|
Hooke (surname) (1874–1968), English scholar of comparative religion
{{surname, Hooke ...
Hooke is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Hilda Mary Hooke (1898–1978), Canadian writer * John Hooke (1270–1275), Chancellor of the University of Cambridge * Luke Joseph Hooke (1716–1796), Irish theologian * Robert Hooke (1635–1703), English natural philosopher who discovered Hooke's law * S. H. Hooke __NOTOC__ Samuel Henry Hooke (January 21, 1874 – January 17, 1968) was an English scholar writing on comparative religion. He is known for his ''Bible in Basic English'' translation. He was born in Cirencester, Gloucestershire. He was educated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilda Mary Hooke
Hilda Mary Hooke (after marriage, Smith; 3 October 1898 – 1978) was an English-born Canadian writer of dramas, poetry, and prose. Her 1938 play, ''Here Will I Nest'' was adapted into Canada's first colour feature-length motion picture, ''Talbot of Canada'', for which she wrote the screenplay. Hooke died in 1978. Biography Hilda Mary Hooke was born at Odcombe, Somerset, England, 3 October 1898. Her parents were Oswald Edgar Smith and Louisa Elizth (Tapscott) Smith."Canada, Ontario Marriages, 1869-1927," database with images, FamilySearch (https://familysearch.org/ark:/61903/1:1:QKMR-SW7W : 8 March 2021), Richard Tapscott Smith and Hilda Mary Hooke, 26 Sep 1925; citing registration , London, Middlesex, Ontario, Canada, Archives of Ontario, Toronto; FHL microfilm 2,413,315. She came to Canada in 1902. For some years after her arrival, she was engaged in musical and dramatic work. Hooke was affiliated with the Little Theatre in London, Ontario, since the 1920s as producer, directo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luke Joseph Hooke
Luke Joseph Hooke (born Dublin in 1716; died in Saint Cloud, near Paris, 16 April 1796) was a controversial Irish theologian, representing in Paris the "Catholicism of the Enlightenment". The laws of civil society should be so designed, he argued, to enable individuals to conform, through their own free will, to the natural rights ordained by God. Biography Because of the Penal Laws which forbade Catholic education in Ireland, he was sent when young to Saint-Nicolas-du-Chardonnet, Paris, where he remained till he received the licentiate. He then entered the Sorbonne and graduated in 1736. In 1742 he was appointed to a chair of theology, and soon reportedly earned a high reputation for learning. On 18 November 1751, he presided at the defence of the thesis of Jean-Martin de Prades, which aroused violent protestations. Among other propositions, de Prades had advanced the notion that the origin of civil law is might, from which are derived all notions of just and of unjust, of goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that he built himself, the other scientist being Antoni van Leeuwenhoek in 1676. An impoverished scientific inquirer in young adulthood, he found wealth and esteem by performing over half of the architectural surveys after London's great fire of 1666. Hooke was also a member of the Royal Society and since 1662 was its curator of experiments. Hooke was also Professor of Geometry at Gresham College. As an assistant to physical scientist Robert Boyle, Hooke built the vacuum pumps used in Boyle's experiments on gas law, and himself conducted experiments. In 1673, Hooke built the earliest Gregorian telescope, and then he observed the rotations of the planets Mars and Jupiter. Hooke's 1665 book ''Micrographia'', in which he coined the term "cell", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
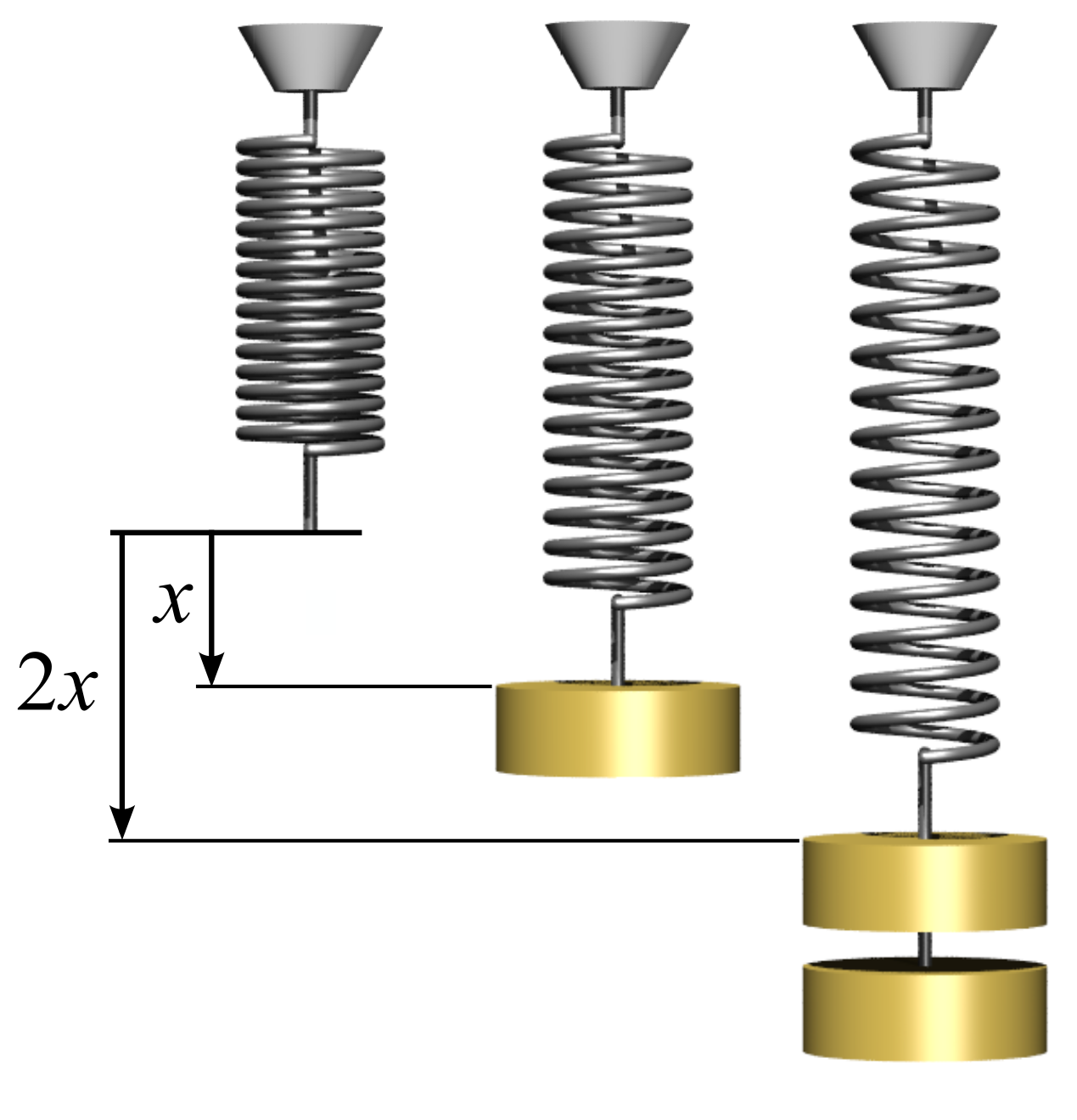
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |