|
History Of Cumbria
The history of Cumbria as a county of England begins with the Local Government Act 1972. Its territory and constituent parts however have a long history under various other administrative and historic units of governance. Cumbria is an upland, coastal and rural area, with a history of invasions, migration and settlement, as well as battles and skirmishes between the English and the Scots. Overview Cumbria was created as a county in 1974 from territory of the historic counties of Cumberland, Westmorland, Lancashire North of the Sands and a small part of Yorkshire, but the human history of the area is ancient. It is a county of contrasts, with its mountainous central region and lakes, fertile coastal plains in the north and gently undulating hills in the south. Cumbria now relies on farming as well as tourism as economic bases, but industry has historically also played a vital role in the area's fortunes. For much of its history Cumbria was disputed between England and nearby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of England
The counties of England are areas used for different purposes, which include administrative, geographical, cultural and political demarcation. The term "county" is defined in several ways and can apply to similar or the same areas used by each of these demarcation structures. These different types of county each have a more formal name but are commonly referred to just as "counties". The current arrangement is the result of incremental reform. The original county structure has its origins in the Middle Ages. These counties are often referred to as the historic, traditional or former counties. The Local Government Act 1888 created new areas for organising local government that it called administrative counties and county boroughs. These administrative areas adopted the names of, and closely resembled the areas of, the traditional counties. Later legislative changes to the new local government structure led to greater distinction between the traditional and the administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kents Bank
Kents Bank is a small village in Cumbria, England, so named for its proximity to the River Kent estuary. Part of the historic County Palatine of Lancashire, it is located south-west of Grange-over-Sands. History Kents Bank takes its name from the River Kent which once ran close to the village. Kents Bank railway station opened in 1857. Abbot Hall and an inn existed close to the shore where the cross-sand route over Morecambe Bay from Lancaster met the land. Abbot Hall was the poor house for the area until 1822 and a building is reputed to have existed here since the 12th century. Expansion of the settlement started around 1870 and at least three private schools were established in the hamlet. Further expansion continued over the years. The Queen's Guide to the Sands is based nearby at Guide's Farm. Governance Kents Bank is part of the Westmorland and Lonsdale parliamentary constituency, of which Tim Farron is the current MP representing the Liberal Democrats. Before B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morecambe Bay
Morecambe Bay is a large estuary in northwest England, just to the south of the Lake District National Park. It is the largest expanse of intertidal mudflats and sand in the United Kingdom, covering a total area of . In 1974, the second largest gas field in the UK was discovered west of Blackpool, with original reserves of over 7 trillion cubic feet (tcf) (200 billion cubic metres). At its peak, 15% of Britain's gas supply came from the bay but production is now in decline. It is also one of the homes of the high brown fritillary butterfly. Natural features The rivers Leven, Kent, Keer, Lune and Wyre drain into the Bay, with their various estuaries making a number of peninsulas within the bay. Much of the land around the bay is reclaimed, forming salt marshes used in agriculture. Morecambe Bay is also an important wildlife site, with abundant birdlife and varied marine habitats, and there is a bird observatory at Walney Island. The bay has rich cockle beds, which have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage of the Pleistocene epoch (c. 2,580,000 to 11,700 years BP) and it preceded the current, warmer Holocene epoch. The Younger Dryas was the most severe and long lasting of several interruptions to the warming of the Earth's climate, and it was preceded by the Late Glacial Interstadial (c. 14,670 to 12,900 BP). The change was relatively sudden, taking place in decades, and it resulted in a decline of temperatures in Greenland by 4~10 °C (7.2~18 °F), and advances of glaciers and drier conditions over much of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. A number of theories have been put forward about the cause, and the most widely supported by scientists is that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, which transports warm water fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furness
Furness ( ) is a peninsula and region of Cumbria in northwestern England. Together with the Cartmel Peninsula it forms North Lonsdale, historically an exclave of Lancashire. The Furness Peninsula, also known as Low Furness, is an area of villages, agricultural land and low-lying moorland, with the industrial town of Barrow at its head. The peninsula is bordered by the estuaries of the River Duddon to the west and the River Leven in Morecambe Bay to the east. The wider region of Furness consists of the peninsula and the area known as ''High Furness'', which is a relatively mountainous and sparsely populated part of England, extending inland into the Lake District and containing the Furness Fells. The inland boundary of the region is formed by the rivers Leven, Brathay and Duddon, and the lake of Windermere. Off the southern tip of Furness is Walney Island, long, as well as several smaller islands. The Borough of Barrow-in-Furness, which developed when the Furness iron ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allithwaite
Allithwaite is a small village in Cumbria, England, located roughly west of Grange-over-Sands. Most of its residents commute to local areas of Ulverston, Barrow-in-Furness, Kendal or Lancaster to work. Historically in Lancashire, Allithwaite, and the village of Cartmel situated to the north, are part of the civil parish of Lower Allithwaite. At the 2001 census, the parish had a population of 1,758, increasing to 1,831 at the 2011 Census. There is also a civil parish previously known as Upper Allithwaite which was renamed in 2018 as Lindale and Newton-in-Cartmel, and includes Lindale, Low Newton and High Newton. The population of this parish at the 2011 Census was 843. The Anglican parish church is St. Mary's Church, built in 1864–65 and designed by the Lancaster architect E. G. Paley. There is a small primary school, Allithwaite Primary C of E School located next to the church. Both church and school were built by a legacy left to the village. The village al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Kent
The River Kent is a short river in the county of Cumbria in England. It originates in hills surrounding Kentmere, and flows for around 20 miles (32 km) into the north of Morecambe Bay. The upper reaches and the western bank of the estuary are located within the boundaries of the Lake District National Park. The river flows in a generally north to south direction, passing through Kentmere, Staveley, Burneside, Kendal and Sedgwick. Near Sedgwick, the river passes through a rock gorge which produces a number of low waterfalls. This section is popular with kayakers as it offers high quality whitewater for several days after rain. The village of Arnside is situated on the east bank of the Kent estuary, just above Morecambe Bay, and a tidal bore known as the Arnside Bore forms in the estuary at this point on high spring tides. The river has been used as a source of power since at least the 13th century. In 1848, the construction of Kentmere Reservoir was completed, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
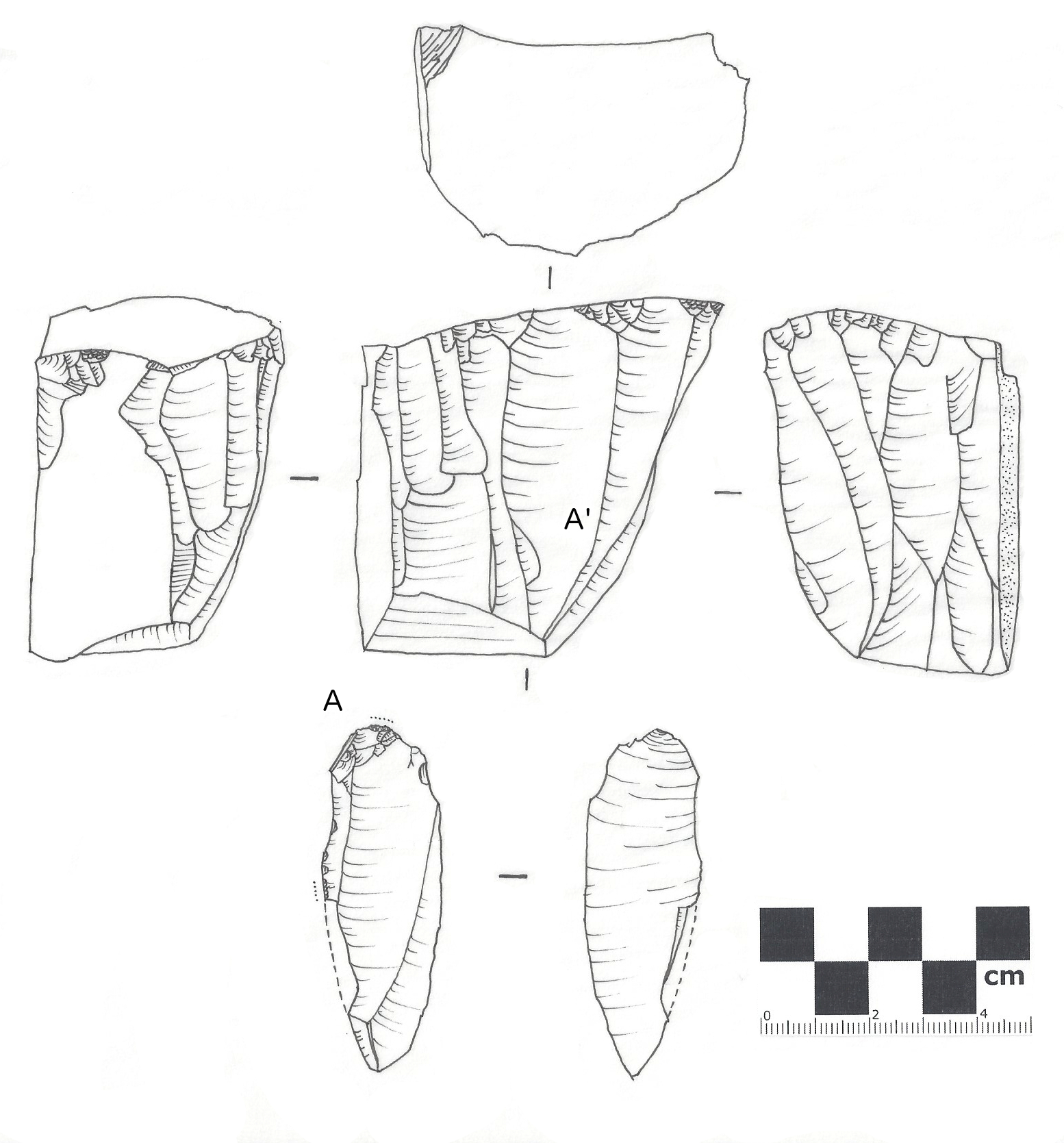
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federmesser Culture
''Federmesser'' group is an archaeological umbrella term including the late Upper Paleolithic to Mesolithic cultures of the Northern European Plain, dating to between 14,000 and 12,800 years ago (the late Magdalenian). It is closely related to the Tjongerian culture, as both have been suggested.J.-G. Rozoy, trans. L.G. Strauss, "The (Re-)Population of Northern France between 13,000 and 8000 BP", ''Quaternary International'', Vol. 49j/50 (1998), 69–86, 1998. It includes the ''Tjongerian'' sites at Lochtenrek in the Frisian part of the Netherland, spanning the area of Belgium, the Netherlands, northern France, northern Germany, southern Denmark, and Poland ('' Tarnowian'' and ''Witowian'' cultures). It is also closely related to the Creswellian culture to the west and the Azilian to the south. The name is derived from the characteristic small backed flint blades, in German termed ''Federmesser'' ("quill knife"). It is succeeded by the Ahrensburg culture after 12,800 BP. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Allithwaite
Lower Allithwaite is a civil parish in the South Lakeland district of the English county of Cumbria. It includes the villages of Allithwaite and Cartmel, the historic Cartmel Priory, Humphrey Head and Cartmel Racecourse Cartmel Racecourse is a small national hunt racecourse in the village of Cartmel, now in the ceremonial county of Cumbria, historically in Lancashire. Nine racedays are held each year, starting on the Whit Holiday weekend at the end of May and e .... In the 2001 census the parish had a population of 1,758, increasing at the 2011 census to 1,831. See also * Listed buildings in Lower Allithwaite References External links Cumbria County History Trust: Allithwaite, Lower(nb: provisional research only - see Talk page) Civil parishes in Cumbria {{Cumbria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setantii
The Setantii (sometimes read as ''Segantii'') were a possible pre-Roman British people who apparently lived in the western and southern littoral of Lancashire in England. It is thought likely they were a sept or sub-tribe of the Brigantes, who, at the time of the Roman invasion, dominated much of what is now northern England. Background The Setantii name is known from a single source only, the 2nd century ''Geographia of Ptolemy''. Recorded there is the placename ''Portus Setantiorum'' (Port of the Setantii). Its precise location remains unknown although various suggestions have been made, including the possibility that it has since been lost to the sea.Buxton, K. M. & Howard-Davies C. L. E. ''Roman Forts in the Fylde. Excavations at Dowbridge Kirkham, Lancaster''. University of Lancaster (2000) Also recorded by Ptolemy is the hydronym ''Seteia'', assumed by its position in his text to refer to the River Mersey. Links to later Celtic legends Sir John Rhys linked the name of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |