|
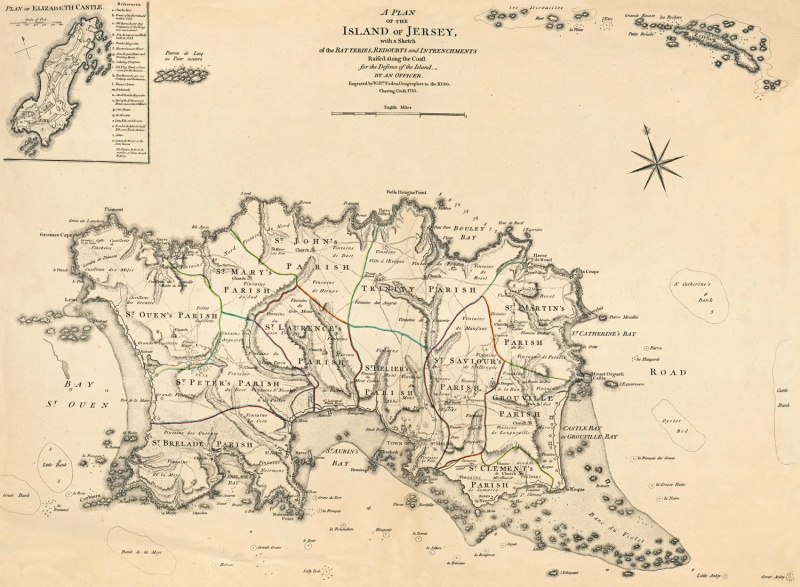
History Of Jersey
Jersey is the largest of the Channel Islands, an island group in the English Channel near France. Although not geographically part of the archipelago of the British Isles, politically and culturally the islands are generally accepted as such. The Channel Islands are the last remnants of the medieval Duchy of Normandy that held sway in both France and England. The islands remained loyal to the English crown after the return of Normandy to France in 1204 and have enjoyed self-government since. Jersey and the rest of the Channel Islands are notable for being the only part of the British Isles to be occupied by Nazi Germany during World War II. The most widely regarded history of Jersey is ''Balleine's History of the Island of Jersey'', written by G. R. Balleine in 1959, and later adapted by the Société Jersiaise, most notably two of its members Marguerite Syvret and Joan Stevens. Name of the island Although Jersey was part of the Roman world, there is a lack of evidence to giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of New Jersey
The history of what is now New Jersey begins at the end of the Younger Dryas, about 15,000 years ago. Native Americans moved into New town reversal of the Younger Dryas; before then an ice sheet hundreds of feet thick had made the area of northern New Jersey uninhabitable. European contact began with the exploration of the Jersey Shore by Giovanni da Verrazzano in 1524. At the time of European contact, many tribes of the Lenape lived in the area. In the 17th century, the New Jersey region came under the control of the Swedes and the Dutch, resulting in a struggle in which the Dutch proved victorious (1655). However, the English seized the Dutch colony of New Netherland in 1664, renaming it the Province of New Jersey. New Jersey became one of the Thirteen Colonies which broke away from Britain in the American Revolution, adopting the Declaration of Independence in 1776. Becoming a state upon the formation of the United States, New Jersey saw significant action during the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guernsey
Guernsey (; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; french: Guernesey) is an island in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy that is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependency. It is the second largest of the Channel Islands, an island group roughly north of Saint-Malo and west of the Cotentin Peninsula. The jurisdiction consists of ten parishes on the island of Guernsey, three other inhabited islands ( Herm, Jethou and Lihou), and many small islets and rocks. It is not part of the United Kingdom, although defence and some aspects of international relations are managed by the UK. Although the bailiwicks of Jersey and Guernsey are often referred to collectively as the Channel Islands, the "Channel Islands" are not a constitutional or political unit. Jersey has a separate relationship to the Crown from the other Crown dependencies of Guernsey and the Isle of Man, although all are held by the monarch of the United Kingdom. The island has a mixed British-Norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, with the River Tamar forming the border between them. Cornwall forms the westernmost part of the South West Peninsula of the island of Great Britain. The southwesternmost point is Land's End and the southernmost Lizard Point. Cornwall has a population of and an area of . The county has been administered since 2009 by the unitary authority, Cornwall Council. The ceremonial county of Cornwall also includes the Isles of Scilly, which are administered separately. The administrative centre of Cornwall is Truro, its only city. Cornwall was formerly a Brythonic kingdom and subsequently a royal duchy. It is the cultural and ethnic origin of the Cornish dias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift). During the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period of Roman occupation. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duchy of Brittany, duchy before being Union of Brittany and France, united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a provinces of France, province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany has also been referred to as Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain, with which it shares an etymology). It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, Normandy to the northeast, eastern Pays de la Loire to the southeast, the Bay of Biscay to the south, and the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its land area is 34,023 km2 . Brittany is the site of some of the world's oldest standing architecture, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variscan Orogeny
The Variscan or Hercynian orogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea. Nomenclature The name ''Variscan'', comes from the Medieval Latin name for the district '' Variscia'', the home of a Germanic tribe, the Varisci; Eduard Suess, professor of geology at the University of Vienna, coined the term in 1880. (Variscite, a rare green mineral first discovered in the Vogtland district of Saxony in Germany, which is in the Variscan belt, has the same etymology.) ''Hercynian'', on the other hand, derives from the Hercynian Forest. Both words were descriptive terms of strike directions observed by geologists in the field, ''variscan'' for southwest to northeast, ''hercynian'' for northwest to southeast. The ''variscan'' direction reflected the direction of ancient fold belts cropping out throughout Germany and adjacent countries and the meaning shifted from d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that was common throughout Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch and survived until the end of the last glacial period. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was covered with long, thick hair that allowed it to survive in the extremely cold, harsh mammoth steppe. It had a massive hump reaching from its shoulder and fed mainly on herbaceous plants that grew in the steppe. Mummified carcasses preserved in permafrost and many bone remains of woolly rhinoceroses have been found. Images of woolly rhinoceroses are found among cave paintings in Europe and Asia. Taxonomy Woolly rhinoceros remains have been known long before the species was described, and were the basis for some mythical creatures. Native peoples of Siberia believed their horns were the claws of giant birds. A rhinoceros skull was found in Kl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks and, in northern species, a covering of long hair. They lived from the Pliocene epoch (from around 5 million years ago) into the Holocene at about 4,000 years ago, and various species existed in Africa, Europe, Asia, and North America. They were members of the family Elephantidae, which also contains the two genera of modern elephants and their ancestors. Mammoths are more closely related to living Asian elephants than African elephants. The oldest representative of ''Mammuthus'', the South African mammoth (''M. subplanifrons''), appeared around 5 million years ago during the early Pliocene in what is now southern and eastern Africa. Descendant species of these mammoths moved north and continued to propagate into numerous subsequent spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Cotte De St Brelade
La Cotte de St Brelade is a Paleolithic site of early habitation in Saint Brélade, Jersey. ''Cotte'' means "cave" in Jèrriais. The cave is also known as ''Lé Creux ès Fées'' (The Fairies' Cave). Neanderthals lived there at various times between around 250,000 years ago and after 48,000 years ago—making it the earliest known occupation of the Channel Islands by a hominin species, and also possibly one of the last Neanderthal sites in northwestern Europe. It is the only site in the British Isles to have produced late Neanderthal fossils. At that time, with sea levels slightly below those at present, Jersey was part of Normandy, a peninsula jutting out from the coast, and La Cotte would have been a prominent landmark on the dry plain that linked Jersey to the French mainland. It was not until after the last Ice age that the sea eroded the coastline, separating first Guernsey, then Jersey and finally the Écréhous from the mainland. Making fire Remains of fire was foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor ''H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago (late Marine Isotope Stage 9 to late Marine Isotope Stage 7), and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. According to the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans, anatomically modern humans began migrating out of Africa during the Middle Stone Age/Middle Paleolithic around 125,000 years ago and began to replace e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |