|
Hydrachnidia
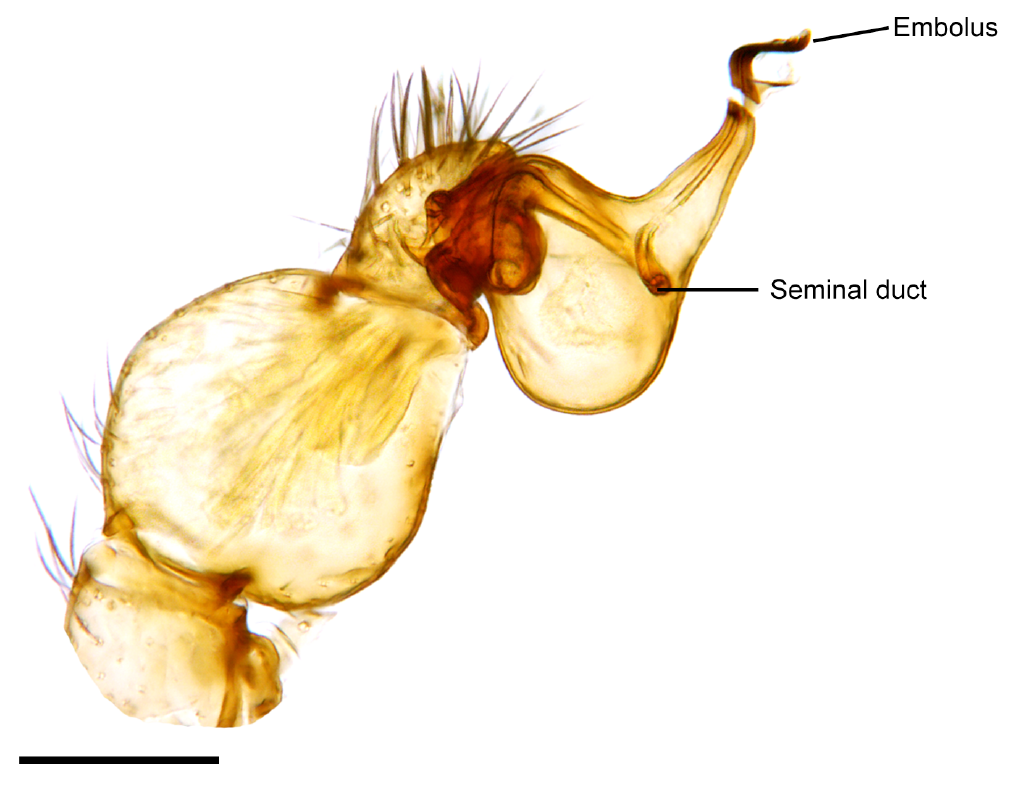
Hydrachnidia, also known as "water mites", Hydrachnidiae, Hydracarina or Hydrachnellae, are among the most abundant and diverse groups of benthic arthropods, composed of 6,000 described species from 57 families. As water mites of Africa, Asia, and South America have not been well-studied, the numbers are likely to be far greater. Other taxa of parasitengone mites include species with semi-aquatic habits, but only the Hydracarina are properly subaquatic. Water mites follow the general Parasitengona life cycle: active larva, inactive (calyptostasic) protonymph, active deutonymph, inactive tritonymph and active adult. Usually, larvae are parasites, while deutonymphs and adults are predators. Description Water mites may be brilliant red or orange in colour, unusual among freshwater invertebrates, but they also display more subtle blues, greens and yellows. They are also unusual among mites in some lineages having movable, internalized eye lenses sunk deep within the prosoma rath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitengona
Parasitengona is a group of mites, variously ranked as a hyporder or a cohort, between the taxonomic ranks of order and family. They are divided into the aquatic Hydrachnidia (water mites) and the terrestrial Trombidia. The latter includes velvet mites and chiggers. Description Many Parasitengona are relatively large (for mite standards) and have a bright red colouration. Other colours include purple, orange, yellow, blue, green and brown. The terrestrial Trombidia are often hypertrichous, meaning they are covered in many irregularly arranged setae. The chelicerae bases are separate, the fixed cheliceral digit is absent and the movable digit is either hooked or linear. The palps are often raptorial with a claw-like seta on the tibia. The gnathosoma is retractable within group Erythraeina. The stigmata and peritremes, when present, are between the cheliceral bases. In Trombidia, there is usually one or two pairs of trichobothria on the prodorsum, and these are often mounted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite I Offer You A Snack!
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive '' Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acari
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive '' Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygrobatoidea
Hygrobatoidea is a superfamily of water mites found in North America North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car .... References Arachnids of North America Trombidiformes {{Trombidiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of a single continent called Americas, America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cephalothorax'' and ''abdomen'' in some groups.) The word ''cephalothorax'' is derived from the Greek words for head (, ') and thorax (, '). This fusion of the head and thorax is seen in chelicerates and crustaceans; in other groups, such as the Hexapoda (including insects), the head remains free of the thorax. In horseshoe crabs and many crustaceans, a hard shell called the carapace covers the cephalothorax. Arachnid anatomy Fovea The fovea is the centre of the cephalothorax and is located behind the head (only in spiders).Dalton, Steve (2008). ''Spiders; The Ultimate Predators''. A & C Black, London. P.p. 19. . It is often important in identification. It can be transverse or procurved Smith, A. M. (1990c). Baboon spiders: Tarantulas of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non-homologous, differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition. Human anatomy In human anatomy, "cuticle" can refer to several structures, but it is used in general parlance, and even by medical professionals, to refer to the thickened layer of skin surrounding fingernails and toenails (the eponychium), and to refer to the superficial layer of overlapping cells covering the hair shaft ( cuticula pili), consisting of dead cells, that locks the hair into its follicle. It can also be used as a synonym for the epidermis, the outer layer of skin. Cuticle of invertebrates In zoology, the invertebrate cuticle or cuticula is a multi-layered structure outside the epidermis of many invertebrates, notably roundworms and arthropods, in which it forms an exoskelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apomorphy And Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") and anterior to the first pair of walking legs. Overview Pedipalps are composed of six segments or articles: the coxa, the trochanter, the femur, the short patella, the tibia, and the tarsus. In spiders, the coxae frequently have extensions called maxillae or gnathobases, which function as mouth parts with or without some contribution from the coxae of the anterior legs. The limbs themselves may be simple tactile organs outwardly resembling the legs, as in spiders, or chelate weapons ( pincers) of great size, as in scorpions. The pedipalps of Solifugae are covered in setae, but have not been studied in detail. Comparative studies of pedipalpal morphology may suggest that leg-like pedipalps are primitive in arachnids. At present, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream ( endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface ( exocrine gland). Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which subsequently becomes tubulated. As growth proceeds, the column of cells may split or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited, in others (salivary, pancreas) a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. As a rule, the branches do not unite with one another, but in one instance, the liver, this does occur when a reticulated compound gland is produced. In compound glands the more typical or secretory epithelium is found formi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms. Animal setae Protostomes Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. They help, for example, earthworms to attach to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion. These hairs make it difficult to pull a worm straight from the ground. Setae in oligochaetes (a group including earthworms) are largely composed of chitin. They are classified according to the limb to which they are attached; for instance, notosetae are attached to notopodia; neurosetae to neuropodia. Crustaceans have mechano- and chemosensory setae. Setae are especially present on the mouthparts of crustaceans and can also be found on grooming limbs. In some cases, setae are modified into scale like structures. Setae on the legs of krill and other small crustaceans help them to gather phytoplankton. It captures them and allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)