|
Hydrastidoideae
''For the magazine from West Virginia see Goldenseal (magazine)'' Goldenseal (''Hydrastis canadensis''), also called orangeroot or yellow puccoon, is a perennial herb in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to North America. It may be distinguished by its thick, yellow knotted rootstock. The stem is purplish and hairy above ground and yellow below ground where it connects to the yellow rhizome. Goldenseal reproduces both clonally through the rhizome and sexually, with clonal division more frequent than asexual reproduction. It takes between 4 and 5 years for a plant to reach sexual maturity, i.e. the point at which it produces flowers. Plants in the first stage, when the seed erupts and cotyledons emerge, can remain in this state one or more years. The second vegetative stage occurs during years two and three (and sometimes longer) and is characterized by the development of a single leaf and absence of a well developed stem. Finally, the third stage is reproductive, at whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranunculaceae
Ranunculaceae (buttercup or crowfoot family; Latin "little frog", from "frog") is a family of over 2,000 known species of flowering plants in 43 genera, distributed worldwide. The largest genera are ''Ranunculus'' (600 species), ''Delphinium'' (365), ''Thalictrum'' (330), ''Clematis'' (325), and ''Aconitum'' (300). Description Ranunculaceae are mostly herbaceous annuals or perennials, but some are woody climbers (such as ''Clematis'') or shrubs (e.g. ''Xanthorhiza''). Most members of the family have bisexual flowers which can be showy or inconspicuous. Flowers are solitary, but are also found aggregated in cymes, panicles, or spikes. The flowers are usually radially symmetrical but are also found to be bilaterally symmetrical in the genera ''Aconitum'' and ''Delphinium''. The sepals, petals, stamens and carpels are all generally free (not fused), the outer flower segments typically number four or five. The outer stamens may be modified to produce only nectar, as in Aqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldenseal (magazine)
''Goldenseal'' is a quarterly magazine devoted to West Virginia traditional life, published by the West Virginia Department of Arts, Culture and History in West Virginia. Mission ''Goldenseal'' documents the state's cultural background and recent history through oral accounts, research articles, and old and new photographs. Subjects covered include labor history, folklore, music, farming, religion, traditional crafts, food, and politics. Pre-20th century history is rarely covered, however. Roughly 70% of the readers are in-state – most of the remainder are former West Virginia residents or frequent visitors. West Virginia Department of Arts, Culture and History, August 2017. Accessed April 17, 2019. The purpose of the magazine is to "serve not only as a device to preserve many aspects of the state's tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 The term ''sepalum'' was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived . Collectively the sepals are called the calyx (plural calyces), the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. The word ''calyx'' was adopted from the Latin ,Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 not to be confused with 'cup, goblet'. ''Calyx'' is derived from Greek 'bud, calyx, husk, wrapping' ( Sanskrit 'bud'), while is derived from Greek 'cup, goblet', and the words have been used interchangeably in botanical Latin. After flowering, most plants have no more use for the calyx which withers or becomes vestigial. Some plants retain a thorny calyx, either dried or live, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicentra Canadensis
''Dicentra canadensis'', the squirrel corn, is a flowering plant from eastern North America with oddly shaped white flowers and finely divided leaves. Description Squirrel corn has small yellow clustered bulblets (looking roughly like kernels of maize, corn), finely dissected leaf, leaves, and white heart-shaped flowers. The flowers are fragrant. It is a ephemeral plant, spring ephemeral, leafing out and flowering in spring and going dormancy, dormant in summer. Distribution and habitat It is native to temperate deciduous forest, deciduous woodland in eastern North America. It is also found among rock outcrops near mountains. References * * Bleeding hearts, Corydalis, and their relatives. Mark Tebbitt, Magnus Lidén, and Henrik Zetterlund. Timber Press. 2008. External links Dicentra, canadensis Ephemeral plants Flora of Eastern Canada Flora of the Eastern United States Flora of the Appalachian Mountains Garden plants of North America {{Ranunculales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffersonia Diphylla
''Jeffersonia'', also known as twinleaf or rheumatism root, is a small genus of herbaceous perennial plants in the family Berberidaceae. They are uncommon spring wildflowers and grow in limestone soils of rich deciduous forests. ''Jeffersonia'' was named for United States President Thomas Jefferson by his contemporary Benjamin Smith Barton. This genus was formerly grouped in genus ''Podophyllum''. Twinleaf is protected by state laws as a threatened or endangered plant in Georgia, Iowa, New York, and New Jersey. Description ''Jeffersonia diphylla'' has leaves and flowers that are smooth and emerge directly from the rhizome. The leaves are divided into two leaflets which are half-ovate in shape with entire or shallowly toothed margins. It has showy white flowers with four sepals, eight petals, eight stamens, and a singly pistil; the flower resembles bloodroot flowers. The short-lived flower appears in April or May before the forest canopy appears (see spring ephemeral). The fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit. The antonym of ''deciduous'' in the botanical sense is evergreen. Generally, the term "deciduous" means "the dropping of a part that is no longer needed or useful" and the "falling away after its purpose is finished". In plants, it is the result of natural processes. "Deciduous" has a similar meaning when referring to animal parts, such as deciduous antlers in deer, deciduous teeth (baby teeth) in some mammals (including humans); or decidua, the uterine lining that sheds off after birth. Botany In botany and horticulture, deciduous plants, including trees, shrubs and herbaceous perennials, are those that lose all of their leaves for part of the year. This process is called abscissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
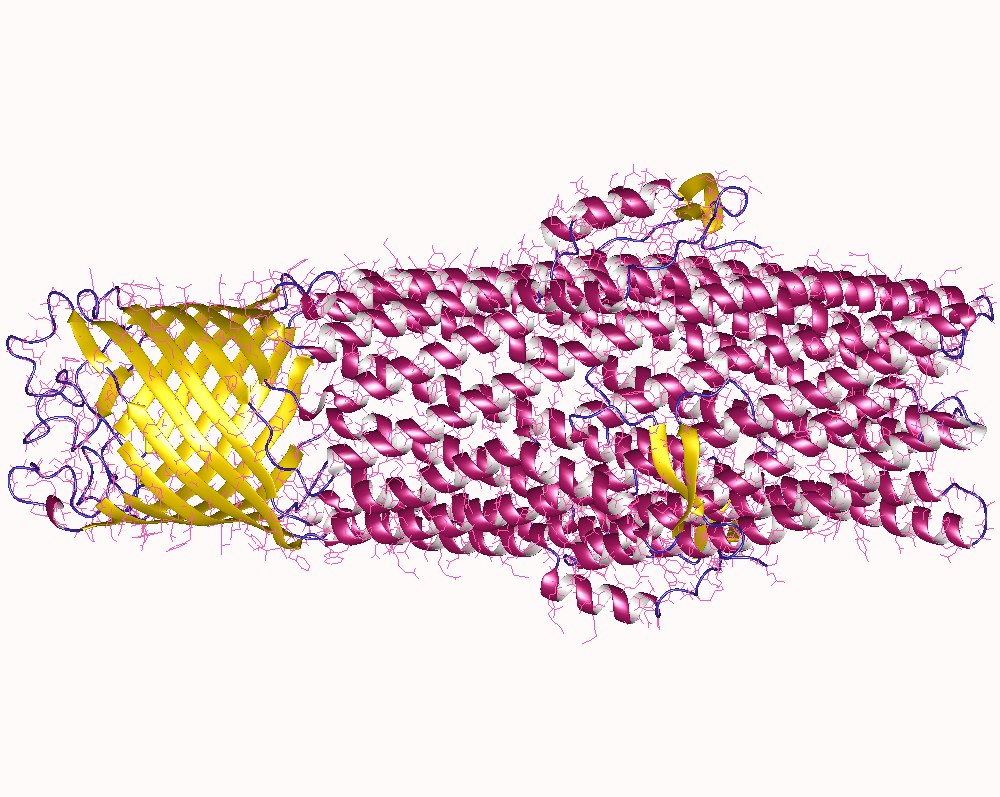
Efflux Pump
In microbiology, efflux is the moving of a variety of different compounds out of cells, such as antibiotics, heavy metals, organic pollutants, plant-produced compounds, quorum sensing signals, bacterial metabolites and neurotransmitters. All microorganisms, with a few exceptions, have highly conserved DNA sequences in their genome that are transcribed and translated to efflux pumps. Efflux pumps actively move substances out of a microorganism, in a process known as active efflux, which is a vital part of xenobiotic metabolism. This active efflux mechanism is responsible for various types of resistance to bacterial pathogens within bacterial species - the most concerning being antibiotic resistance because microorganisms can have adapted efflux pumps to divert toxins out of the cytoplasm and into extracellular media. Efflux systems function via an energy-dependent mechanism (active transport) to pump out unwanted toxic substances through specific efflux pumps. Some efflux system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Pharmacopeia
The ''United States Pharmacopeia'' (''USP'') is a pharmacopeia (compendium of drug information) for the United States published annually by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (usually also called the USP), a nonprofit organization that owns the trademark and also owns the copyright on the pharmacopeia itself. The ''USP'' is published in a combined volume with the ''National Formulary'' (a formulary) as the USP-NF. If a drug ingredient or drug product has an applicable ''USP'' quality standard (in the form of a ''USP-NF'' monograph), it must conform in order to use the designation "USP" or "NF". Drugs subject to ''USP'' standards include both human drugs ( prescription, over-the-counter, or otherwise) and animal drugs. ''USP-NF'' standards also have a role in US federal law; a drug or drug ingredient with a name recognized in ''USP-NF'' is considered adulterated if it does not satisfy compendial standards for strength, quality or purity. USP also sets standards for diet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadine
(''S'')-Canadine, also known as (''S'')-tetrahydroberberine and xanthopuccine, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid (BIA), of the protoberberine structural subgroup, and is present in many plants from the family Papaveraceae, such as '' Corydalis yanhusuo'' and '' C. turtschaninovii''. Biosynthesis Metabolically, (''S'')-canadine is derived from (''S'')-reticuline, a pivotal intermediate in the biosynthesis of numerous BIA structural subgroups, through three enzymatic steps: 1) Berberine bridge enzyme to (''S'')-scoulerine; 2) (''S'')-scoulerine 9-''O''-methyltransferase to (''S'')-tetrahydrocolumbamine; and 3) (''S'')-canadine synthase/CYP719A21 to (''S'')-canadine. (''S'')-Canadine is the immediate metabolic precursor of berberine, which is obtained through the action of the enzyme (''S'')-tetrahydroprotoberberine oxidase. It is also an intermediate in the complex biosynthesis of noscapine, which is likewise a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, but of the phthalideisoquinoline struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |