|
Hua Xin
Hua Xin (158 – 30 January 232), courtesy name Ziyu, was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. He initially served directly under the central government of the Eastern Han dynasty. Later, he served under the warlord Sun Ce and then under the warlord Cao Cao. He continued to serve in the Cao Wei state during the Three Kingdoms period. Biography As a clerk in Gaotang County, Hua Xin was nominated as xiaolian, and appointed as Langzhong (郎中). In 187, Hua was appointed as Shangshu Lang (尚书郎). When Dong Zhuo evacuated the court from Luoyang to Chang'an, Hua requested a position as the administrator of Shanggui County (上邽) . He encountered Yuan Shu's army en route and was accepted to the latter's court. However, Hua left after his advice for Yuan to attack Dong Zhuo was dismissed. In 192, Hua was appointed as the administrator of Yuzhang (豫章) Commandery. After Liu Yao, governor of Yang Province died, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Ducal Ministers
The Three Ducal Ministers (), also translated as the Three Dukes, Three Excellencies, or the Three Lords, was the collective name for the three highest officials in Ancient China and Imperial China. These posts were abolished by Cao Cao in 208 AD and replaced with the position of Grand Chancellor. Overview Each minister was responsible for different areas of government, but the boundaries were often blurred. Together, the Three Ducal Ministers were the emperor's closest advisors. Toward the end of a dynasty, the positions were often sold to men of wealth to raise state revenue. Starting in the late Shang dynasty and Zhou dynasty, the top three were: * Grand Preceptor (); * Grand Tutor (); * Grand Protector (). During the Western Han dynasty, the three positions were: * Chancellor () * Grand Secretary (); * Grand Commandant (). In the Eastern Han dynasty, the names of the Three Ducal Ministers were changed to: * Minister of War (); * Minister of the Masses (); * Minister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy Name
A courtesy name (), also known as a style name, is a name bestowed upon one at adulthood in addition to one's given name. This practice is a tradition in the East Asian cultural sphere, including China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.Ulrich TheobaldNames of Persons and Titles of Rulers/ref> A courtesy name is not to be confused with an art name, another frequently mentioned term for an alternative name in East Asia, which is closer to the concept of a pen name or a pseudonym. Usage A courtesy name is a name traditionally given to Chinese men at the age of 20 ''sui'', marking their coming of age. It was sometimes given to women, usually upon marriage. The practice is no longer common in modern Chinese society. According to the ''Book of Rites'', after a man reached adulthood, it was disrespectful for others of the same generation to address him by his given name. Thus, the given name was reserved for oneself and one's elders, whereas the courtesy name would be used by adults of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Province
Yangzhou, Yangchow or Yang Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China mentioned in historical texts such as the ''Tribute of Yu'', ''Erya'' and ''Rites of Zhou''. Name There are four different theories regarding the origin of the name "Yangzhou": * Yangzhou's etymological root is related to trees. The ''Chunqiu Yuan Ming Bao'' recorded, "The soil is damp and moist, poplars and willows thrive there, that is how the name originated." Shen Kuo (1031–1095) wrote that "Yangzhou is suitable for poplars (楊; ''yang'') and Jingzhou is suitable for brambles (荊; ''jing'')." Li Dou (fl. 18th century) wrote that "Yangzhou is suitable for poplars (楊; ''yang'') and those growing on dykes are even larger. There is one (poplar tree) every five steps and two every ten steps, in pairs and threes they stand in gardens." Yangzhou is also sometimes written in Chinese as 楊州 instead of 揚州; 楊 means "poplar". * The origin of the name "Yangzhou" has something to do with wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
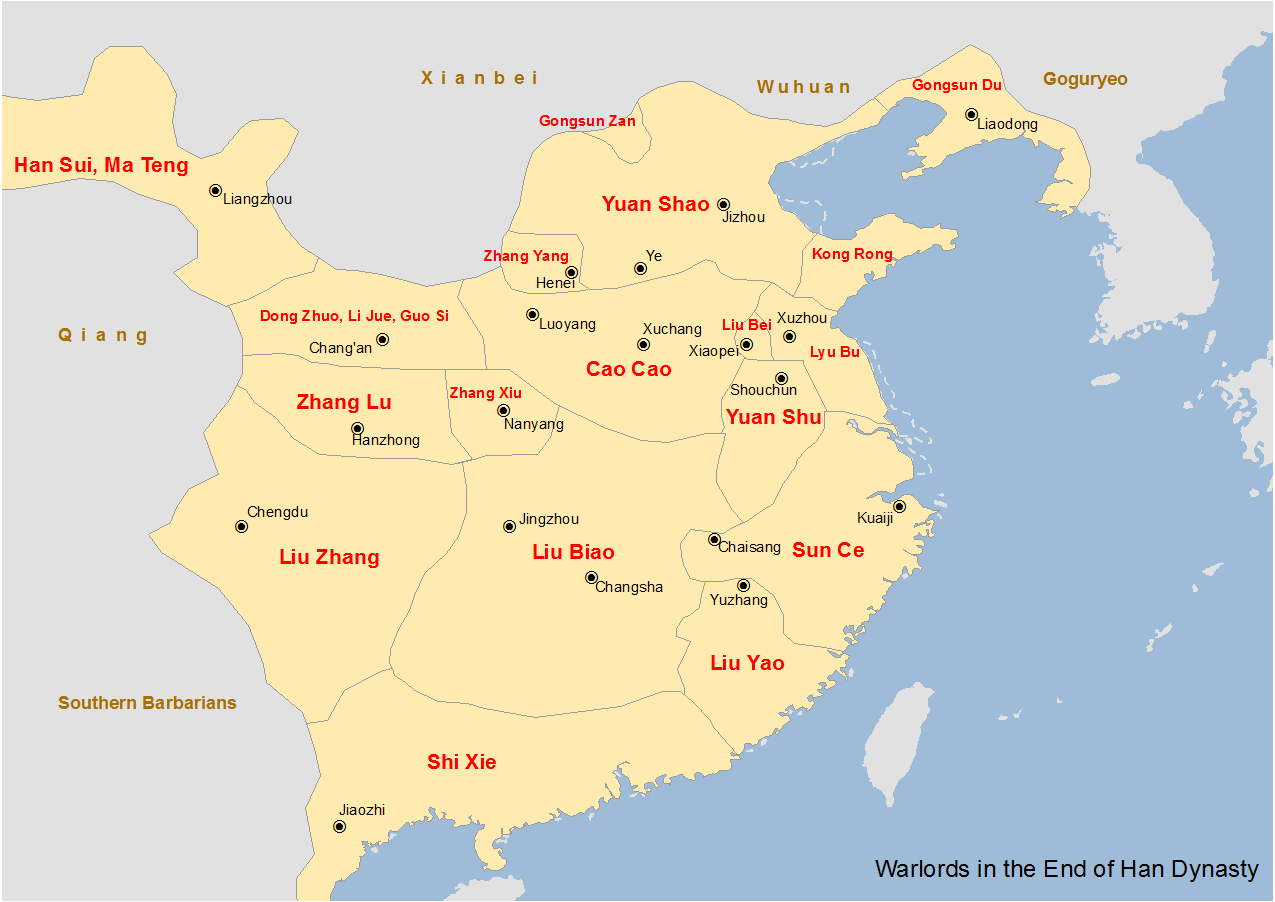
Liu Yao (warlord)
Liu Yao (157–198), courtesy name Zhengli, was a Chinese politician and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was a descendant of Liu Fei, the eldest son of the Han dynasty's founding emperor, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao). When he was 18, he became famous after rescuing a relative who was being held hostage by bandits. He started his career in the Han civil service after being nominated as a ''xiaolian'', and was known for his incorruptibility. In 194, although he was appointed by the Han imperial court as the governor of Yang Province, he barely managed to gain a foothold over his jurisdiction because the warlord Yuan Shu controlled a large part of the territories around the Huai River region in Yang Province. In 195, conflict broke out between Liu Yao and Yuan Shu, who sent his ally Sun Ce to attack Liu Yao. Sun Ce defeated Liu Yao and forced him to retreat south into present-day Jiangxi, where Liu Yao defeated a minor warlord Ze Rong and died of illn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Shu
Yuan Shu () (died July or August 199), courtesy name Gonglu, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. He rose to prominence following the collapse of the Han central government in 189. He declared himself Emperor of China in 197 under the short-lived Zhong dynasty, two years before his death in 199. Life Early life Yuan Shu was from Ruyang County (), Runan Commandery, which is in present-day Shangshui County, Henan. His family had for over four generations been a prominent force in the Han civil service, having produced numerous members in high positions since the first century CE. Descended from Yuan An, who served during the reign of Emperor Zhang, Yuan Shu was a son of the Minister of Works Yuan Feng () and his principal wife. Yuan Shu is sometimes described to be a younger cousin(绍之从弟也) ''Sanguozhi'' vol. 6. of the warlord Yuan Shao, but was actually Yuan Shao's younger half-brother. As a young man h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianshui
Tianshui is the second-largest cities in Gansu, city in Gansu list of Chinese provinces, Province, China. The city is located in the southeast of the province, along the upper reaches of the Wei River and at the boundary of the Loess Plateau and the Qinling, Qinling Mountains. As of the 2020 census, its population was 2,984,659 inhabitants, of which 1,212,791 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of the 2 urban districts of Qinzhou and Maiji District, Maiji. The city and its surroundings have played an important role in the early history of China, as still visible in the form of historic sites such as the Maijishan Grottoes. History state of Qin, Qin, whose House of Ying were the Qin dynasty, founding dynasty of the Early Imperial China, Chinese empire, developed from Quanqiu (present-day Li County, Gansu, Lixian) to the south. After the invasions of the Xirong, Rong which unseated the Western Zhou dynasty, Western Zhou, Qin recovered the territory of Tianshui from the nomad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin Shi Huang of the Qin dynasty, China's first emperor, held his imperial court, and constructed his massive mausoleum guarded by the Terracotta Army. From its capital at Xianyang, the Qin dynasty ruled a larger area than either of the preceding dynasties. The imperial city of Chang'an during the Han dynasty was located northwest of today's Xi'an. During the Tang dynasty, the area that came to be known as Chang'an included the area inside the Ming Xi'an fortification, plus some small areas to its east and west, and a substantial part of its southern suburbs. Thus, Tang Chang'an was eight times the size of the Ming Xi'an, which was reconstructed upon the site of the former imperial quarters of the Sui and Tang city. During its heyday, Chang'an w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. Situated on the Central Plain (China), central plain of China, Luoyang is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China and one of the History of China#Ancient China, cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earliest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dong Zhuo
Dong Zhuo () (died 22 May 192), courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minister of the imperial government. Yet he forced the young Emperor Shao of Han to abdicate and replaced him with his half-brother Emperor Xian of Han while he sought to become the de facto ruler of China in the boy-emperor's name. The Eastern Han dynasty regime survived in name only. Dong Zhuo seized control of the imperial capital Luoyang in 189 when it entered a state of turmoil following the death of Emperor Ling of Han and a massacre of the eunuch faction by the court officials led by General-in-Chief He Jin. Dong Zhuo subsequently deposed Liu Bian (Emperor Shao) and replaced him with his half-brother, the puppet Emperor Xian of Han. Dong Zhuo's rule was brief and characterized by cruelty and tyranny. In the following year, a coalition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaolian
Xiaolian (; literally "filial and incorrupt"), was the standard of nominating civil officers started by Emperor Wu of Han in 134 BC. It lasted until its replacement by the imperial examination system during the Sui Dynasty. In Confucian philosophy, filial piety is a virtue of respect for one's parents and ancestors. onfucianism in Context Classic Philosophy and Contemporary Issues, East Asia and Beyond/ref> Under the advice of Dong Zhongshu, Emperor Wu ordered each commandery to recommend one filial and one incorrupt candidate for civil offices. Later the nomination became proportional; Emperor He of Han changed the proportion to one candidate for every 200,000 residents, and one for every 100,000 residents in ethnic minority regions. The nominator was also responsible if the nominee was charged with corruption, and could be punished if he refused to nominate qualified individuals. After the Han dynasty, high positions were usually nominated according to the Nine-rank system, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaotang County
Gaotang County () is a county of northwestern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is administered by Liaocheng City. The population was in 2010 (2010 Census). Administrative divisions As 2012, this county is divided to 3 subdistricts, 6 towns and 3 townships. ;Subdistricts *Yuqiuhu Subdistrict () *Huili Subdistrict () * Renhe Subdistrict () ;Towns ;Townships *Yangtun Township () *Zhaozhaizi Township () *Jiangdian Township () Climate References External links *Official homepage {{County-level divisions of Shandong Gaotang Gaotang County () is a county of northwestern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is administered by Liaocheng City. The population was in 2010 (2010 Census). Administrative divisions As 2012, this county is divided to 3 subdis ... Liaocheng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < : *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter |



.jpg)