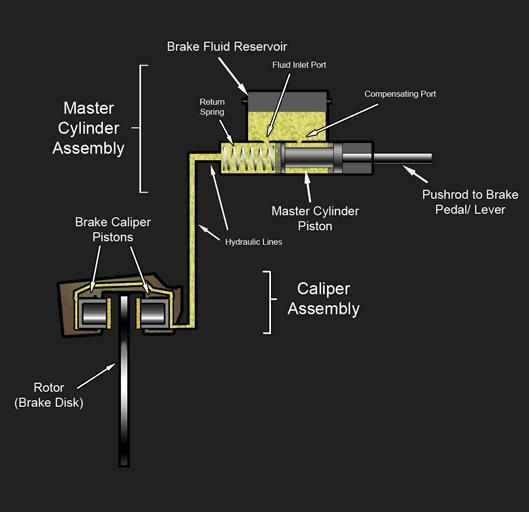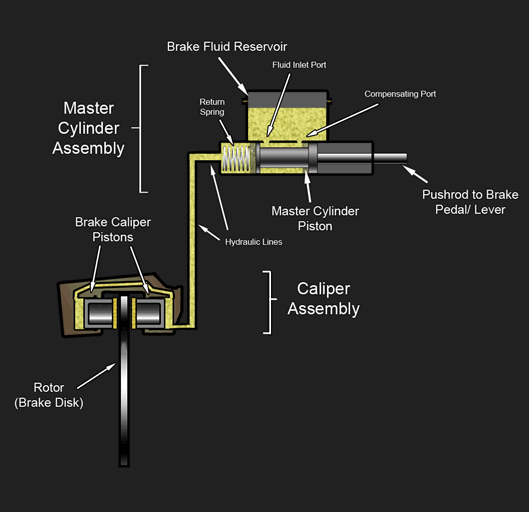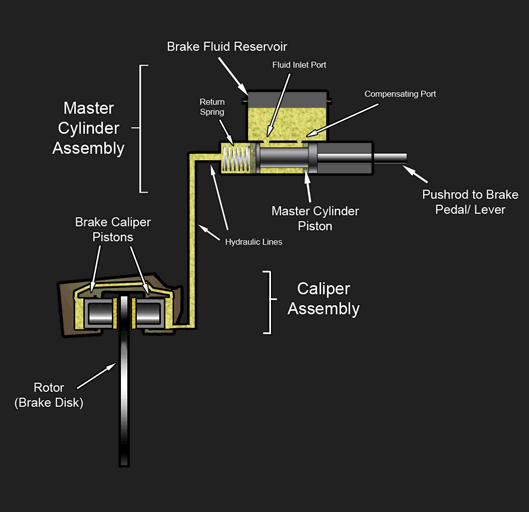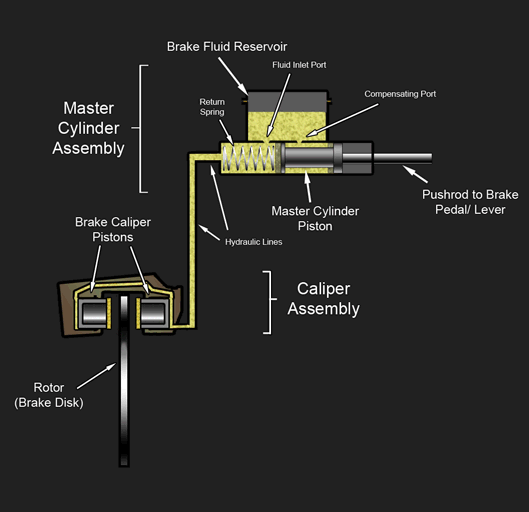
Hydraulic Brake
A hydraulic brake is an arrangement of braking mechanism which uses brake fluid, typically containing glycol ethers or diethylene glycol, to transfer pressure from the controlling mechanism to the braking mechanism. History During 1904, Frederick George Heath (Heath Hydraulic Brake Co., Ltd.), Redditch, England devised and fitted a hydraulic (water/glycerine) brake system to a cycle using a handlebar lever and piston. He obtained patent GB190403651A for “Improvements in hydraulic actuated brakes for cycles and motors”, as well as subsequently for improved flexible rubber hydraulic pipes. In 1908, Ernest Walter Weight of Bristol, England devised and fitted a four-wheel hydraulic (oil) braking system to a motor car. He patented it in Great Britain (GB190800241A) in December 1908, later in Europe and the USA and then exhibited it at the 1909 London Motor Show. His brother, William Herbert Weight improved the patent (GB190921122A) and both were assigned to the Weight Patent Autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque Converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the power source to the load. It is usually located between the engine's flexplate and the transmission. The equivalent location in a manual transmission would be the mechanical clutch. The main characteristic of a torque converter is its ability to increase torque when the output rotational speed is so low that it allows the fluid coming off the curved vanes of the turbine to be deflected off the stator while it is locked against its one-way clutch, thus providing the equivalent of a reduction gear. This is a feature beyond that of the simple fluid coupling, which can match rotational speed but does not multiply torque and thus reduces power. Hydraulic systems By far the most common form of torque converter in automobile transmissions is the hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient Energy Use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses. There are many motivations to improve energy efficiency. Decreasing energy use reduces energy costs and may result in a financial cost saving to consumers if the energy savings offset any additional costs of implementing an energy-efficient technology. Reducing energy use is also seen as a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)