|
Hugh De Sigillo
Hugh or Hugo de Sigillo († 1229) was 13th century bishop of Dunkeld, Atholl, Scotland. Little is known of his general background before becoming bishop. What is known in that he was a clerk of King William of Scotland and Abbot of Newbattle. Hugh succeeded John de Leicester as bishop on 5 October 1214. He was a frequent witness to royal charters in the period. The date of his consecration is not known. On 29 September 1226 he gave benediction to Radulf II, Abbot of Melrose The Abbot Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a .... He died sometime in 1229. References * Dowden, John, ''The Bishops of Scotland'', ed. J. Maitland Thomson, (Glasgow, 1912) 'The Historical Works of James Balfour', James Haig (1824), vol.1, p. 38. {{DEFAULTSORT:Sigillo, Hugh de 12th-century b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Dunkeld
The Bishop of Dunkeld is the ecclesiastical head of the Diocese of Dunkeld, one of the largest and more important of Scotland's 13 medieval bishoprics, whose first recorded bishop is an early 12th-century cleric named Cormac. However, the first known abbot dates to the 10th century, and it is often assumed that in Scotland in the period before the 12th century, the roles of both bishop and abbot were one and the same. The Bishopric of Dunkeld ceased to exist as a Catholic institution after the Scottish Reformation but continued as a royal institution into the 17th century. The diocese was restored (with a different boundary) by Pope Leo XIII on 4 March 1878; it is now based in the city of Dundee. List of known abbots Dunkeld Abbey was an offshoot of Iona, perhaps founded in the early 9th century, in the reign of Caustantín mac Fergusa, King of the Picts. It is not clear when its abbots got independence from the Abbots of Iona, but a notable event is the alleged transfer of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
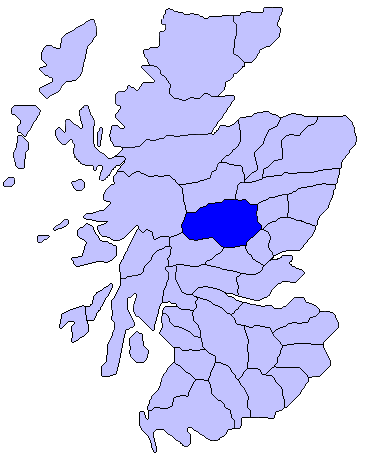
Atholl
Atholl or Athole ( gd, Athall; Old Gaelic ''Athfhotla'') is a large historical division in the Scottish Highlands, bordering (in anti-clockwise order, from Northeast) Marr, Badenoch, Lochaber, Breadalbane, Strathearn, Perth, and Gowrie. Historically it was a Pictish kingdom, becoming one of the original provinces of the Kingdom of Alba before being incorporated into the sheriffdom and later county of Perthshire. Today it forms the northern part of Perth and Kinross, Scotland. Etymology In Scottish Gaelic the name is ''Athall'', which traditionally has been interpreted as deriving from the Old Irish ''Ath-fhotla'', or 'New Ireland' ( Fotla being a traditional name for Ireland). The explanation given for this relates to a conjectured Gaelic settlement of Scotland, which was previously inhabited by the Picts. James E. Fraser has called the "New Ireland" interpretation into question. On the basis of the early spelling ''Athochlach'', the first element has been proposed as rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerk (position)
A clerk is a white-collar worker who conducts general office tasks, or a worker who performs similar sales-related tasks in a retail environment. The responsibilities of clerical workers commonly include record keeping, filing, staffing service counters, screening callers, and other administrative tasks. History and etymology The word ''clerk'' is derived from the Latin ''clericus'' meaning "cleric" or "clergyman", which is the latinisation of the Greek ''κληρικός'' (''klērikos'') from a word meaning a "lot" (in the sense of drawing lots) and hence an "apportionment" or "area of land". Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, "A Greek-English Lexicon", at Perseus The association derived from medieval courts, where writing was mainly entrusted to |
William I Of Scotland
William the Lion, sometimes styled William I and also known by the nickname Garbh, "the Rough"''Uilleam Garbh''; e.g. Annals of Ulster, s.a. 1214.6; Annals of Loch Cé, s.a. 1213.10. ( 1142 – 4 December 1214), reigned as King of Scots from 1165 to 1214. His 48-year-long reign was the second longest in Scottish history, and the longest for a Scottish monarch before the Union of the Crowns in 1603. Early life William was born around 1142, during the reign of his grandfather King David I of Scotland. His parents were the king's son Henry and Ada de Warenne. William was around 10 years old when his father died in 1152, making his elder brother Malcolm the heir apparent to their grandfather. From his father, William inherited the Earldom of Northumbria. David I died the next year, and William became heir presumptive to the new king, Malcolm IV. In 1157, William lost the Earldom of Northumbria to Henry II of England. Reign Malcolm IV did not live for long, and upon his death on 9 D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John De Leicester
John de Leicester (or Johannes de Lacester) († 1214) was an early 13th-century bishop of Dunkeld. Before becoming bishop, he had been archdeacon of Lothian. He was elected to the bishopric on 22 July 1211. As bishop-elect, he is present when King William of Scotland paid homage to King John of England in 1212. He had been consecrated by June 1212, when a letter from Pope Innocent III to Walter, bishop of Glasgow, and Radulphus, bishop of Brechin, writes of the election and consecration of John, archdeacon of Lothian. John's episcopate would only last a few years; he died on 7 October 1214. His death occurred at Cramond, Midlothian, and was buried on Inchcolm Inchcolm (from the Scottish Gaelic "Innis Choluim", meaning Columba's Island) is an island in the Firth of Forth in Scotland. It was repeatedly attacked by English raiders during the Wars of Scottish Independence, and was fortified during both Wo .... References * Dowden, John, ''The Bishops of Scotland'', ed. J. Mait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benediction
A benediction (Latin: ''bene'', well + ''dicere'', to speak) is a short invocation for divine help, blessing and guidance, usually at the end of worship service. It can also refer to a specific Christian religious service including the exposition of the eucharistic host in the monstrance and the blessing of the people with it. Christianity From the earliest church, Christians adopted ceremonial benedictions into their liturgical worship, particularly at the end of a service. Such benedictions have been regularly practiced both in the Christian East and West. Among the benedictions of the Roman Catholic Church, include thApostolic Benedictionmade by the Pope and his delegates, and th"last blessing"of the dying. The Anglican Church retained the principle of benediction after the Protestant Reformation, and as a result, the benediction or blessing ends most Anglican, as well as Methodist, services of worship. A common form of benediction in Baptist and liturgical Protestant chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
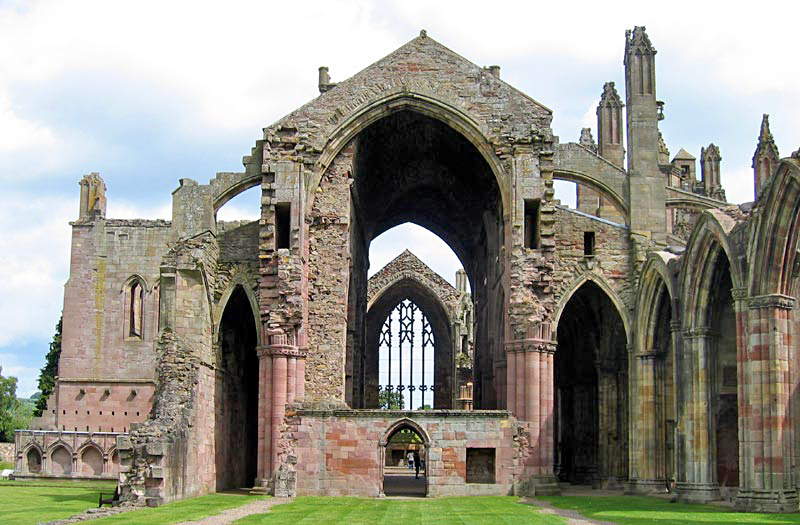
Abbot Of Melrose
The Abbot and then Commendator of Melrose was the head of the monastic community of Melrose Abbey, in Melrose in the Borders region of Scotland. The abbots of the earlier Northumbrian foundation from Lindisfarne are not included here. The second abbey was founded in 1136 on the patronage of David I (''Dabíd mac Maíl Choluim''), King of Scots, by Cistercian monks from Rievaulx Abbey, Yorkshire. Control of the abbey was secularized in the 16th century and after the accession of James Stewart, the abbey was held by commendators. The last commendator, James Douglas of Lochleven, resigned the abbacy to William Douglas, 6th Earl of Morton (his nephew) in December 1606, and the abbey itself to the king in 1608. The abbey (or most of its lands) was then erected into a secular lordship for viscount Haddington, John Ramsay, who in 1609 was created "Lord Melrose". Lochleven however resumed the title of commendator in 1613 until his death in 1620. List of Abbots * Richard, 1136-1148 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dowden
John Dowden /d͡ʒɒn ˈdaʊdən/ (29 June 1840 – 30 January 1910) was an Irish-born bishop and ecclesiastical historian. He served in the Scottish Episcopal Church as the Bishop of Edinburgh. Life He was born in Cork on 29 June 1840, as the fifth of five children of John Wheeler Dowden and Alicia Bennett. His famous brother was the poet, professor and literary critic Edward Dowden. Although his father was Presbyterian, John followed his mother by becoming an Anglican, although he attended both churches in his youth. When he was sixteen he became a student at Queen's College, Cork as a medical student. John began encountering health problems, problems which made it difficult to pursue his original career. In 1858, while contemplating a religious career, he enrolled at Trinity College Dublin. He graduated in 1864 and was ordained as a deacon, moving to Sligo. In the same year he married, wedding a woman named Louisa Jones, by whom he would eventually father six children. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Dunkeld
The Bishop of Dunkeld is the ecclesiastical head of the Diocese of Dunkeld, one of the largest and more important of Scotland's 13 medieval bishoprics, whose first recorded bishop is an early 12th-century cleric named Cormac. However, the first known abbot dates to the 10th century, and it is often assumed that in Scotland in the period before the 12th century, the roles of both bishop and abbot were one and the same. The Bishopric of Dunkeld ceased to exist as a Catholic institution after the Scottish Reformation but continued as a royal institution into the 17th century. The diocese was restored (with a different boundary) by Pope Leo XIII on 4 March 1878; it is now based in the city of Dundee. List of known abbots Dunkeld Abbey was an offshoot of Iona, perhaps founded in the early 9th century, in the reign of Caustantín mac Fergusa, King of the Picts. It is not clear when its abbots got independence from the Abbots of Iona, but a notable event is the alleged transfer of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew The Scot
Matthew the Scot (died 1229) was a 13th-century Scottish cleric. Biography Matthew had been the Chancellor of Scotland in the late reign of king Alexander II of Scotland. He was appointed in 1227 after the death of Thomas, Archdeacon of Lothian. His name indicates that he was a Gael The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languag ... or had some personal connection with Gaeldom, but we do not know anything else about his background, other than perhaps the fact that he supposedly had some kind of defect of birth. Matthew was postulated to the see of Aberdeen, before in turn being postulated to the higher-ranking See of Dunkeld. He was not consecrated as bishop of Aberdeen, and probably died before being consecrated for Dunkeld. He died in 1229. References * Dowden, John, ''The Bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Births
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |