|
House Of The Centenary
The House of the Centenary (Italian ''Casa del Centenario'', also known as the House of the Centenarian) was the house of a wealthy resident of Pompeii, preserved by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The house was discovered in 1879, and was given its modern name to mark the 18th centenary of the disaster. Built in the mid-2nd century BC, it is among the largest houses in the city, with private baths, a nymphaeum, a fish pond ''(piscina)'', and two atria. The Centenary underwent a remodeling around 15 AD, at which time the bath complex and swimming pool were added. In the last years before the eruption, several rooms had been extensively redecorated with a number of paintings. Although the identity of the house's owner eludes certainty, arguments have been made for either Aulus Rustius Verus or Tiberius Claudius Verus, both local politicians. Among the varied paintings preserved in the House of the Centenary is the earliest known depiction of Vesuvius, as well as explicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii - Casa Del Centenario - MAN
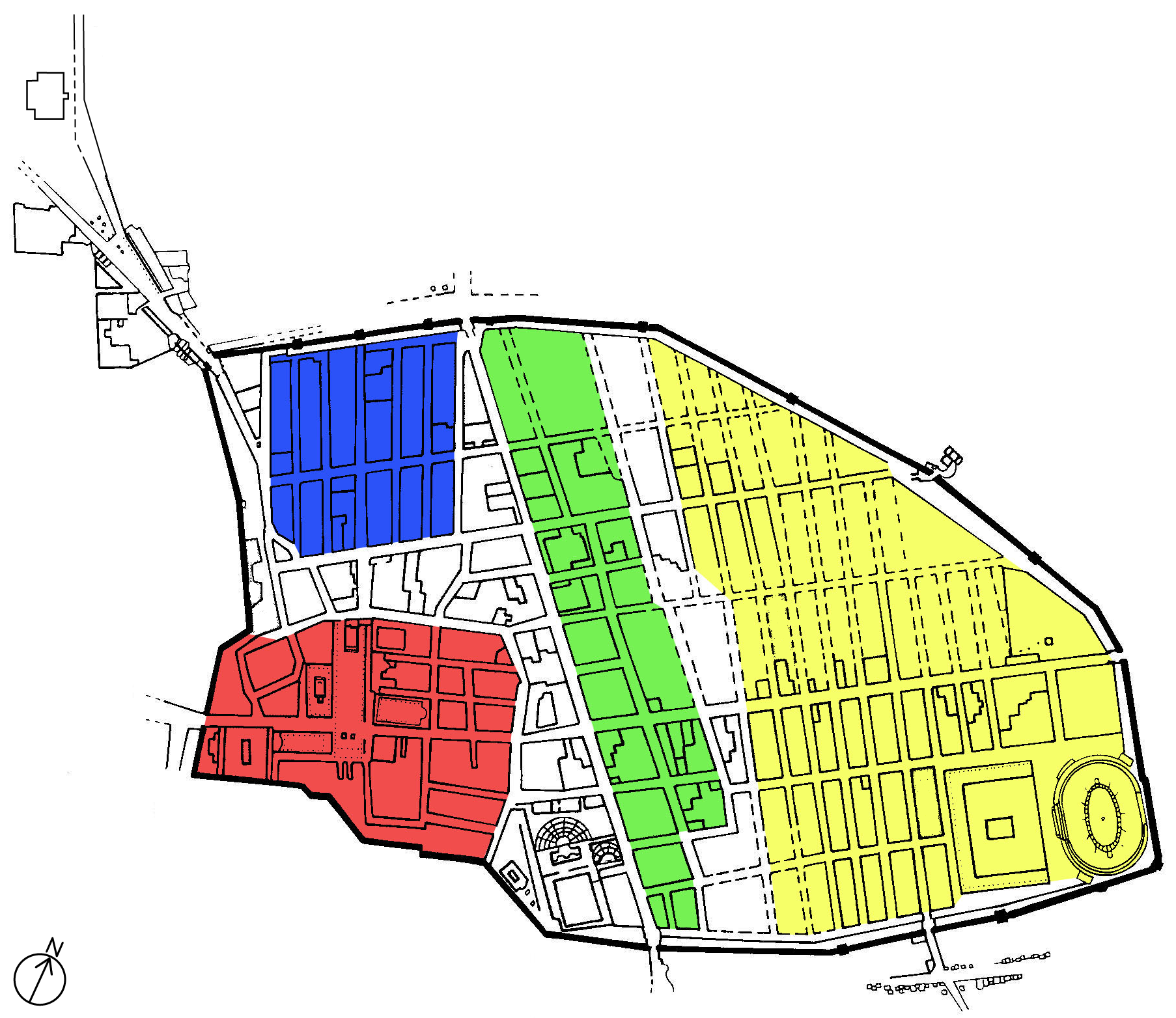
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Villa Boscoreale, Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offered a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost in the excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and 103, during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. In these short, witty poems he cheerfully satirises city life and the scandalous activities of his acquaintances, and romanticises his provincial upbringing. He wrote a total of 1,561 epigrams, of which 1,235 are in elegiac couplets. Martial has been called the greatest Latin epigrammatist, and is considered the creator of the modern epigram. Early life Knowledge of his origins and early life are derived almost entirely from his works, which can be more or less dated according to the well-known events to which they refer. In Book X of his ''Epigrams'', composed between 95 and 98, he mentions celebrating his fifty-seventh birthday; hence he was born during March 38, 39, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphinx
A sphinx ( , grc, σφίγξ , Boeotian: , plural sphinxes or sphinges) is a mythical creature with the head of a human, the body of a lion, and the wings of a falcon. In Greek tradition, the sphinx has the head of a woman, the haunches of a lion, and the wings of a bird. She is mythicized as treacherous and merciless, and will kill and eat those who cannot answer her riddle. This deadly version of a sphinx appears in the myth and drama of Oedipus. Unlike the Greek sphinx, which was a woman, the Egyptian sphinx is typically shown as a man (an androsphinx ( grc, ανδρόσφιγξ)). In addition, the Egyptian sphinx was viewed as benevolent but having a ferocious strength similar to the malevolent Greek version. Both were thought of as guardians and often flank the entrances to temples. In European decorative art, the sphinx enjoyed a major revival during the Renaissance. Later, the sphinx image, initially very similar to the original Ancient Egyptian concept, was exported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balustrade
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its construction are wood, stone, and less frequently metal and ceramic. A group of balusters supporting a handrail, coping, or ornamental detail are known as a balustrade. The term baluster shaft is used to describe forms such as a candlestick, upright furniture support, and the stem of a brass chandelier. The term banister (also bannister) refers to a baluster or to the system of balusters and handrail of a stairway. It may be used to include its supporting structures, such as a supporting newel post. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', "baluster" is derived through the french: balustre, from it, balaustro, from ''balaustra'', "pomegranate flower" rom a resemblance to the swelling form of the half-open flower (''illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions. Typology and distribution Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas near Rome: the ''villa urbana'', a country seat that could easily be reached from Rome (or another city) for a night or two; and the ''villa rustica'', the farmhouse estate permanently occupied by the servants who generally had charge of the estate. The Roman Empire contained many kinds of villas, not all of them lavishly appointed with mosaic floors and frescoes. In the provinces, any country house with some decorative features in the Roman style may be called a "villa" by modern scholars. Some were pleasure houses, like Hadrian's Villa at Tivoli, that were sited in the cool hills within easy reach of Rome or, like the Villa of the Papyri at Herculaneum, on picturesque sites overlooking the Bay of Naples. Some villas were more like the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeian Styles
The Pompeian Styles are four periods which are distinguished in ancient Roman mural painting. They were originally delineated and described by the German archaeologist August Mau (1840–1909) from the excavation of wall paintings at Pompeii, which is one of the largest group of surviving examples of Roman frescoes. The wall painting styles have allowed art historians to delineate the various phases of interior decoration in the centuries leading up to the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, which both destroyed the city and preserved the paintings, and between stylistic shifts in Roman art during late Republican and Augustan periods. In the succession of styles, there is a reiteration of stylistic themes. The paintings also tell a great deal about the prosperity of the area and specific tastes during the times. The main purpose of these frescoes was to reduce the claustrophobic interiors of Roman rooms, which were windowless and dark. The paintings, full of color and life, br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii - Casa Del Centenario - Nymphaeum
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offered a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost in the excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found could be used as moulds to make plaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubiculum
A ''cubiculum'' (plural ''cubicula'') was a private room in a ''domus'', an ancient Roman house occupied by a high-status family. It usually led directly from the ''atrium'', but in later periods it was sometimes adjacent to the ''peristyle''. It was used for the functions of a modern bedroom, sleep and sex, as well as for business meetings, the reception of important guests and the display of the most highly prized works of art in the house. The ''cubiculum'' was used for quiet or secret meetings and could have been used as a library. It was also a preferred venue for murder and suicide. A room used only for sleeping was not classed as a ''cubiculum''. The private nature of the ''cubiculum'' made it a place for contemplation and religious observance, especially when illicit. According to the ''Actus Silvestri'', Constantine the Great first learned of Christianity in his ''cubiculum'' and fasted there for a week before his first confession and baptism Baptism (from grc-x- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taberna
A ''taberna'' (plural ''tabernae'') was a type of shop or stall in Ancient Rome. Originally meaning a single-room shop for the sale of goods and services, ''tabernae'' were often incorporated into domestic dwellings on the ground level flanking the fauces, the main entrance to a home, but with one side open to the street. As the Roman Empire became more prosperous, tabernae were established within great indoor markets and were often covered by a barrel vault. Each taberna within a market had a window above it to let light into a wooden attic for storage and had a wide doorway. A famous example of such an indoor market is the Markets of Trajan in Rome, built in the early 1st century by Apollodorus of Damascus. According to the ''Cambridge Ancient History'', a taberna was a "retail unit" within the Roman Empire and was where many economic activities and many service industries were provided, including the sale of cooked food, wine, and bread. The plural form ''tabernae'' was al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostitution In Ancient Rome
Prostitution in ancient Rome was legal and licensed. In ancient Rome, even Roman men of the highest social status were free to engage prostitutes of either sex without incurring moral disapproval, as long as they demonstrated self-control and moderation in the frequency and enjoyment of sex. Brothels were considered a popular place of entertainment for Roman men, and it was undoubtedly a part of the culture of ancient Rome. At the same time, the prostitutes themselves were considered shameful: most were either slaves or former slaves, or if free by birth relegated to the ''infames'', people utterly lacking in social standing and deprived of most protections accorded to citizens under Roman law, a status they shared with actors and gladiators, all of whom, however, exerted sexual allure. Some large brothels in the 4th century, when Rome was becoming officially Christianized, seem to have been counted as tourist attractions and were possibly state-owned. There were two types of sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of The Vettii
The House of the Vettii is a domus located in the Roman town Pompeii, which was preserved by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. The house is named for its owners, two successful freedmen: Aulus Vettius Conviva, an Augustalis, and Aulus Vettius Restitutus. Its careful excavation has preserved almost all of the wall frescos, which were completed following the earthquake of 62 AD, in the manner art historians term the Pompeiian Fourth Style. The House of Vetti is located in region VI, near the Vesuvian Gate, bordered by the Vicolo di Mercurio and the Vicolo dei Vettii. The house is one of the largest domus in Pompeii, spanning the entire southern section of block 15. The plan is fashioned in a typical Roman domus with the exception of a tablinum, which is not included. There are twelve mythological scenes across four cubiculum and one triclinium. Plan The plan of the House of the Vettii is commonly divided into five major sections: the large atrium, the small atrium, the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Junius Silanus (consul AD 15)
Marcus Junius C. f. M. n. Silanus (c. 26 BC – AD 37) Barrett (1989), p. 76 was an Ancient Roman senator who became suffect consul in AD 15. Barrett (1989), p. 32 His daughter Junia Claudilla was the first wife of Emperor Caligula. Biography Early life Marcus father was Gaius Junius Silanus who was the son of Marcus Junius Silanus the consul of 25 BC. Syme (1986), p.194–195 Marcus had two brothers Decimus Junius Silanus and Gaius Junius Silanus, and a sister named Junia Torquata. Decimus was banished for having an affair with Vipsania Julia during the reign of Augustus. Their mother may have been an Atia, daughter of Marcus Atius Balbus and Claudia. Balbus was the uncle of emperor Augustus. Syme (1986), p. 194 Political career Ancient historians considered Marcus Silanus a highly respected man. When Tiberius came to power, if a judicial decision made by Silanus was appealed to the emperor, Tiberius invariably rejected the appeal, trusting Silanus' decision, and Tiberi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






%2C_Pompeia_50-40_a.C..jpg)
