|
Hugh Jewett
Hugh Judge Jewett (July 1, 1817 – March 6, 1898) was an American railroader and politician. He served as the United States representative from Ohio's 12th congressional district in the 43rd United States Congress. Early life Jewett was born at Harford County, Maryland but spent most of his life in Ohio at Zanesville and Columbus. He was the son of John Jewett (1777–1854) and Susannah Judge (1778–1853). He was also the younger brother of Joshua Husband Jewett (1815–1861), a United States Congressman from Kentucky. Career He attended Hopewell Academy in Chester County, Pennsylvania, before moving to Ohio as a young man and attending Hiram College. He was admitted to the bar at St. Clairsville in 1840 after studying with James Black Groome, who later became Governor of Maryland. He formed a law practice with Isaac Eaton, who became a prominent lawyer in Kansas. In 1848, he moved to Zanesville, where he formed a law practice with John O'Neill, a member of Congress. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelph Van Trump
Philadelph Van Trump (November 15, 1810 – July 31, 1874) was an American politician who served as a U.S. Representative from Ohio from 1867 to 1873. Biography Born in Lancaster, Ohio, Van Trump attended a public school. He learned the art of printing and subsequently became editor of the ''Gazette and Enquirer'' at Lancaster. He also studied law and was admitted to the bar. He started practice in Lancaster on May 14, 1838. He served as delegate to the Whig National Convention in 1852. In 1856, Van Trump was an unsuccessful candidate of the American Party for Governor. He served as delegate to the Bell and Everett State convention in 1860 and served as president. He served as judge of the court of common pleas from 1862 to 1867. Van Trump failed in elections to be a judge on the Supreme Court of Ohio in 1863, 1864, and 1865. Van Trump was elected as a Democrat to the Fortieth, Forty-first, and Forty-second Congresses (March 4, 1867 – March 3, 1873). He was not a candida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The state's capital and largest city is Columbus, with the Columbus metro area, Greater Cincinnati, and Greater Cleveland being the largest metropolitan areas. Ohio is bordered by Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the west, and Michigan to the northwest. Ohio is historically known as the "Buckeye State" after its Ohio buckeye trees, and Ohioans are also known as "Buckeyes". Its state flag is the only non-rectangular flag of all the U.S. states. Ohio takes its name from the Ohio River, which in turn originated from the Seneca word ''ohiːyo'', meaning "good river", "great river", or "large creek". The state arose from the lands west of the Appalachian Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pennsylvania Press
The University of Pennsylvania Press (or Penn Press) is a university press affiliated with the University of Pennsylvania located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The press was originally incorporated with the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania on 26 March 1890, and the imprint of the University of Pennsylvania Press first appeared on publications in the 1890s, among the earliest such imprints in America. One of the press's first book publications, in 1899, was a landmark: ''The Philadelphia Negro: A Social Study'', by renowned black reformer, scholar, and social critic W.E.B. Du Bois, a book that remains in print on the press's lists. Today the press has an active backlist of roughly 2,000 titles and an annual output of upward of 120 new books in a focused editorial program. Areas of special interest include American history and culture; ancient, medieval, and Renaissance studies; anthropology; landscape architecture; studio arts; human rights; Jewish studies; and political science. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
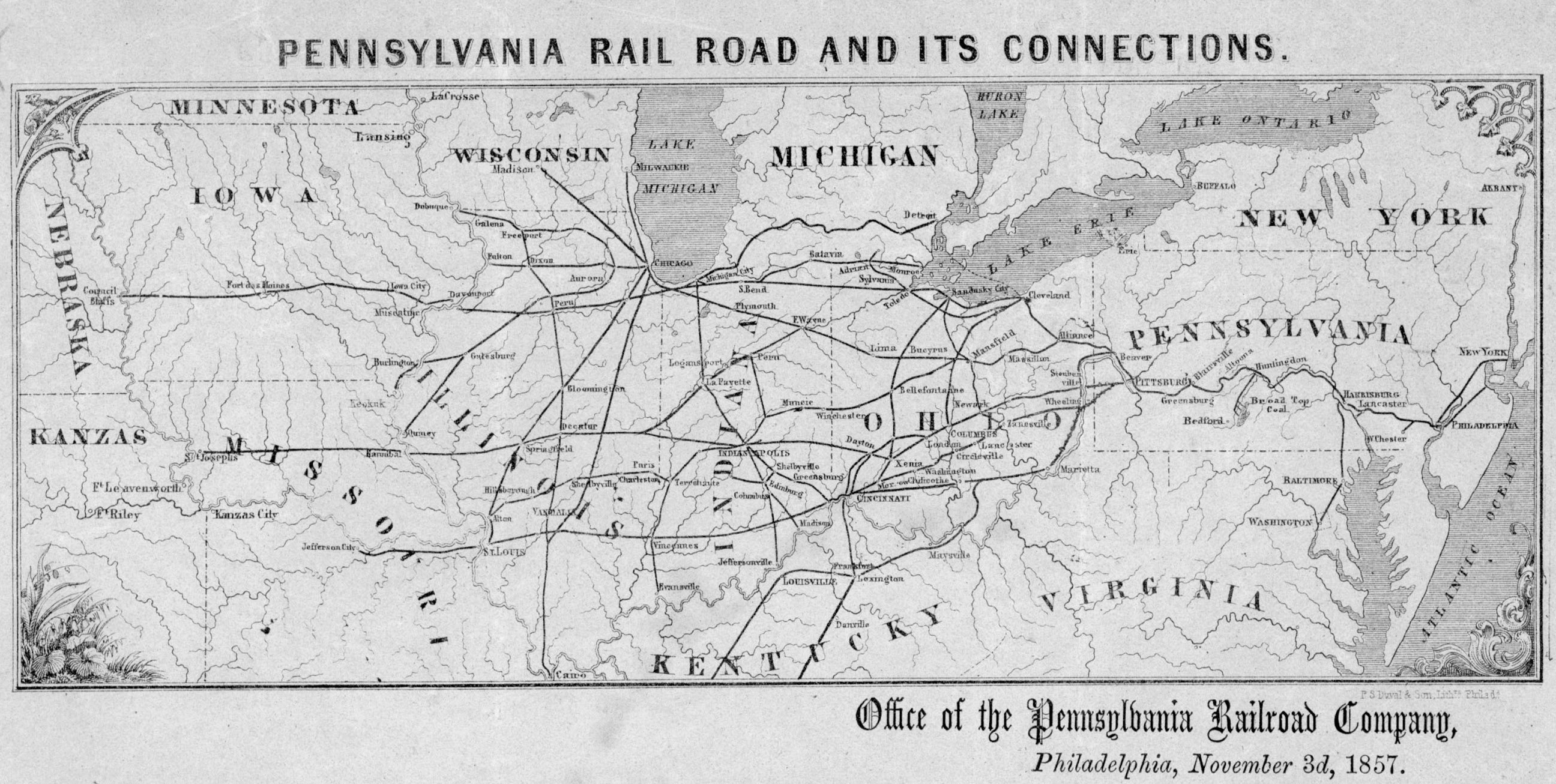
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Ohio Railroad
The Central Ohio Railroad was the third railroad to enter Columbus, Ohio, and the first to connect Columbus with the east coast. It eventually became a part of the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. History It was realized that a railroad from Bellaire on the west side of the Ohio River across from Wheeling would be a valuable franchise for moving goods to and from the east coast. Chartered in February, 1847 by interests in Zanesville, the CO was to prove difficult to construct. Construction challenges Eastern Ohio proved a difficult location for a railroad. Obstacles included the Muskingum River at Zanesville, of excavation through the hard sandstone of the Blackhand Gorge along the Licking River between Zanesville and Newark, and large quantities of fill and trestle work along the Big Walnut Creek. A tunnel in Cambridge had rockfalls and a cut near Barnesville had landslides. Operation begins On January 19, 1852, trains began running between Zanesville and Newark. A year late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John O'Neill (congressman)
John O'Neill (December 17, 1822 – May 25, 1905) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a U.S. Representative from Ohio for one term from 1863 to 1865, Early life and career Born in Philadelphia, O'Neill attended the common schools at Frederick, Maryland, and Georgetown College, Washington, D.C. He was graduated from Mount St. Mary's College, Emmitsburg, Maryland, and from the law department of Georgetown College, Washington, D.C., in 1841. He was admitted to the bar in 1842. He moved to Zanesville, Ohio, in 1844 and commenced the practice of law. He served as the prosecuting attorney of Muskingum County in 1845. He also held various county offices. He was United States Attorney for the Southern District of Ohio 1856-1858. Congress O'Neill was elected as a Democrat to the Thirty-eighth Congress (March 4, 1863 - March 3, 1865). He resumed the practice of his profession. Later career and death He served as member of the Ohio Senate 1883-1885. He then prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor Of Maryland
The Governor of the State of Maryland is the head of government of Maryland, and is the commander-in-chief of the state's National Guard units. The Governor is the highest-ranking official in the state and has a broad range of appointive powers in both the state and local governments, as specified by the Maryland Constitution (1867, and revisions/amendments). Because of the extent of these constitutional powers, the Governor of Maryland has been ranked as being among the most powerful governors in the United States. The current Governor is Larry Hogan, a Republican who has been in office since 2015. He will be succeeded by Wes Moore, a Democrat who will take office on January 18, 2023. Selection and qualifications Like most state chief executives in the United States, the Governor is elected by the citizens of Maryland to serve a four-year term. Under the Constitution of Maryland, the Governor can run any number of times, but not more than twice in a row. This makes it possi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Black Groome
James Black Groome (April 4, 1838October 5, 1893), a member of the United States Democratic Party, was the 36th Governor of Maryland in the United States from 1874 to 1876. He was also a member of the United States Senate, representing Maryland, from 1879–1885. Early life and career Groome was born in Elkton, Maryland and completed preparatory studies in the Tennent School of Hartsville, Pennsylvania, with hopes of attending Princeton University. However, a severe injury during that time that left him sickly the rest of his life forced him to abandon his college aspirations. Groome instead studied law with his father—the wealthy and former gubernatorial candidate Colonel John Groome—and was admitted to the bar in 1861. Due to his ill health, Groome did not serve during the American Civil War. In 1867, Groome was a strong voice in favor of a new constitution for the state of Maryland, and served as a representative from Cecil County, Maryland to the state constitutional c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admission To The Bar In The United States
Admission to the bar in the United States is the granting of permission by a particular court system to a lawyer to practice law in the jurisdiction and before those courts. Each U.S. state and similar jurisdiction (e.g. territories under federal control) has its own court system and sets its own rules for bar admission, which can lead to different admission standards among states. In most cases, a person is "admitted" or "called" to the bar of the highest court in the jurisdiction and is thereby authorized to practice law in the jurisdiction. Federal courts, although often overlapping in admission standards with states, set their own requirements for practice in each of those courts. Typically, lawyers seeking admission to the bar of one of the U.S. states must earn a Juris Doctor degree from a law school approved by the jurisdiction, pass a bar exam administered by the regulating authority of that jurisdiction, pass a professional responsibility examination, and undergo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram College
Hiram College ( ) is a private liberal arts college in Hiram, Ohio. It was founded in 1850 as the Western Reserve Eclectic Institute by Amos Sutton Hayden and other members of the Disciples of Christ Church. The college is nonsectarian and coeducational. It is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission. Hiram's most famous alumnus is James A. Garfield, who served as a college instructor and principal before he was elected the 20th President of the United States. History On June 12, 1849, representatives of the Disciples of Christ voted to establish an academic institution, which would later become Hiram College. On November 7 that year, they chose the village of Hiram as the site for the school because the founders considered this area of the Western Reserve to be "healthful and free of distractions". The following month, on December 20, the founders accepted the suggestion of Isaac Errett and named the school the Western Reserve Eclectic Institute. The institute's origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester County, Pennsylvania
Chester County (Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania Dutch: ''Tscheschter Kaundi''), colloquially known as Chesco, is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in the Delaware Valley region of the state. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 534,413, increasing by 7.1% from 498,886 in 2010 United States census, 2010. The county seat and most populated municipality is West Chester, Pennsylvania, West Chester. Chester County was one of the three original Pennsylvania counties created by William Penn in 1682. It was named for Chester, England. Chester County is part of the Philadelphia-Camden, New Jersey, Camden-Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington, PA-New Jersey, NJ-Delaware, DE-Maryland, MD Delaware Valley, Metropolitan Statistical Area. Eastern Chester County is home to many communities that comprise part of the Philadelphia Main Line western suburbs outside of Philadelphia, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpeg)

.jpg)