|
Hryhory Bazhul
Hryhory Ivanovych Bazhul ( uk, Григорій Іванович Бажул transcribed as Georg Baschul) Note: Name was transcribed via German on Australian Government documents. (January 22, 1906 — October 17, 1989) was a Ukrainian bandurist and publisher of articles on bandura history from Poltava, Russian Empire.http://histpol.pl.ua/pages/content.php?page=1261 After World War II he emigrated to Australia settling in Sydney. Early life Hryhory Ivanovych Bazhul was born in the Poltava Governorate of the Russian Empire (in present-day Ukraine), his father was a rail road engineer and his family moved to Kharkiv in 1911. After completing his studies at the Institute of Grain Culture, he was employed as an agronomist.Dibrivny, I. "Григорій І. Бажул (некролог)", ''Вільна Думка'', Sydney, Australia, 12.ХІ.89 In the late 1920s he was arrested and spent 2 years of penal labour at the Berdyansk agricultural labour colony. On his return to Khar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkiv-style Bandura
Kharkiv-style banduras are banduras that allow for the playing of the Kharkiv style, i.e. using the left hand to play melodic figures primarily over the side of the instrument as opposed to the Kyiv style where the left hand primarily plays the basses. To allow for the added required dexterity of the left hand, the instrument is held parallel to the body of the player. These instruments are in comparison quite rare because they are all individually crafted primarily made by craftsmen outside of Ukraine. In recent times, they have become quite sought after in Ukraine. They are strung either diatonically (with 31–36 strings) (8 basses and 23 prystrunky) or chromatically (with 61–65 strings). Early instruments The first standard Kharkiv bandura was designed and manufactured in 1926. This instrument was based on the Starosvitska bandura used by Hnat Khotkevych and was modified somewhat by Leonid Haydamaka. It was intended for use by the bandura students of Hnat Khotkevych at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinoviy Shtokalko
Zinoviy Shtokalko (25 May 1920 – 28 June 1968). Amongst the more renowned performers of bandura art, one of the prominent is that of bandurist virtuoso Zinoviy Shtokalko. Biography Shtokalko was born 25 May 1920 in the West Ukrainian town of Berezhany, the son of a priest. As a youth he showed a great interest in music and folk songs. His family had a bandura which his father rev. Pavlo Shtokalko had purchased in 1925 in Prague. Shtokalko initially took private bandura lessons from Yukhym Klevchutsky, and later, during his studies in Lviv took lessons from the Galician bandurist Yuri Singalevych, and during the war was strongly influenced by Kharkiv bandurists Hryhory Bazhul and Leonid Haydamaka. Shtokalko consistently collected the smallest snippets of information about the bandura and the kobzari and was able to include them in his performances. He consistently worked on collecting and studying everything associated with the bandura and the development of bandura te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
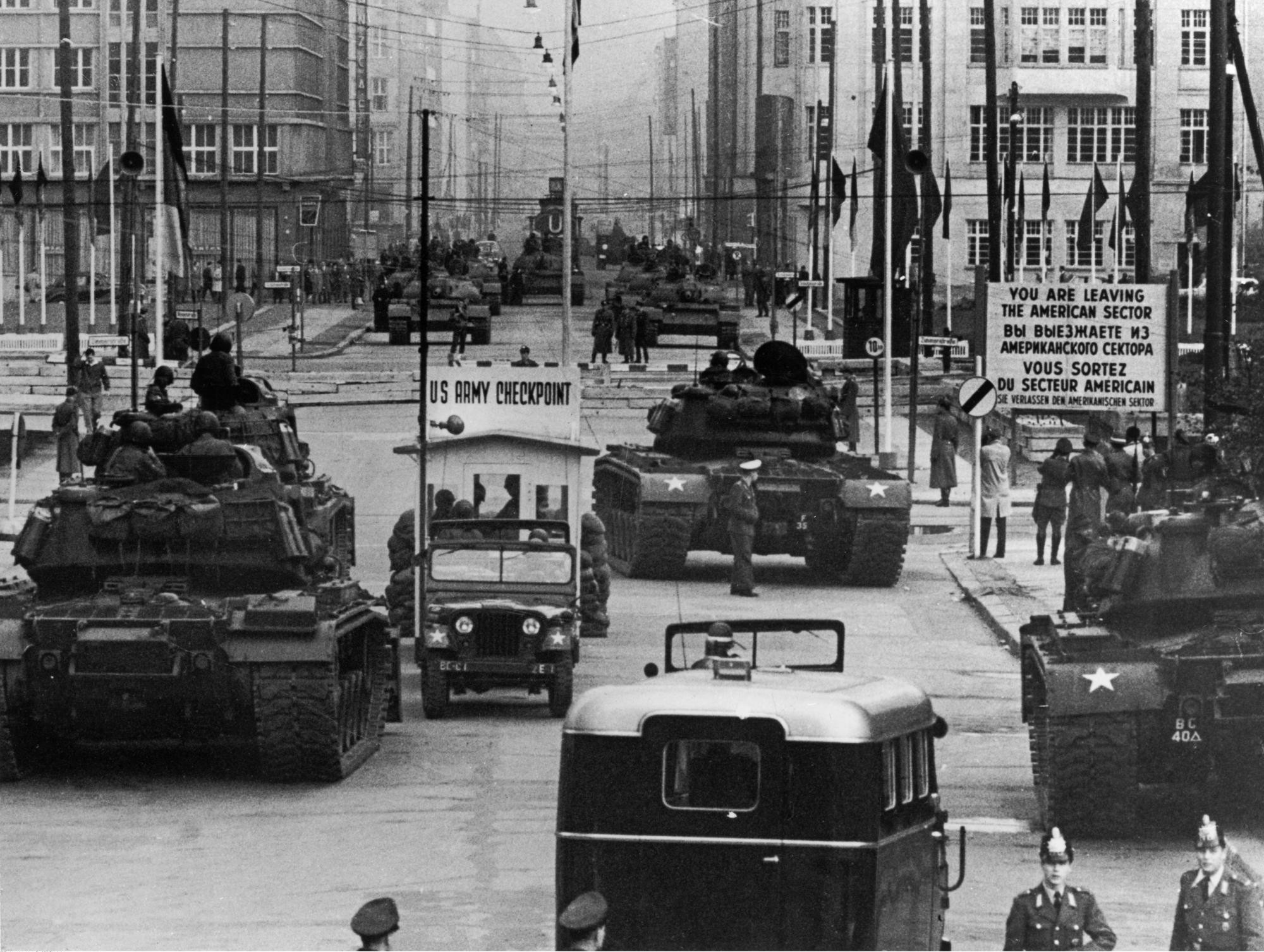
Soviet Army
uk, Радянська армія , image = File:Communist star with golden border and red rims.svg , alt = , caption = Emblem of the Soviet Army , start_date = 25 February 1946 , country = (1946–1991)' (1991–1992) , branch = , type = Army , role = Ground warfare, Land warfare , size = 3,668,075 active (1991) 4,129,506 reserve (1991) , command_structure = , garrison = , garrison_label = , nickname = "Red Army" , patron = , motto = ''За нашу Советскую Родину!(Za nashu Sovetskuyu Rodinu!)''"For our Soviet Motherland!" , colors = Red and yellow , colors_label = , march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandurist Capella
A banduryst ( uk, бандури́ст) is a person who plays the Ukrainian plucked string instrument known as the bandura. Types of performers There are a number of different types of bandurist who differ in their particular choice of instrument, the specific repertoire they play and manner in which they approach their vocation. *Kobzari, who play authentic ethnographic instruments or copies. This group can also be further categorized into ''authentic'', ''reproduction'', and ''stage'' performers. *Academic players, playing more sophisticated contemporary concert banduras. These performers have a tertiary education majoring in bandura performance and typically perform works by Western classical composers in addition to, or instead of, Ukrainian folk music. This category can be further divided into instrumentalists (who only perform instrumental works) and vocalists (who primarily use the bandura to accompany their voice). The most common academic bandurists play in the Kiev acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Occupation Of Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.Kharkiv "never had eastern-western conflicts" '''' (23 October 2014) Located in the northeast of the country, it is the largest city of the historic region. Kharkiv is the of < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union. Established in 1917 as NKVD of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, the agency was originally tasked with conducting regular police work and overseeing the country's prisons and labor camps. It was disbanded in 1930, with its functions being dispersed among other agencies, only to be reinstated as an all-union commissariat in 1934. The functions of the OGPU (the secret police organization) were transferred to the NKVD around the year 1930, giving it a monopoly over law enforcement activities that lasted until the end of World War II. During this period, the NKVD included both ordinary public order activities, and secret police activities. The NKVD is known for its role in political repression and for carrying out the Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tayshet
Tayshet ( rus, Тайшет, p=tɐjˈʂɛt, lit. ''cold river'' in the Kott language) is a town and the administrative center of Tayshetsky District in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, located northwest of Irkutsk, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: History It was founded in 1897 as a supply point and station on the Trans-Siberian Railway and was granted town status in 1938. During the 1930s–1950s, Tayshet was the center of administration for gulag labor camps Ozerlag and Angarstroy. Construction of the first section of the Baikal–Amur Mainline started in 1937 and was managed from here. According to some survivor accounts, between Tayshet and Bratsk there is "a dead man under every sleeper." Along with Japanese prisoners from the Kwantung Army, German prisoners of war formed a large proportion of the forced labor contingent, generally under a 25-year sentence, such as Dietrich von Saucken. Surviving German POWs were repatriated in autumn of 1955, after West German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically been considered as a natural barrier between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Mount Elbrus in Russia, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands, part of which is in Turkey. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is occupied by several independent states, mostly by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western and Eastern. Siberia stretches southwards from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of north-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
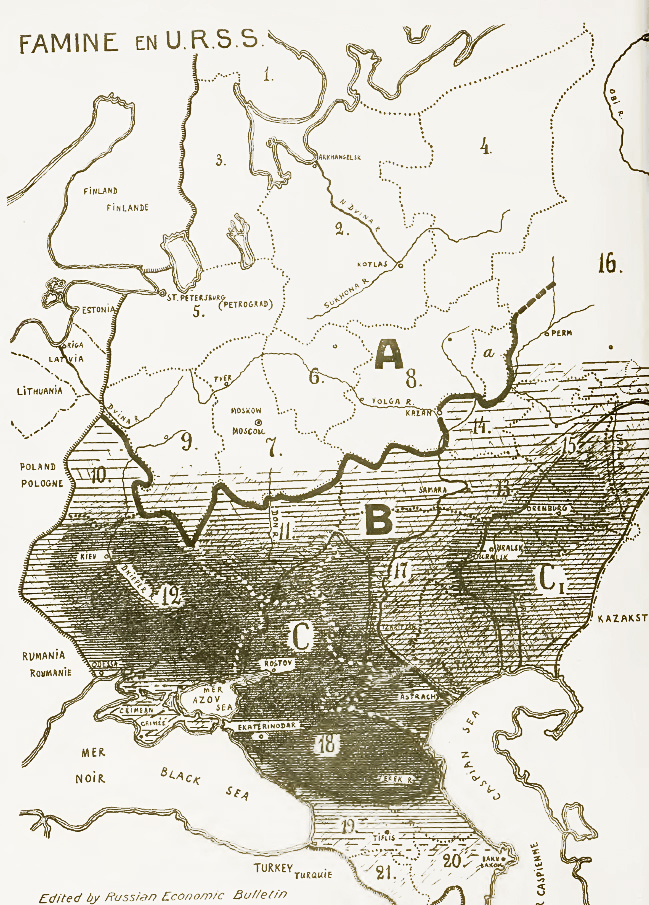
Holodomor
The Holodomor ( uk, Голодомо́р, Holodomor, ; derived from uk, морити голодом, lit=to kill by starvation, translit=moryty holodom, label=none), also known as the Terror-Famine or the Great Famine, was a man-made famine in Soviet Ukraine from 1932 to 1933 that killed millions of Ukrainians. The Holodomor was part of the wider Soviet famine of 1932–1933 which affected the major grain-producing areas of the Soviet Union. While scholars universally agree that the cause of the famine was man-made, whether the Holodomor constitutes a genocide remains in dispute. Some historians conclude that the famine was planned and exacerbated by Joseph Stalin in order to eliminate a Ukrainian independence movement. This conclusion is supported by Raphael Lemkin. Others suggest that the famine arose because of rapid Soviet industrialisation and collectivization of agriculture. Ukraine was one of the largest grain-producing states in the USSR and was subject to unre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
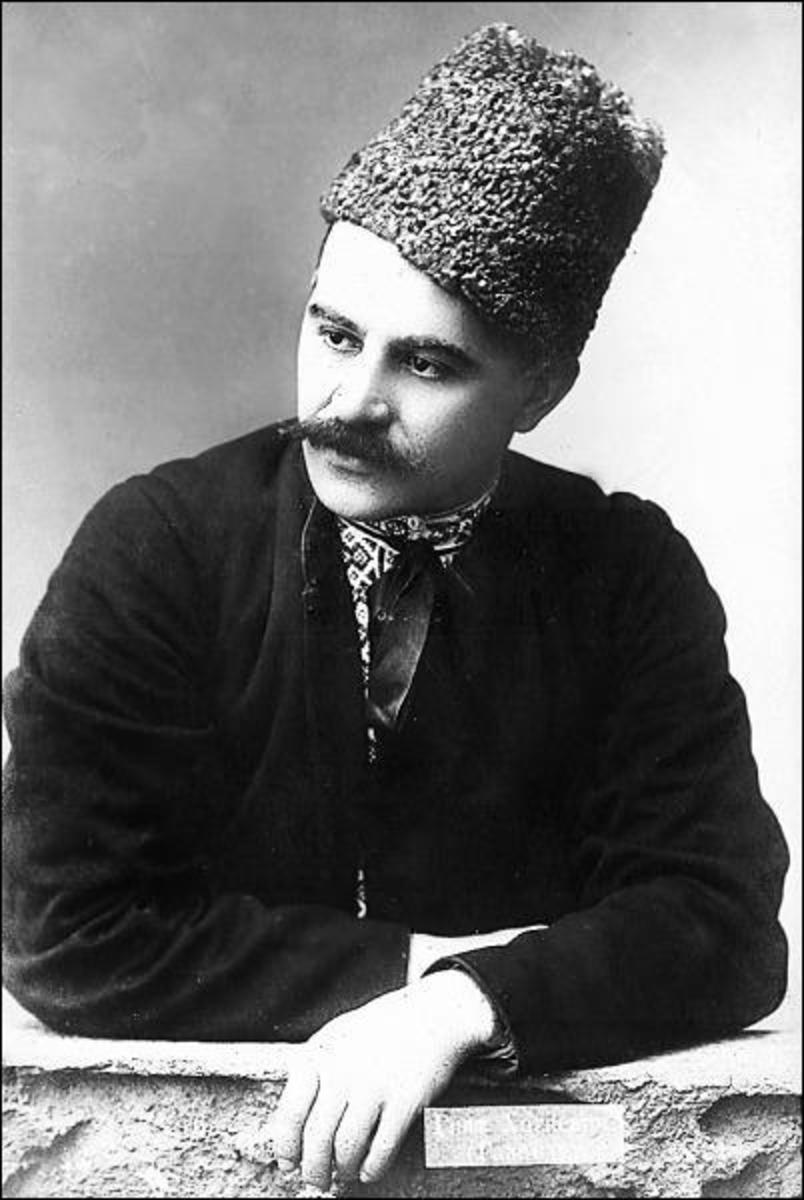
Hnat Khotkevych
Hnat Martynovych Khotkevych ( uk, Гнат Мартинович Хоткевич, also ''Gnat Khotkevich'' or ''Hnat Khotkevych'', born December 31, 1877 – died October 8, 1938) was a Ukrainian writer, ethnographer, playwright, composer, musicologist, and bandurist. Khotkevych was a renaissance man and was multi-talented. Although he was trained as a professional engineer, he is known more as a prolific Ukrainian literary figure, and also as a dramatist, composer and ethnographer, and father of the modern bandura. Early life and education Khotkevych was born in Kharkiv in 1877. His mother was a domestic worker, though little is known about his father, who left the family in the mid-1880s. As a youth he learned to play the piano and violin and later learned to play the bandura through observing the blind folk kobzars of the region. He completed his tertiary studies in engineering at the Kharkiv Polytechnic Institute in 1900, and then worked as a railway engineer. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |