|
History Of Poliomyelitis
The history of polio (poliomyelitis) infections began during prehistory. Although major polio epidemics were unknown before the 20th century, the disease has caused paralysis and death for much of human history. Over millennia, polio survived quietly as an endemic (epidemiology), endemic pathogen until the 1900s when major epidemics began to occur in Europe. Soon after, widespread epidemics appeared in the rest of the world. By 1910, frequent epidemics became regular events throughout the developed world primarily in cities during the summer months. At its peak in the 1940s and 1950s, polio would paralyze or kill over half a million people worldwide every year. The fear and the collective response to these epidemics would give rise to extraordinary public reaction and mobilization spurring the development of new methods to prevent and treat the disease and revolutionizing medical philanthropy. Although the development of two polio vaccines has Poliomyelitis eradication, eliminated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrospective Diagnosis
A retrospective diagnosis (also retrodiagnosis or posthumous diagnosis) is the practice of identifying an illness after the death of the patient (sometimes a historical figure) using modern knowledge, methods and disease classifications. Alternatively, it can be the more general attempt to give a modern name to an ancient and ill-defined scourge or plague. Historical research Retrospective diagnosis is practised by medical historians, general historians and the media with varying degrees of scholarship. At its worst it may become "little more than a game, with ill-defined rules and little academic credibility". The process often requires "translating between linguistic and conceptual worlds separated by several centuries", and assumes our modern disease concepts and categories are privileged. Crude attempts at retrospective diagnosis fail to be sensitive to historical context, may treat historical and religious records as scientific evidence, or ascribe pathology to behaviours tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram M
Hiram may refer to: People * Hiram (name) Places * Hiram, Georgia ** Hiram High School, Hiram, Georgia * Hiram, Maine * Hiram, Missouri * Hiram, Ohio ** Hiram College Hiram College ( ) is a private liberal arts college in Hiram, Ohio, United States. It was founded in 1850 as the Western Reserve Eclectic Institute by Amos Sutton Hayden and other members of the Disciples of Christ Church. The college is nonse ..., a private liberal arts college located in Hiram, Ohio *** Hiram Terriers, the school's sports teams * Hiram, Texas * Hiram, West Virginia * Hiram Township, Cass County, Minnesota Other uses * ''Hiram'' (TV series), a TV drama series in the Philippines * Hiram's Highway, a road in Hong Kong * Hiram House, one of the first settlement houses in the United States * Hiram Masonic Lodge No. 7, a gothic revival building in Franklin, Tennessee; also the oldest masonic lodge in Tennessee * Operation Hiram, a three-day military operation in the Upper Galilee laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been exposed to a communicable disease, yet do not have a confirmed medical diagnosis. It is distinct from medical isolation, in which those confirmed to be infected with a communicable disease are isolated from the healthy population. The concept of quarantine has been known since biblical times, and is known to have been practised through history in various places. Notable quarantines in modern history include the village of Eyam in 1665 during the bubonic plague outbreak in England; East Samoa during the 1918 flu pandemic; the Diphtheria outbreak during the 1925 serum run to Nome, the 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak, the SARS pandemic, the Ebola pandemic and extensive quarantines applied throughout the world during the COVID-19 pande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn, New York
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelve original counties established under English rule in 1683 in what was then the Province of New York. As of the 2020 United States census, the population stood at 2,736,074, making it the most populous of the five boroughs of New York City, and the most populous Administrative divisions of New York (state)#County, county in the state.Table 2: Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State - 2020 New York State Department of Health. Accessed January 2, 2024. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
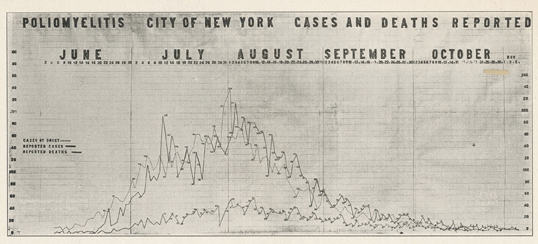
1916 Brooklyn Polio Epidemic
The 1916 New York City polio epidemic was an infectious disease epidemic of polio ultimately infecting several thousand people, and killing over two thousand, in New York City, primarily in the borough of Brooklyn. The epidemic was officially announced in June 1916, and a special field force was assembled under the authority of Dr. Simon R. Blatteis of the New York City Health Department's Bureau of Preventable Diseases, with broad authority to quarantine those infected with polio and institute hygiene measures thought to slow the transmission of the disease. Polio was a poorly understood disease in this era, and no polio vaccine existed at this time. Official efforts to stem its spread consisted primarily of quarantines, the closure of public places, and the use of chemical disinfectants to cleanse areas where the disease had been present. Special polio clinics were established at various locations in the city for the treatment and quarantine of patients. In addition, many info ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Rhodes
Richard Lee Rhodes (born July 4, 1937) is an American historian, journalist, and author of both fiction and nonfiction, including the Pulitzer Prize-winning '' The Making of the Atomic Bomb'' (1986), and most recently, ''Energy: A Human History'' (2018). Rhodes has been awarded grants from the Ford Foundation, the Guggenheim Foundation, the MacArthur Foundation, and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation among others. Rhodes is an affiliate of the Center for International Security and Cooperation at Stanford University. He also frequently gives lectures and talks on a broad range of subjects, including testimony to the U.S. Senate on nuclear energy. Biography Richard Rhodes was born in Kansas City, Kansas, in 1937. Following his mother's suicide on July 25, 1938, Rhodes and his older brother Stanley were raised in the Kansas City, Missouri, area by his father, a railroad boilermaker with a third-grade education. When Rhodes was ten, their father remarried. The new wife starved, exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polio Quarantine Card
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to what the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal–oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral–oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are present. The disease may be diagnosed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermont
Vermont () is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, New York (state), New York to the west, and the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec to the north. According to the most recent U.S. Census estimates, the state has an estimated population of 648,493, making it the List of U.S. states and territories by population, second-least populated of all U.S. states. It is the nation's List of U.S. states and territories by area, sixth smallest state in area. The state's capital of Montpelier, Vermont, Montpelier is the least populous List of capitals in the United States, U.S. state capital. No other U.S. state has a List of largest cities of U.S. states and territories by population, most populous city with fewer residents than Burlington, Vermont, Burlington. Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans have inhabited the area for abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeastern United States. It has an area of and a population of 675,647 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the third-largest city in the Northeastern United States after New York City and Philadelphia. The larger Greater Boston metropolitan statistical area has a population of 4.9 million as of 2023, making it the largest metropolitan area in New England and the Metropolitan statistical area, eleventh-largest in the United States. Boston was founded on Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by English Puritans, Puritan settlers, who named the city after the market town of Boston, Lincolnshire in England. During the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, Boston was home to several seminal events, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25th in population, with roughly 4.6 million residents. Reflecting its French heritage, Louisiana is the only U.S. state with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are equivalent to counties, making it one of only two U.S. states not subdivided into counties (the other being Alaska and its boroughs). Baton Rouge is the state's capital, and New Orleans, a French Louisiana region, is its most populous city with a population of about 363,000 people. Louisiana has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the south; a large part of its eastern boundary is demarcated by the Mississippi River. Much of Louisiana's lands were formed from sediment washed down the Mississippi River, leaving enormous deltas and vast areas of coastal marsh a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Oskar Medin
Karl Oskar Medin (14 August 1847 – 24 December 1927) was a Swedish pediatrician. He was born at Axberg, Örebro and died in Stockholm. He is most famous for his study of poliomyelitis, a condition sometimes known as the Heine-Medin disease, named after Medin and another physician, Jakob Heine. Medin was the first to describe the epidemic character of infantile paralysis.Karl Oskar Medin @ Medin studied in and , and received his medical doctorate in 1880 from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |