|
Hushen Glacier
Hushen Glacier () is a glacier lying at the southwestern part of the base of the Mendelssohn Inlet, an inlet lying between Derocher Peninsula and Eroica Peninsula indenting the north face of Beethoven Peninsula, in the southwestern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The glacier flows northeast while joining Reuning Glacier which discharges into the south part of Mendelssohn Inlet. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken 1967–68 and from Landsat imagery taken 1972–73, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for W. Timothy Hushen, Director of the Polar Research Board at the National Academy of Sciences, 1981–88. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Alyabiev Glacier * Asafiev Glacier Asafiev Glacier () is a glacier that flows north-west into Schubert Inlet from the western side of the Walton Mountains, Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was named by the USSR Academy of Sciences in 1987 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
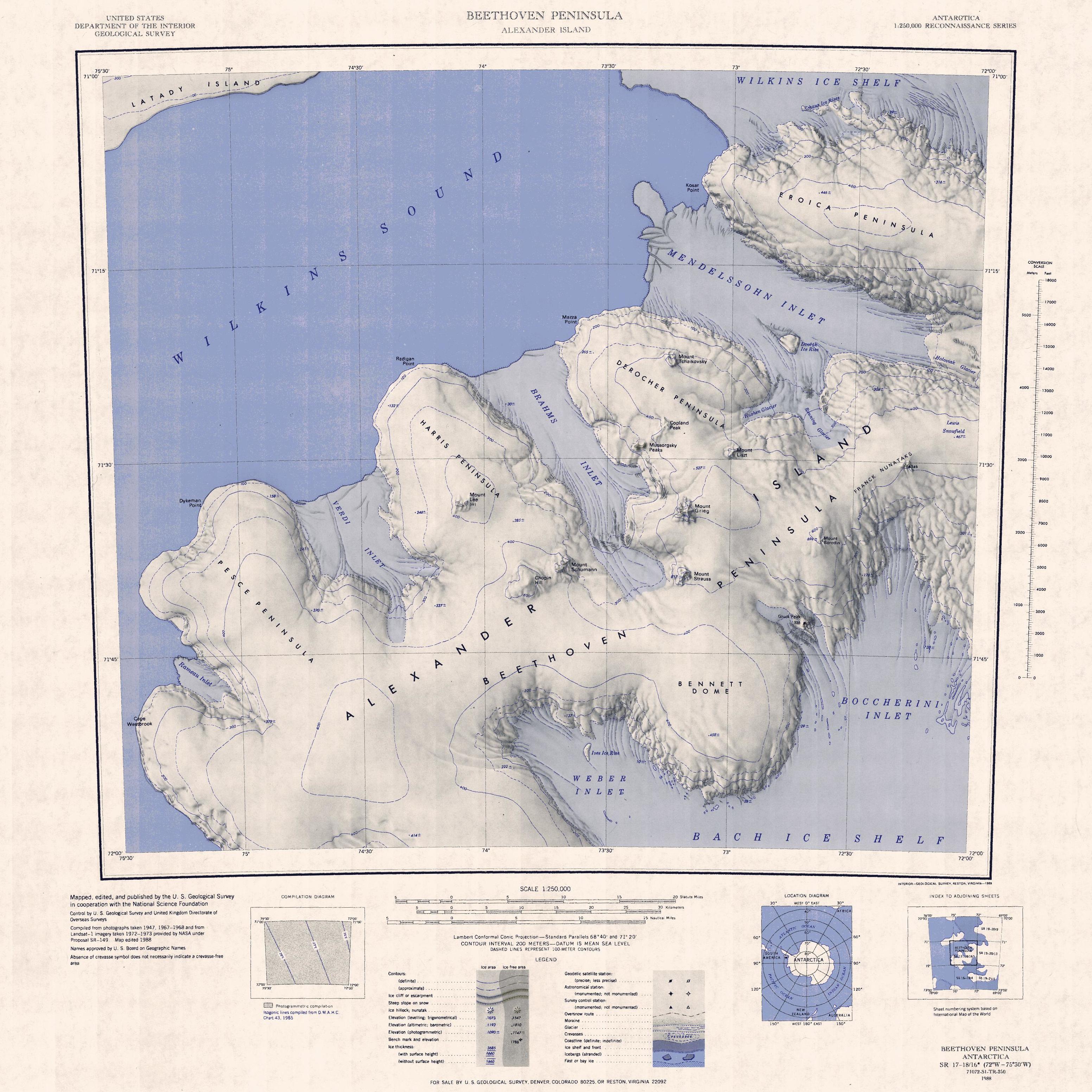
Mendelssohn Inlet
Mendelssohn Inlet () is an ice-filled inlet, long and wide, situated between Derocher Peninsula and Eroica Peninsula on the north side of Beethoven Peninsula, in the southwest part of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The inlet was first sighted from the air and roughly mapped by the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and was resighted and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48. It was remapped from the RARE photos by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1960, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after German composer Felix Mendelssohn. See also * Haydn Inlet * Verdi Inlet * Weber Inlet Further reading * Defense Mapping Agency 1992, Sailing Directions (planning Guide) and (enroute) for Antarctica', P 379 * Ted A. Scambos, Christina Hulbe, Mark Fahnestock, Jennifer Bohlander, The link between climate warming and break-up of ice shelves in the Antarctic Peninsula', Journal of Glaciology, V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derocher Peninsula
Derocher Peninsula () is a snow-covered peninsula between Brahms Inlet and Mendelssohn Inlet on the north side of Beethoven Peninsula, Alexander Island, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and mapped from these photographs by D. Searle of the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS), 1960. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Commander Paul J. Derocher, U.S. Navy, commanding officer, Antarctic Development Squadron Six (VXE-6), May 1985 to May 1986. Derocher Peninsula is one of the eight peninsulas of Alexander Island. See also * Eroica Peninsula * Harris Peninsula * Pesce Peninsula Pesce Peninsula () is a broad snow-covered peninsula lying between Rameau Inlet and Verdi Inlet on the north side of the Beethoven Peninsula, situated in the southwest portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. Dykeman Point is the main and only ... References Peninsulas of Alexander Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eroica Peninsula
Eroica Peninsula () is an ice-covered peninsula lying north of Beethoven Peninsula and Mendelssohn Inlet in western Alexander Island, Antarctica. The tip of the peninsula is Kosar Point, marking the western extremity of the Eroica Peninsula. It was mapped from trimetrogon air photography taken by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, 1947–48, and from survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1948–50. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after Beethoven's ''Eroica'' symphony, in association with Beethoven Peninsula. Eroica Peninsula is one of the eight peninsulas of Alexander Island. See also * Derocher Peninsula * Harris Peninsula * Shostakovich Peninsula Shostakovich Peninsula is an ice-covered peninsula lying north of Stravinsky Inlet and extending into Bach Ice Shelf in southern Alexander Island, Antarctica. The peninsula was first mapped by Directorate of Overseas Surveys from satellite image ... Further reading * Cook, Alison & Vaugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beethoven Peninsula
The Beethoven Peninsula is a deeply indented, ice-covered peninsula, long in a northeast–southwest direction and wide at its broadest part, forming the southwest part of Alexander Island, which lies off the southwestern portion of the Antarctic Peninsula. The south side of the peninsula is supported by the Bach Ice Shelf whilst the north side of the peninsula is supported by the Wilkins Ice Shelf. The Mendelssohn Inlet, the Brahms Inlet and the Verdi Inlet apparently intrude into it. The Bach Ice Shelf, Rossini Point and Berlioz Point are some distance away, on the Ronne Entrance from the Southern Ocean. Beethoven Peninsula is one of the eight peninsulas of Alexander Island. The peninsula was first seen and photographed from the air in 1940 by the US Antarctic Service, which compiled the first rough map of southwest Alexander Island. It was resighted and photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, and remapped from RARE photo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Island
Alexander Island, which is also known as Alexander I Island, Alexander I Land, Alexander Land, Alexander I Archipelago, and Zemlja Alexandra I, is the largest island of Antarctica. It lies in the Bellingshausen Sea west of Palmer Land, Antarctic Peninsula from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. The George VI Ice Shelf entirely fills George VI Sound and connects Alexander Island to Palmer Land. The island partly surrounds Wilkins Sound, which lies to its west.Stewart, J. (2011) ''Antarctic An Encyclopedia'' McFarland & Company Inc, New York. 1776 pp. . Alexander Island is about long in a north–south direction, wide in the north, and wide in the south. Alexander Island is the second-largest uninhabited island in the world, after Devon Island. History Alexander Island was discovered on January 28, 1821, by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, who named it Alexander I Land for the reigning Tsar Alexander I of Russia. Wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuning Glacier
Reuning Glacier () is a glacier situated on the north side of Beethoven Peninsula, lying within the southwest portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica. The glacier flows in a northwest direction and joins Hushen Glacier in discharging into south Mendelssohn Inlet. The glacier was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from U.S. Navy aerial photographs taken 1967-68 and U.S. Landsat imagery taken 1972–73. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Winifred M. Reuning, Office of Polar Programs, National Science Foundation (NSF), Editor, Antarctic Journal of the United States, from 1980 to 2015. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Alyabiev Glacier * Palestrina Glacier Palestrina Glacier () is a glacier lying in the northern portion of Alexander Island, Antarctica, 11 nautical miles (20 km) long and 8 nautical miles (15 km) wide, flowing west from Nichols Snowfield into Lazarev Bay. The glacier was map ... * Yozola Glac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers In The Antarctic
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheets, ice caps or ice fields, such as the Antarctic ice sheet, but includes glacial features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice streams. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier. Ice shelves are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System). List by letters * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: A–H * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: I–Z See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * List of Antarctic ice rises * List of Antarctic ice shelves * List of Antarctic ice streams * List of glaciers * List of subantar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |