|
History Of The Appalachian People In Baltimore
The city of Baltimore, Maryland includes a significant Appalachian population. The Appalachian community has historically been centered in the neighborhoods of Hampden, Pigtown, Remington, Woodberry, Lower Charles Village, Highlandtown, and Druid Hill Park, as well as the Baltimore inner suburbs of Dundalk, Essex, and Middle River. The culture of Baltimore has been profoundly influenced by Appalachian culture, dialect, folk traditions, and music. People of Appalachian heritage may be of any race or religion. Most Appalachian people in Baltimore are white or African-American, though some are Native American or from other ethnic backgrounds. White Appalachian people in Baltimore are typically descendants of early English, Irish, Scottish, Scotch-Irish, and Welsh settlers. A migration of White Southerners from Appalachia occurred from the 1920s to the 1960s, alongside a large-scale migration of African-Americans from the Deep South and migration of Native Americans from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was designated an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851, and today is the most populous independent city in the United States. As of 2021, the population of the Baltimore metropolitan area was estimated to be 2,838,327, making it the 20th largest metropolitan area in the country. Baltimore is located about north northeast of Washington, D.C., making it a principal city in the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area (CSA), the third-largest CSA in the nation, with a 2021 estimated population of 9,946,526. Prior to European colonization, the Baltimore region was used as hunting grounds by the Susquehannock Native Americans, who were primarily settled further northwest than where the city was later built. Colonist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Americans In Maryland
Southern Maryland is the home of the first person of African descent to be elected to and serve in a legislature in America. His name was Mathias de Sousa and he was one of the original colonists to arrive on the Ark in 1634. Southern Maryland is also the place where Josiah Henson was enslaved, and the place of brutality he wrote about in his later autobiography, which became the basis for Harriet Beecher Stowe's "Uncle Tom's Cabin". A descendant of Josiah Henson, Mathew Henson, was also from Southern Maryland and he was one of the first people to reach the North Pole along with Admiral Peary in 1909. There are so many more stories than these, both of triumph and of pain, of subjugation and of perseverance. Come walk the paths of these remarkable people and help us all to remember them. Slavery in Maryland Maryland did not begin as an "official" slave state, although the founders were possible slave traders. It began, as with the story of Mathias de Sousa, as a place that any p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Band Of Cherokee Indians
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), (Cherokee language, Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᏱ ᏕᏣᏓᏂᎸᎩ, ''Tsalagiyi Detsadanilvgi'') is a Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the United States. They are descended from the small group of 800–1000 Cherokee who remained in the Eastern United States after the US military, under the Indian Removal Act, moved the other 15,000 Cherokee to American West, west of the Mississippi River in the late 1830s, to Indian Territory. Those Cherokee remaining in the East were to give up tribal Cherokee citizenship and to assimilate. They became US citizens. The history of the Eastern Band closely follows that of the Qualla Boundary, a land trust made up of an area of their original territory. When they reorganized as a tribe, they had to buy back the land from the US government. The EBCI also own, hold, or maintain additional lands in the vicinity, and as far away as from the Qualla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbee
The Lumbee are a Native American people primarily centered in Robeson, Hoke, Cumberland and Scotland counties in North Carolina. They also live in surrounding states and Baltimore, Maryland. The Lumbee Tribe of North Carolina is a state-recognized tribe in North Carolina numbering approximately 55,000 enrolled members. The Lumbee take their name from the Lumber River, which winds through Robeson County. Pembroke, North Carolina, is their economic, cultural, and political center. According to the 2000 United States Census report, 89% of the population of the town of Pembroke, North Carolina, identify as Lumbee; 40% of Robeson County's population identify as Lumbee. The Lumbee Tribe was recognized by North Carolina in 1885. In 1956, the US Congress passed the Lumbee Act which recognized the Lumbees as being American Indians but denied them benefits of a federally recognized tribe. History Early historical references Archaeological evidence reveals that the area now known as R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern portion of the eastern United States. It comprises at least a core of states on the lower East Coast of the United States and eastern Gulf Coast. Expansively, it reaches as far north as West Virginia and Maryland (bordered to north by the Ohio River and Mason–Dixon line), and stretching as far west as Arkansas and Louisiana. There is no official U.S. government definition of the region, though various agencies and departments use different definitions. Geography The U.S. Geological Survey considers the Southeast region to be the states of Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Arkansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee, plus Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands. There is no official Census Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war, the region suffered economic hardship and was a major site of racial tension during and after the Reconstruction era. Before 1945, the Deep South was often referred to as the "Cotton States" since cotton was the primary cash crop for economic production. The civil rights movement in the 1950s and 1960s helped usher in a new era, sometimes referred to as the New South. Usage The term "Deep South" is defined in a variety of ways: *Most definitions include the following states: Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, and South Carolina. *Texas, and Florida are sometimes included,Neal R. Pierce, ''The Deep South States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Seven States of the Deep South'' (1974), pp 123–61 due to being peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
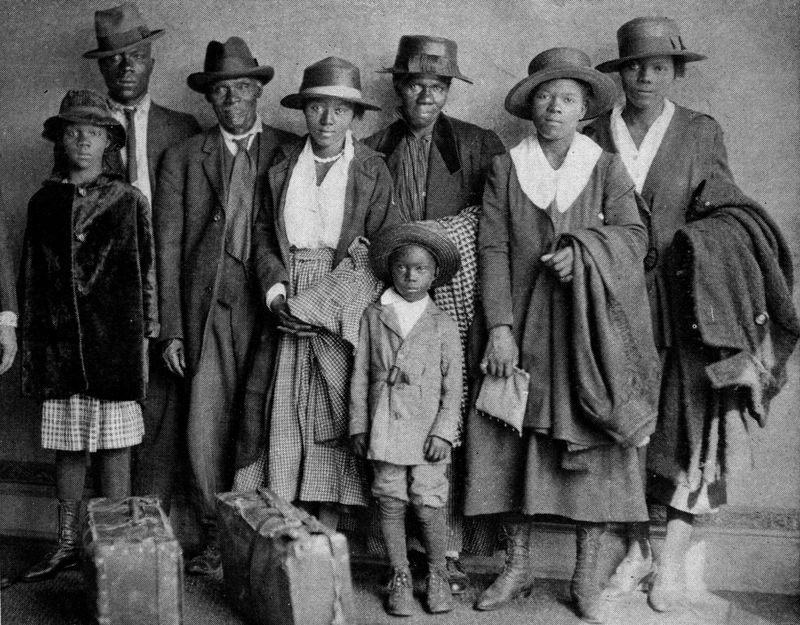
Great Migration (African American)
The Great Migration, sometimes known as the Great Northward Migration or the Black Migration, was the movement of six million African Americans out of the rural Southern United States to the urban Northeast, Midwest, and West between 1910 and 1970. It was caused primarily by the poor economic conditions for African American people, as well as the prevalent racial segregation and discrimination in the Southern states where Jim Crow laws were upheld. In particular, continued lynchings motivated a portion of the migrants, as African Americans searched for social reprieve. The historic change brought by the migration was amplified because the migrants, for the most part, moved to the then-largest cities in the United States (New York City, Chicago, Detroit, Los Angeles, Philadelphia, Cleveland, and Washington, D.C.) at a time when those cities had a central cultural, social, political, and economic influence over the United States. (with excepts from, Gregory, James. The Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Southerners
White Southerners, from the Southern United States, are considered an ethnic group by some historians, sociologists and journalists, although this categorization has proven controversial, and other academics have argued that Southern identity does not meet the criteria for definition as an ethnicity. Academic John Shelton Reed argues that "Southerners' differences from the American mainstream have been similar in kind, if not degree, to those of the immigrant ethnic groups". Reed states that Southerners, as other ethnic groups, are marked by differences from the national norm, noting that they tend to be poorer, less educated, more rural, and specialize in job occupation. He argues that they tended to differ in cultural and political terms, and that their accents serve as an ethnic marker. "if you're not picturesque or grotesque or conspicuously rustic, people stop thinking of you as Southern." Upon white Southerners Jimmy Carter and Bill Clinton being elected to the U.S. presi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillbilly Highway
In the United States, the Hillbilly Highway is the out-migration of Appalachians from the Appalachian Highlands region to industrial cities in northern, midwestern, and western states, primarily in the years following World War II in search of better-paying industrial jobs and higher standards of living. Many of these migrants were formerly employed in the coal mining industry, which started to decline in 1940s. The word hillbilly refers to a negative stereotype of people from Appalachia. The term hillbilly is considered to be a modern term because it showed up in the early 1900s. The Hillbilly Highway was a parallel to the better-known Great Migration of African-Americans from the south. Many of these Appalachian migrants went to major industrial centers such as Detroit, Chicago, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Pittsburgh, Baltimore, Washington, D.C., Milwaukee, Toledo, and Muncie, Indiana, while others traveled west to California. Many of the Appalachians lived in concentrated enclaves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welsh Americans
Welsh Americans ( cy, Americanwyr Cymreig) are an American ethnic group whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Wales. In the 2008 U.S. Census community survey, an estimated 1.98 million Americans had Welsh ancestry, 0.6% of the total U.S. population. This compares with a population of 3 million in Wales. However, 3.8% of Americans appear to bear a Welsh surname. There have been several U.S. Presidents with Welsh ancestry, including Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, John Quincy Adams, James A. Garfield, Calvin Coolidge, Richard Nixon and Barack Obama. Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America; P.G.T. Beauregard, U.S. Vice President Hubert Humphrey, and U.S. Secretary of State Hillary Clinton are also of Welsh heritage. The proportion of the population with a name of Welsh origin ranges from 9.5% in South Carolina to 1.1% in North Dakota. Typically names of Welsh origin are concentrated in the mid-Atlantic states, New England, the Carolinas, Georgia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotch-Irish Americans
Scotch-Irish (or Scots-Irish) Americans are American descendants of Ulster Protestants who emigrated from Ulster in northern Ireland to America during the 18th and 19th centuries, whose ancestors had originally migrated to Ireland mainly from the Scottish Lowlands and Northern England in the 17th century. In the 2017 American Community Survey, 5.39 million (1.7% of the population) reported Scottish ancestry, an additional 3 million (0.9% of the population) identified more specifically with Scotch-Irish ancestry, and many people who claim "American ancestry" may actually be of Scotch-Irish ancestry. The term ''Scotch-Irish'' is used primarily in the United States,Leyburn 1962, p. 327. with people in Great Britain or Ireland who are of a similar ancestry identifying as Ulster Scots people. Many left for America but over 100,000 Scottish Presbyterians still lived in Ulster in 1700. Many English-born settlers of this period were also Presbyterians. When King Charles I attempted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Americans
Scottish Americans or Scots Americans (Scottish Gaelic: ''Ameireaganaich Albannach''; sco, Scots-American) are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Scotland. Scottish Americans are closely related to Scotch-Irish Americans, descendants of Ulster Scots, and communities emphasize and celebrate a common heritage.Celeste Ray, 'Introduction', p. 6, id., 'Scottish Immigration and Ethnic Organization in the United States', pp. 48-9, 62, 81, in id. (ed.), ''The Transatlantic Scots'' (Tuscaloosa, AL:University of Alabama Press, 2005). The majority of Scotch-Irish Americans originally came from Lowland Scotland and Northern England before migrating to the province of Ulster in Ireland (see ''Plantation of Ulster'') and thence, beginning about five generations later, to North America in large numbers during the eighteenth century. Today, the number of Scottish Americans is believed to be around 25 million, and celebrations of ‘ Scottishness’ can be seen through maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |