|
Hunter Fracture Zone
The Hunter Fracture Zone is a sinistral (left-lateral) transform faulting fracture zone, that to its south is part of a triple junction with the New Hebrides Trench, and the North Fiji Basin Central Spreading Ridge. The Hunter Fracture Zone, with the Hunter Ridge, an area with recent volcanic activity to its north, is the southern boundary of the North Fiji Basin. This boundary area in the south-western part of the Hunter Fracture Zone is associated with hot subduction, and a unique range of volcanic geochemistry. Geography The Hunter Fracture Zone is located to the south and southwest of Fiji and starts where the southern part of the New Hebrides Trench ends due to the increasing obliqueness of convergence lending to more strike slip faulting than subducting. It terminates around the International Date Line, with the Kadavu Islands immediately to its north. However some earlier work has postulated that the fault structures around Suva on Fiji itself are related and different au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Island And Hunter Island
Hunter Island and Matthew Island are two small and uninhabited high islands in the South Pacific, located east of New Caledonia and south-east of Vanuatu archipelago. Hunter Island and Matthew Island, apart, are claimed by Vanuatu as part of Tafea Province, and considered by the people of Aneityum part of their custom ownership, and were claimed by France as part of New Caledonia. Small, arid, without fresh water and not easily accessible, the islands had no interest for Britain or France during their colonisation of the Pacific in the course of the 18th and 19th centuries. France officially annexed both islands in 1929. In 1965, the United Kingdom also claimed the two islands, as part of the New Hebrides. France conducted a symbolic occupation in 1975. In 1980, on its independence, Vanuatu claimed sovereignty, but made no occupation of the islands. In 1979, Météo-France set up an automatic weather station on one of the islands, and the French Navy regularly visits bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter Ridge
The Hunter Ridge (previously known as Hunter Island Ridge, Matthew Ridge), is an active volcanic arc oceanic ridge located on the oceanic New Hebrides Plate in the south-west Pacific Ocean extending at least . It defines the south-western limit of the North Fiji Basin (NFB) and is an area of unique range in volcanic geochemistry, which transpires to have been due partially to a new, previously unrecognised, subduction zone. Geography The ridge contains Matthew Island and Hunter Island and extends from southern Vanuatu near the Volsmar seamount via the region of Ceva-i-Ra (Conway Reef) towards Fiji. Its length on this definition is about but earlier work included other parts of the Hunter Fracture Zone that are now known to be discontinuous topographically and on such historic definitions the length approached or more. The West Matthew volcano had its the most recent eruption in 1956, still had steam admissions in 1983, having formed a new volcanic cone from below the sea surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
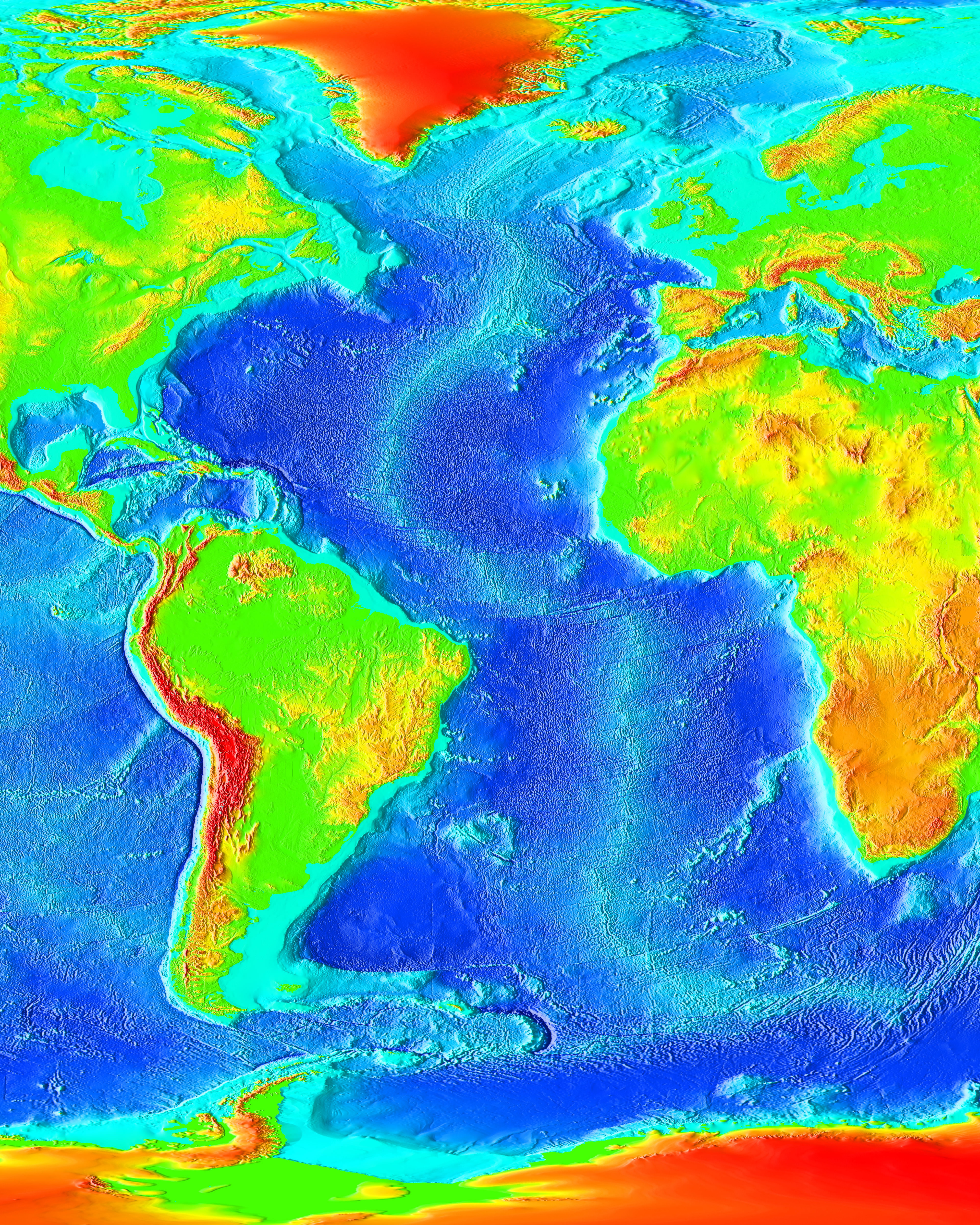
Fracture Zones
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band or dislocation. Brittle fractures occur with no apparent deformation before fracture. Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen fails via fracture. This is usually determined for a given specimen by a tensile test, which charts the stress–strain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fracture Zones
Fracture zones are common features in the geology of oceanic basins. Globally most fault zones are located on divergent plate boundaries on oceanic crust. This means that they are located around mid-ocean ridges and trend perpendicular to them. The term fracture zone is used almost exclusively for features on oceanic crust; similar structures on continental crust are instead termed transform or strike slip faults, a denomination active fracture zones also can have. Some fracture zones have been created by mid-ocean ridge segments that have been subducted and may not longer exist. Pacific Ocean Most fracture zones in the Pacific Ocean originate from large mid-ocean ridges (also called "rises") such as the East Pacific Rise, Chile Rise and Juan de Fuca Ridge. The plates that host the fractures are Nazca, Pacific, Antarctic, Juan de Fuca and Cocos among others. Fracture zones being subducted under Southern and Central America are generally southwest-northeast oriented reflecting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanuatu Subduction Zone
The Vanuatu subduction zone (previously called New Hebrides subduction zone) is currently one of the most active subduction zones on earth, producing great earthquakes (magnitude 8.0 or greater), with potential for tsunami hazard to all coastlines of the Pacific ocean. There are active volcanoes associated with arc volcanism. Geography The zone includes most of the islands of Vanuatu , the Santa Cruz islands of the southern Solomon Islands, and the Loyalty Islands. A number of ocean floor features are related to the zone, in particular the New Hebrides Trench (South New Hebridies Trench) and the North New Hebrides Trench (Torres Trench) which is separated from the southern trench by the d'Entrecasteaux Ridge and the island of Espiritu Santo. The d'Entrecasteaux Ridge is at this point of intersection two parallel, east-west trending ridges that are above the surrounding abyssal plain. Geology Shore based observations had characterised the islands of the volcanic arc as having ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. ''Failed rifts'' are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to the poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more Plate tectonics, lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, Orogeny, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and Deformation (geology), deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Of Focus (tectonics)
In seismology, the depth of focus or focal depth refers to the depth at which an earthquake occurs. Earthquakes occurring at a depth of less than are classified as shallow-focus earthquakes, while those with a focal depth between and are commonly termed mid-focus or intermediate-depth earthquakes. In subduction zones, where older and colder oceanic crust sinks under another tectonic plate, deep-focus earthquakes may occur at much greater depths in the mantle, ranging from up to . The cause of deep-focus earthquakes is still not entirely understood since subducted lithosphere at that pressure and temperature regime should not exhibit brittle behavior. A possible mechanism for the generation of deep-focus earthquakes is faulting caused by olivine undergoing a phase transition into a spinel structure, with which they are believed to be associated. Earthquakes at this depth of focus typically occur at oceanic-continental convergent boundaries, along Wadati–Benioff zones. Discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suva
Suva () is the capital and largest city of Fiji. It is the home of the country's largest metropolitan area and serves as its major port. The city is located on the southeast coast of the island of Viti Levu, in Rewa Province, Central Division. In 1877, the capital of Fiji was moved to Suva from Levuka, the main European colonial settlement at the time, due to its restrictive geography and environs. The administration of the colony was transferred from Levuka to Suva in 1882. As of the 2017 census, the city of Suva had a population of 93,970, and Suva's metropolitan area, which includes its independent suburbs, had a population of 185,913. The combined urban population of Suva and the towns of Lami, Nasinu, and Nausori that border it was around 330,000: over a third of the nation's population. (This urban complex, excluding Lami, is also known as the Suva-Nausori corridor.) Suva is the political, economic, and cultural centre of Fiji. It is also the economic and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadavu Group
The Kadavu Group is an archipelago south of Viti Levu, one of Fiji's two main islands. Dominated by Kadavu Island, the fourth largest island in Fiji, the group also includes Ono, Dravuni, Galoa and a number of islets in the Great Astrolabe Reef The Great Astrolabe Reef is in Fiji and surrounds the fourth largest island, Kadavu Island, which is approximately 65 km in length. Kadavu Island is approximately 100 km south of Viti Levu, the main island of Fiji. The Great Astrolabe ....Kadavu Group - satellite view Archipelagoes of Fiji Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean {{Fiji-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific Ocean, roughly following the 180° line of longitude and deviating to pass around some territories and island groups. Crossing the date line eastbound decreases the date by one day, while crossing the date line westbound increases the date. Geography Circumnavigating the globe People traveling westward around the world must set their clocks: *Back by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Forward by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. People traveling eastward must set their clocks: *Forward by one hour for every 15° of longitude crossed, and *Back by 24 hours upon crossing the International Date Line. Failing to do this would make their time inaccurate to the local time. The Arab geographer Abulfed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |