|
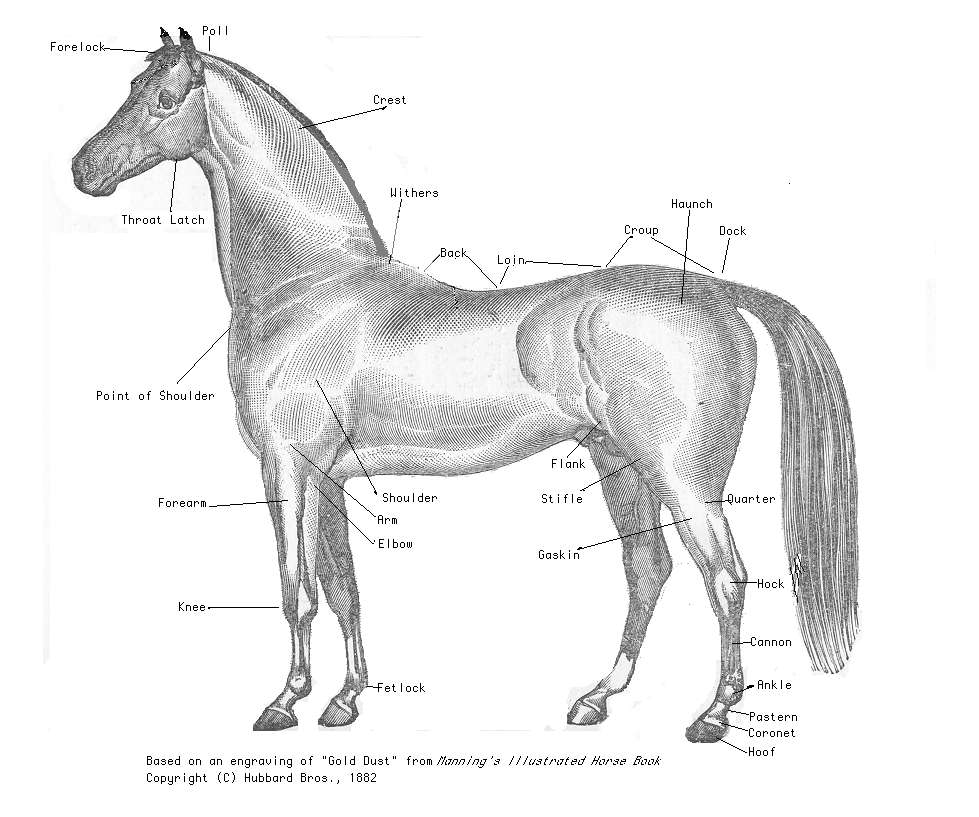
Hock (zoology)
The hock, or gambrel, is the joint between the tarsal bones and tibia of a digitigrade or unguligrade quadrupedal mammal, such as a horse, cat, or dog. This joint may include articulations between tarsal bones and the fibula in some species (such as cats), while in others the fibula has been greatly reduced and is only found as a vestigial remnant fused to the distal portion of the tibia (as in horses).{{citation needed, date=January 2016 It is the anatomical homologue of the ankle of the human foot. While homologous joints occur in other tetrapods, the term is generally restricted to mammals, particularly long-legged domesticated species. Horse Although the ''tarsus'' refers specifically to the bones and joints of the hock, most people working with horses refer to the ''hock'' in such a way to include the bones, joints, and soft tissue of the area. The hock is especially important in equine anatomy, due to the great strain it receives when the horse is worked. Jumping, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hock or Hock tide, an English holiday consisting of Hock Monday and Hock Tuesday
{{disambig ...
Hock may refer to: Common meanings: * Hock (wine), a type of wine * Hock (anatomy), part of an animal's leg * To leave an item with a pawnbroker People: * Hock (surname) * Richard "Hock" Walsh (1948-1999), Canadian blues singer Other uses: * A type of wine bottle used primarily for German or Alsatian wine See also * Hock Mountain, a summit in Washington state * Hocktide Hocktide, Hock tide or Hoke Day is a very old term used to denote the Monday and Tuesday in the second week after Easter. It was an English medieval festival; both the Tuesday and the preceding Monday were the Hock-days. Together with Whitsuntide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the lateral and medial malleoli) that articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of its surface area covered by articular cartilage. It is also unusual in that it has a retrograde blood supply, i.e. arterial blood enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-legged
Post-legged describes a condition in which the joints in an animal are not set correctly. When an animal is post-legged, the leg joints are far too straight, with almost no bend in the legs. Four-legged animals must have some bend in the hocks, otherwise the hooves would wear unevenly, and this may result in lameness, or at least a rougher gait. The animal will not stand squarely on the ground, and this also increases the possibility of injury to the animal. When an animal is post-legged, the animal will have a much higher risk of lameness, perhaps even permanent. This means the animal can hardly move at all, and results in an extremely stressed animal. This may also result in the animal not being able to move to food, and could be life-threatening. Also, since the animal is in such pain, it may be so stressed that it won't calve well, and it will not produce good quality milk, -or any milk at all- in a cow. Animals with a problem in their leg joints are recommended to be remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle-hocked
A sickle-hocked leg structure is one in which the back leg joints of an animal, usually a horse or other equine mammal, are set with too much angle, resulting in the hock also being excessively angled. This can result in uneven hoof wear, which is incredibly painful for the affected horse. If the leg joints are not set properly, there is a high chance that the back joints are also set incorrectly, resulting in a poorly conformed horse. Horses with sickle-hocks are at an increased risk of developing thoroughpin, curb and bog or bone spavins. Very severe cases of sickle-hocks can result in permanent lameness and may require euthanization to prevent further pain. However, many horses with sickle-hock are not affected to this degree, and may live a life with uneven wearing hooves. Corrective shoeing can help the horse's balance and strength. Horses with sickle-hocks should be monitored closely for signs of lameness, and if possible a veterinarian should be consulted before extensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Conformation
Equine conformation evaluates a horse's bone structure, musculature, and its body proportions in relation to each other. Undesirable conformation can limit the ability to perform a specific task. Although there are several faults with universal disadvantages, a horse's conformation is usually judged by what its intended use may be. Thus "form to function" is one of the first set of traits considered in judging conformation. A horse with poor form for a Grand Prix show jumper could have excellent conformation for a World Champion cutting horse, or to be a champion draft horse. Every horse has good and bad points of its conformation and many horses (including Olympic caliber horses) excel even with conformation faults. Conformation of the head and neck The standard of the ideal head varies dramatically from breed to breed based on a mixture of the role the horse is bred for and what breeders, owners and enthusiasts find appealing. Breed standards frequently cite large eyes, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stringhalt
Stringhalt is a sudden flexion of one or both hind legs in the horse, most easily seen while the horse is walking or trotting. It is most evident when the horse is backing up slowly, turning on the affected leg, or suddenly frightened. It can involve one or both hind legs of the horse. It is a spasmodic contraction of the lateral extensor tendons of the hind legs. There are four forms of stringhalt: *Australian stringhalt: a flatweed ('' Hypochaeris radicata'') is the suspected cause *Pseudostringhalt: the apparent result of a painful condition in the affected leg *Unilateral stringhalt: cause unknown, but often relieved by section of the lateral extensor tendon *Bilateral stringhalt: in two out of two affected horses necropsied, abnormal thalamus Treatment varies. Australian stringhalt Australian stringhalt was described and differentiated from classical stringhalt in 1884. Australian stringhalt is differentiated from classical stringhalt by the severity, occurrence of outbreaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curb (horse)
Curb is defined in older literature as enlargement secondary to inflammation and thickening of the long plantar ligament in horses.Stashak (1987) ''Adams' Lameness in Horses'', Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, pp. 715-718, However, with the widespread use of diagnostic ultrasonography in equine medicine, curb has been redefined as a collection of soft tissue injuries of the distal plantar hock region. Curb is a useful descriptive term when describing swelling in this area. Structures affected Besides swelling in the long plantar ligament, injury to the deep digital flexor tendon, superficial digital flexor tendon, tarsocrural lateral collateral ligament or peritendonous/periligamentous tissues in this region can contribute to the appearance of curb. Sickle-hocked conformation is a predisposing risk factor for the development of curb. (See hind leg conformation) Fluid accumulation and/or swelling are almost always found in the peritendonous/periligamentous tissues in curb, often wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Spavin
Bone spavin is a bony growth within the lower hock joint of horse or cattle. It is caused by osteoarthritis, and the degree of lameness that results can be serious enough to end a horse's competitive career. Description Bone spavin is osteoarthritis, or the final phase of degenerative joint disease (DJD), in the lower three hock joints. It usually affects the two lowest joints of the hock (the tarsometatarsal and the distal intertarsal joints), with the third joint, the proximal intertarsal, being the least likely to develop bone spavin. This condition has various types: jack spavin when lesion on the tarsal and carpal bones is large, and high spavin when the pathology occurs higher in the joint than is typical. Conversely, occult spavin does not produce any significant exostoses on the small tarsals, whilst bog spavin and blood spavin do not involve bony changes. Causes Cartilage compression Excessive compression can cause, over time, the cartilage between the upper and low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovium
The synovial membrane (also known as the synovial stratum, synovium or stratum synoviale) is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage-like synovial cells (type A) and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce hyaluronan, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid. Structure The synovial membrane is variable but often has two layers: * The outer layer, or subintima, can be of almost any type of connective tissue – fibrous (dense collagenous type), adipose (fatty; e.g. in intra-articular fat pads) or areolar (loose collagenous t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bog Spavin
Bog spavin is a swelling of the tibiotarsal joint of the horse's hock which, in itself, does not cause lameness. The joint becomes distended by excess synovial fluid and/or thickened synovial tissue bringing about a soft, fluctuant swelling on the front of the joint, as well as in the medial and lateral plantar pouches. Bog spavin is generally an indication of underlying pathology within the joint. Causes Bog spavin is a physical finding, and does not directly create lameness. Causes include synovitis (inflammation of the lining of the joint capsule), degenerative joint disease, or excessive strain of the joint capsule. In horses younger than the age of three, most cases of bog spavin are caused by a defect in the tibiotarsal joint, while in older, fully mature horses, it is most likely because of chronic strain of the joint capsule. Infection of the joint causes a severe synovitis, and should be treated as an emergency. Many horses with bog spavin will not be lame. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lameness (equine)
Lameness is an abnormal gait or stance of an animal that is the result of dysfunction of the locomotor system. In the horse, it is most commonly caused by pain, but can be due to neurologic or mechanical dysfunction. Lameness is a common veterinary problem in racehorses, sport horses, and pleasure horses. It is one of the most costly health problems for the equine industry, both monetarily for the cost of diagnosis and treatment, and for the cost of time off resulting in loss-of-use. Causes of lameness Lameness is most commonly caused by pain, but may also be the result of neuromuscular disease or mechanical restriction. Lameness itself is a clinical sign, and not a diagnosis. Pain Pain is the most common cause of lameness in the horse. It is usually the result of trauma or orthopedic disease, but other causes such as metabolic dysfunction, circulatory disease, and infection can also cause pain and subsequent lameness. Orthopedic causes of lameness are very common and may be the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blunt Trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound and bruise. Blunt trauma can result in contusions, abrasions, lacerations, internal hemorrhages, bone fractures, as well as death. Blunt trauma represents a significant cause of disability and death in people under the age of 35 years worldwide. Classification Blunt abdominal trauma Blunt abdominal trauma (BAT) represents 75% of all blunt trauma and is the most common example of this injury. 75% of BAT occurs in motor vehicle crashes, in which rapid deceleration may propel the driver into the steering wheel, dashboard, or seatbelt, causing contusions in less serious cases, or rupture of internal organs from briefly increased intraluminal pressure in the more serious, depending on the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_(14585578040).jpg)

_(14769128971).jpg)