|
Human Body Model
The human-body model (HBM) is the most commonly used model for characterizing the susceptibility of an electronic device to damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD). The model is a simulation of the discharge which might occur when a human touches an electronic device. The HBM definition most widely used is the test model defined in the United States military standard, MIL-STD-883, Method 3015.9, Electrostatic Discharge Sensitivity Classification. This method establishes a simplified equivalent electrical circuit and the necessary test procedures required to model an HBM ESD event. An internationally widely used standard iJEDEC standard JS-001 HBM is used primarily for manufacturing environments to quantify an integrated circuit to survive the manufacturing process. A similar standard, IEC 61000-4-2, is used for system level testing and quantifies protection levels for a real world ESD event in an uncontrolled environment. Model In both JS-001-2012 and MIL-STD-883H the charged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESD (Susceptible)
ESD may refer to: Science * ESD (gene), a human gene/enzyme * Electrostatic discharge, a sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects * Electrostatic-sensitive device, any component which can be damaged by common static charges * Energy spectral density, a part of a function in statistical signal processing * Environmental secondary detector, a gaseous detection device used with environmental scanning electron microscopes * Equivalent spherical diameter, a diameter of a sphere of equivalent volume * Extreme subdwarf, a type of star Medicine * End-systolic dimension, the diameter across a ventricle in the heart * Endoscopic submucosal dissection, a medical therapy with endoscopy Education * Education for sustainable development, international learning methodology * Educational service district (other), regional education unit in some U.S. states * Episcopal School of Dallas, day school in Texas, U.S. * Evangelical School for the Dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Discharge
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is a sudden and momentary flow of electric current between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an electrical short or dielectric breakdown. A buildup of static electricity can be caused by tribocharging or by electrostatic induction. The ESD occurs when differently-charged objects are brought close together or when the dielectric between them breaks down, often creating a visible spark. ESD can create spectacular electric sparks (lightning, with the accompanying sound of thunder, is a large-scale ESD event), but also less dramatic forms which may be neither seen nor heard, yet still be large enough to cause damage to sensitive electronic devices. Electric sparks require a field strength above approximately 40 kV/cm in air, as notably occurs in lightning strikes. Other forms of ESD include corona discharge from sharp electrodes and brush discharge from blunt electrodes. ESD can cause harmful effects of importance in industry, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response. A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEC 61000-4-2
IEC 61000-4-2 is the International Electrotechnical Commission's immunity standard on electrostatic discharge (ESD). The publication is one of the basic EMC standards of the IEC 61000–4 series. The European equivalent of the standard is called EN 61000-4-2. The current version of the IEC standard is the second edition dated 2008-12-09. The basic standards (61000-4) are usually called by product or family specific standards, which use these basic standards as a common reference. Scope The publication describes requirements, levels and test methods to achieve immunity compliance of an electronic product. The purpose is to create a reproducible ground for product compliance and the standard defines: ranges, levels, test equipment, setups, procedures, calibrations, generator waveforms and general uncertainties. The intention is not to define product specific tests but instead establish a basic common reference. Product specific tests are instead defined in standards such as EN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
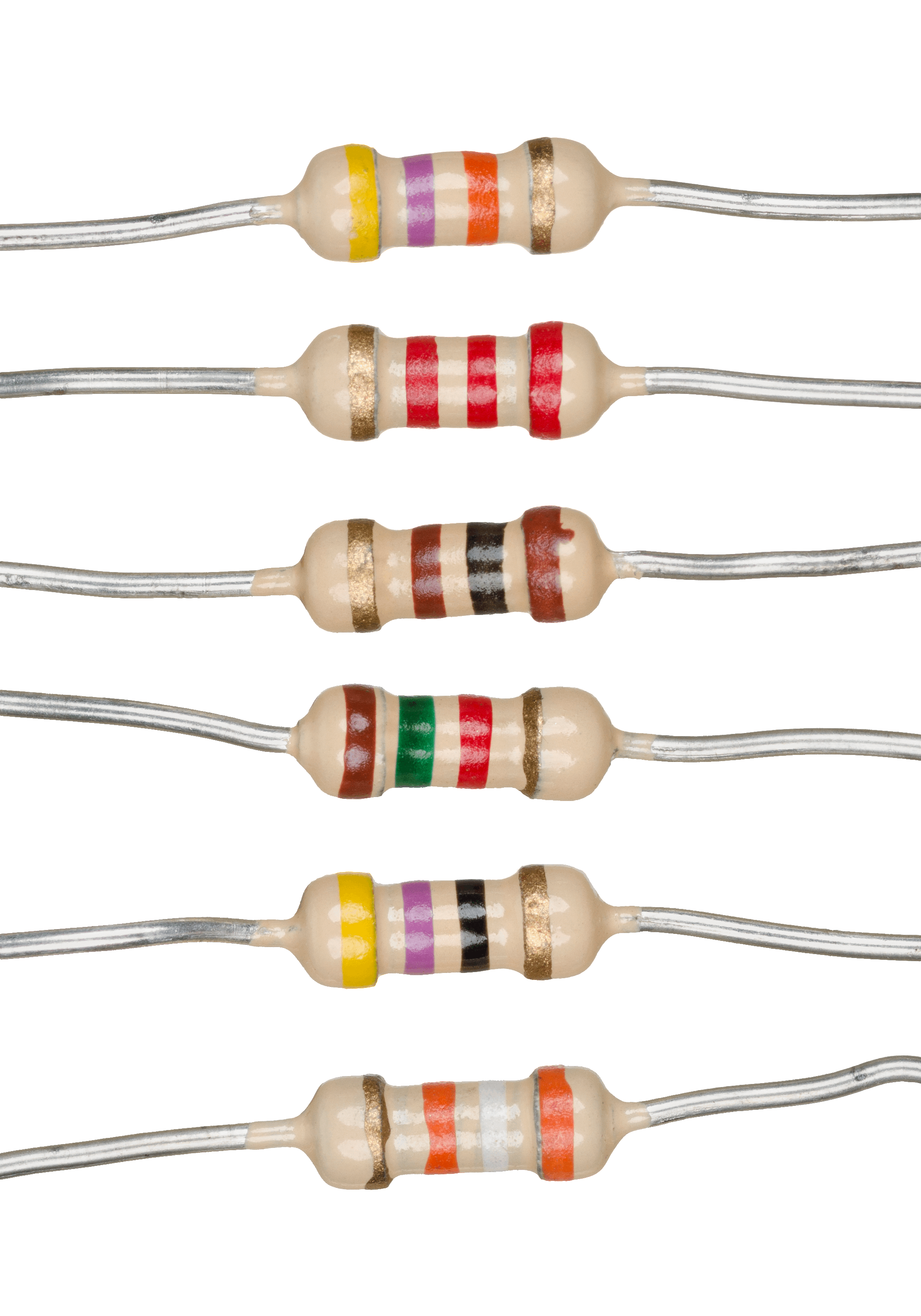
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device Under Test
A device under test (DUT), also known as equipment under test (EUT) and unit under test (UUT), is a manufactured product undergoing testing, either at first manufacture or later during its life cycle as part of ongoing functional testing and calibration checks. This can include a test after repair to establish that the product is performing in accordance with the original product specification. Electronics testing In the electronics industry a DUT is any electronic assembly under test. For example, cell phones coming off of an assembly line may be given a final test in the same way as the individual chips were earlier tested. Each cell phone under test is, briefly, the DUT. For circuit boards, the DUT is often connected to the test equipment using a bed of nails tester of pogo pins. Semiconductor testing In semiconductor testing, the device under test is a die on a wafer or the resulting packaged part. A connection system is used, connecting the part to automatic or manual test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charged-device Model
The charged-device model (CDM) is a model for characterizing the susceptibility of an electronic device to damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD). The model is an alternative to the human-body model (HBM). Devices that are classified according to CDM are exposed to a charge at a standardized voltage level, and then tested for survival. If it withstands this voltage level, it is tested at the next level and so on, until the device fails. CDM is standardized as ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC joint standard JS-002. See also * Human-body model * Transmission-line pulse Transmission-Line Pulse (TLP) is a way to study integrated circuit technologies and circuit behavior in the current and time domain of electrostatic-discharge (ESD) events. The concept was described shortly after WWII in pp. 175–189 oPulse ... External links JEDEC standard JS-002-2014 ESDA/JEDEC Joint Standard for Electrostatic Discharge Sensitivity Testing - Charged Device Model (CDM) - Device Level Electrical bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission-line Pulse
Transmission-Line Pulse (TLP) is a way to study integrated circuit technologies and circuit behavior in the current and time domain of electrostatic-discharge (ESD) events. The concept was described shortly after WWII in pp. 175–189 oPulse Generators Vol. 5 of the MIT Radiation Lab Series. Also, D. Bradley, J. Higgins, M. Key, and S. Majumdar realized a TLP-based laser-triggered spark gap for kilovolt pulses of accurately variable timing in 1969. For investigation of ESD and electrical-overstress (EOS) effects a measurement system using a TLP generator has been introduced first bT. Maloney and N. Khurana in 1985 Since then, the technique has become indispensable for integrated circuit ESD protection development. The TLP technique is based on charging a long, floating cable to a pre-determined voltage, and discharging it into a Device-Under-Test (DUT). The cable discharge emulates an electro-static discharge event, but employing time-domain reflectometry (TDR), the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by the Internet Archive, a nonprofit based in San Francisco, California. Created in 1996 and launched to the public in 2001, it allows the user to go "back in time" and see how websites looked in the past. Its founders, Brewster Kahle and Bruce Gilliat, developed the Wayback Machine to provide "universal access to all knowledge" by preserving archived copies of defunct web pages. Launched on May 10, 1996, the Wayback Machine had more than 38.2 million records at the end of 2009. , the Wayback Machine had saved more than 760 billion web pages. More than 350 million web pages are added daily. History The Wayback Machine began archiving cached web pages in 1996. One of the earliest known pages was saved on May 10, 1996, at 2:08p.m. Internet Archive founders Brewster Kahle and Bruce Gilliat launched the Wayback Machine in San Francisco, California, in October 2001, primarily to address the problem of web co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)