|
Hvítá (Árnessýsla)
Hvítá (Icelandic language, Icelandic , "white river") is a river in Iceland that begins at Hvítárvatn glacier lake on Langjökull glacier in the highlands of Iceland at . The river flows for before dropping down into a narrow gorge at Gullfoss waterfall. Thereafter, the river flows between Biskupstungur and Hrunamannahreppur districts. Here, Hvítá Confluence, combines with three other rivers: Tungufljót , Brúará, and Stóra-Laxá , doubling the volume of the river. It proceeds to run through the flatlands near Grímsnes and behind Ingólfsfjall mountain. Just north of Selfoss (town), Selfoss town, it meets Sog River where it becomes Ölfusá as it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Because of danger of flooding, especially during winter, Hvítá has a reputation of being the most dangerous river in Iceland. Organised rafting excursions take place on parts of the river. The river is bridged at 4 locations, thrice at the lowland and once near the source in the highland w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hvítá02
{{disambiguation There are some rivers in Iceland named Hvítá (= engl. White river). The most important ones are: *Hvítá (Árnessýsla) in the south of Iceland and * Hvítá (Vesturland) in the west of the country (Vesturland Western Region (, ) is one of the traditional eight regions of Iceland The regions of Iceland are eight areas of Iceland that roughly follow the arrangement of parliamentary constituencies as they were between 1959 and 2003. These regions are ...) with the waterfalls Barnafoss and Hraunfossar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
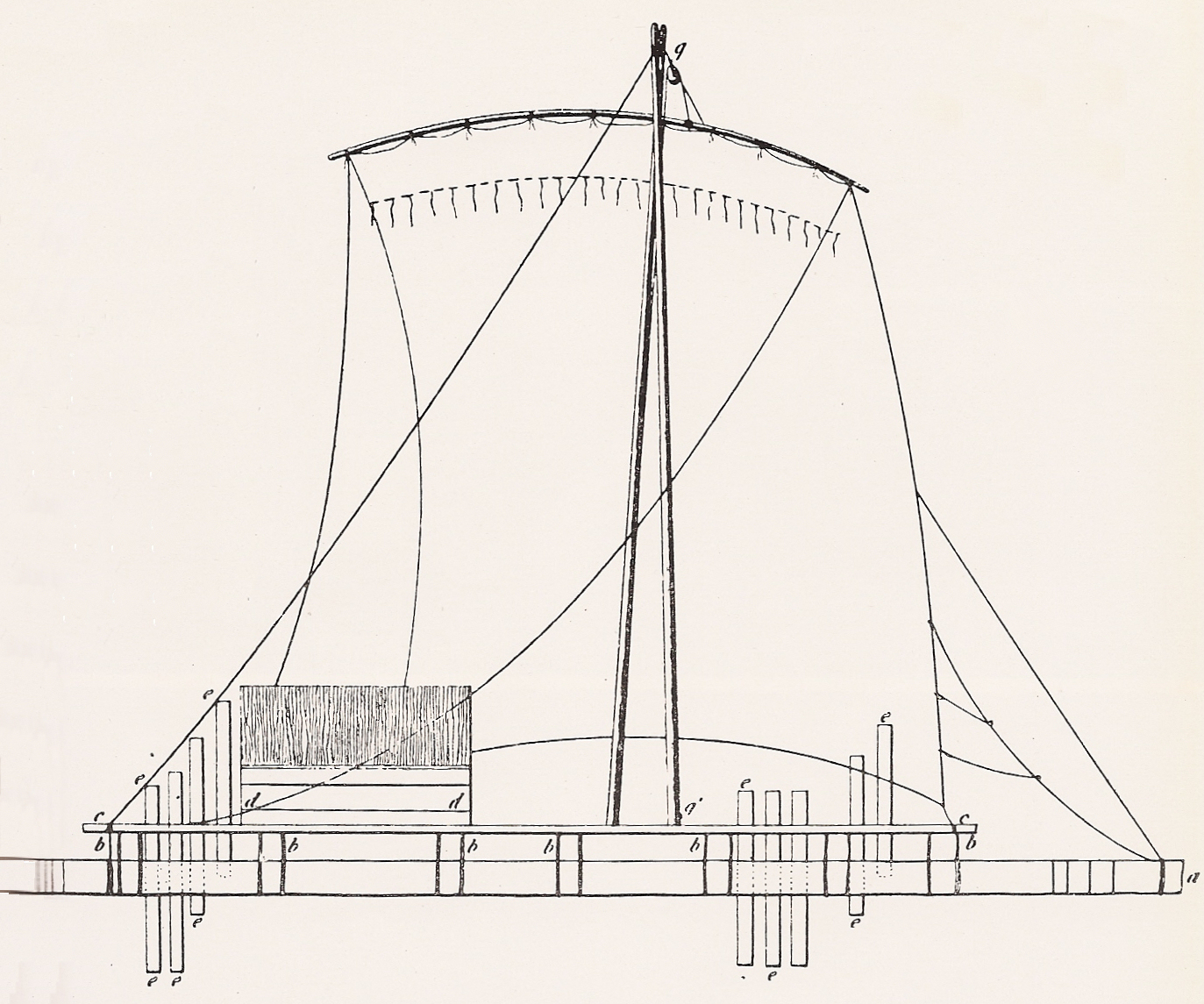
Raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood, bamboo or reeds; early buoyed or float rafts use inflated animal skins or sealed clay pots which are lashed together. Modern float rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, by tying them together into rafts and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse colonization of North America, Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an Age of Discovery, age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portuguese Empire, Portugal, Spanish Empire, Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ölfusá
The Ölfusá () is a river in Iceland. It begins at the junction between the Hvítá, Árnessýsla, Hvítá and Sog River, Sog rivers, just north of the town of Selfoss (town), Selfoss, and flows for 25 km into the Atlantic Ocean. It is Iceland's largest river by volume with an average discharge (hydrology), discharge of 423 m³/s. Its drainage basin is 5760 km2. The Ölfusá is home to a large salmon fishing industry. The Flói Nature Reserve is located on its eastern shore near its mouth. See also *List of rivers of Iceland References External linksOlfusa Rivers of Iceland {{Iceland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sog River
Sog (; more commonly Sogið ) is a river in Iceland. It runs from the lake Þingvallavatn for to its confluence with the river Hvítá, forming the river Ölfusá which then runs for another 25 km into the Atlantic Ocean. Its average discharge is . There are three hydroelectric power stations on the riverLjósafossstöð (15 MW)Írafossstöð (48 MW) anSteingrímsstöð (27 MW). The river runs through two lakes, Úlfljótsvatn and Álftavatn . It has a healthy stock of arctic char and Atlantic salmon. The size of the char can be anywhere from 0.5 pounds up the 5.0 pounds with an average size of one pound. The most common weight for salmon is 5.0 to 10.0 pounds with a few fish caught each year from 20.0 to 30.0 pounds. There are also brown trout Trout (: trout) is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', ''Salmo'' and ''Salvelinus'', all of which are members of the subfam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selfoss (town)
Selfoss () is a town in southern Iceland on the banks of the Ölfusá river. It is the seat of the municipality of Árborg. The Icelandic Route 1 (Iceland), Route 1 runs through the town on its way between Hveragerði and Hella, Iceland, Hella. The town is a centre of commerce and small industries with a population of around 10,000 (2023), making it the largest residential area in South Iceland. History Overview Selfoss was settled by Þórir Ásason sometime after 1000, but the sagas of Icelanders mention that Ingólfur Arnarson was there during the winter of 873-74, under the Ingólfsfjall mountain, which is west of the Ölfusá river. In the summer of 1891, due to the lobbying of Tryggvi Gunnarsson, a member of the Alþing, the first suspension bridge was built over the Ölfusá. That was a major breakthrough in Icelandic infrastructure. The current bridge was built in 1945 after the original structure collapsed. The cabin built to house workers constructing the bridge i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingólfsfjall
Ingólfsfjall () is a tuya in Iceland in the vicinity of Hveragerði. Name The name is derived from Iceland's official first settler, Ingólfur Arnarson. The Medieval Landnámabók says that he passed here his third winter in Iceland after his arrival from Norway with his clan, and before his slaves found the columns of his high seat and he went to the region of Reykjavík to settle there. The source also states that the chief was buried within the small mound on top of Ingólfsfjall. Geology Ingólfsfjall consists mostly of basalt and palagonite and has its origin in subglacial eruptions which turned in the end subaerial and produced some lava at its top.Ari Trausti Guðmundsson, Pétur Þorleifsson: Íslensk Fjöll. Gönguleiðir á 151 tind. Reykjavík 2004, p.140 A quarry at the southern side of the mountain near the National Road no. 1 (Hringvegur/Suðurlandsvegur) shows some of these layers which consist mostly of igneous as well as sedimentary rocks. The oldest of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grímsnes
Grímsnes () is a relatively small fissure vent, fissure or crater row Volcanic systems of Iceland, volcanic system located in South Iceland, located south–east of Þingvallavatn, Lake Thingvallavatn and east of the en echelon group of volcanic systems extending across the Reykjanes Peninsula, that erupted last in the Holocene. Geography The lava fields are spread out to the south-east of the older edifice of Búrfell (Grímsnes), Búrfell being bounded to the east by the water body of Álftavatn , on the river Sog (river), Sog (Sogið) and reaches to the south the confluence of the Sog with the Hvítá (Árnessýsla), Hvítá. From these river boundaries at about the field reaches its highest point at the Seyðishólar cone of . Most of the lava fields are covered by birch and willow. Geology Tephrochronology approximates the volcano's last eruption as about 7000 years ago. There are at least ten vents and all have erupted olivine tholeiite basalt in effusive erupt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brúará
The Brúará (, "bridge river") is a river of Iceland Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi .... It is fed by springs and discharges at the Rótarsandur area and the Brúará Canyons. It is a right tributary of the Hvítá. The whole river course is designated as a nature protected area. The name comes from a type of natural bridge that overpassed the river near the bishop-seat in Skalholt. According to sources from the bishop a worker of the bishop broke the bridge in 1602 because the seat didn't want dirty wanderers to have it to easy to approach. References Rivers of Iceland {{Iceland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confluence
In geography, a confluence (also ''conflux'') occurs where two or more watercourses join to form a single channel (geography), channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); or where two streams meet to become the river source, source of a river of a new name (such as the confluence of the Monongahela River, Monongahela and Allegheny River, Allegheny rivers, forming the Ohio River); or where two separated channels of a river (forming a river island) rejoin downstream from their point of separation. Scientific study Confluences are studied in a variety of sciences. Hydrology studies the characteristic flow patterns of confluences and how they give rise to patterns of erosion, bars, and scour pools. The water flows and their consequences are often studied with mathematical models. Confluences are relevant to the distribution of living organisms (i.e., ecology) as well; "the general pattern [downstream o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |