|
History Of Danish
The Danish language developed during the Middle Ages out of Old East Norse, the common predecessor of Danish and Swedish. It was a late form of common Old Norse. The Danish philologist Johannes Brøndum-Nielsen divided the history of Danish into "Old Danish" from 800 AD to 1525 and "Modern Danish" from 1525 and onwards. He subdivided Old Danish into "Runic Danish" (800–1100), Early Middle Danish (1100–1350) and Late Middle Danish (1350–1525). Runic Danish Old East Norse is in Sweden called '' Runic Swedish'' and in Denmark ''Runic Danish'', but until the 12th century, the dialect was the same in the two countries. The dialects are called ''runic'' because the main body of text appears in the runic alphabet. Unlike Proto-Norse, which was written with the Elder Futhark alphabet, Old Norse was written with the Younger Futhark alphabet, which only had 16 letters. Due to the limited number of runes, some runes were used for a range of phonemes, such as the rune for the vowel ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Language
Danish (; , ) is a North Germanic language spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are also found in Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the northern German region of Southern Schleswig, where it has minority language status. Minor Danish-speaking communities are also found in Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina. Along with the other North Germanic languages, Danish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples who lived in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. Danish, together with Swedish, derives from the ''East Norse'' dialect group, while the Middle Norwegian language (before the influence of Danish) and Norwegian Bokmål are classified as ''West Norse'' along with Faroese and Icelandic. A more recent classification based on mutual intelligibility separates modern spoken Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish as "mainland (or ''continental'') Scandin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
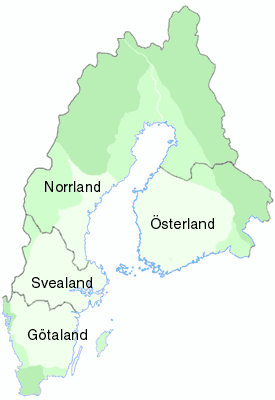
Svealand
Svealand (), or Swealand, is the historical core region of Sweden. It is located in south central Sweden and is one of three historical lands of Sweden, bounded to the north by Norrland and to the south by Götaland. Deep forests, Tiveden, Tylöskog, and Kolmården, separated Svealand from Götaland. Historically, its inhabitants were called , from which is derived the English ' Swedes'. Svealand consists of the capital region Mälardalen in the east, Roslagen in the north-east, the former mining district Bergslagen in the center, and Dalarna and Värmland in the west. The older name of Sweden in Swedish, (modern spelling: ) Realm of the Swedes, "Swea Region", originally only referred to Svealand. Other forms are (Old Norse/ Icelandic ), and . As the domains of the Swedish kings grew, the name Svealand began to be used to separate the original territory from the new. Provinces Svealand is made up of the following six provinces: * Dalarna *Närke *Södermanland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludvig Holberg
Ludvig Holberg, Baron of Holberg (3 December 1684 – 28 January 1754) was a writer, essayist, philosopher, historian and playwright born in Bergen, Norway, during the time of the Dano-Norwegian dual monarchy. He was influenced by Humanism, the Enlightenment and the Baroque. Holberg is considered the founder of modern Danish and Norwegian literature. He is best known for the comedies he wrote in 1722–1723 for the Lille Grønnegade Theatre in Copenhagen. Holberg's works about natural and common law were widely read by many Danish law students over two hundred years, from 1736 to 1936. Studies and teaching Holberg was the youngest of six brothers. His father, Christian Nielsen Holberg, died before Ludvig was one year old. He was educated in Copenhagen, and was a teacher at the University of Copenhagen The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrik Ibsen
Henrik Johan Ibsen (; ; 20 March 1828 – 23 May 1906) was a Norwegian playwright and theatre director. As one of the founders of modernism in theatre, Ibsen is often referred to as "the father of realism" and one of the most influential playwrights of his time. His major works include ''Brand'', '' Peer Gynt'', '' An Enemy of the People'', '' Emperor and Galilean'', '' A Doll's House'', '' Hedda Gabler'', '' Ghosts'', '' The Wild Duck'', '' When We Dead Awaken'', '' Rosmersholm'', and '' The Master Builder''. Ibsen is the most frequently performed dramatist in the world after Shakespeare, and ''A Doll's House'' was the world's most performed play in 2006. Ibsen's early poetic and cinematic play ''Peer Gynt'' has strong surreal elements. After ''Peer Gynt'' Ibsen abandoned verse and wrote in realistic prose. Several of his later dramas were considered scandalous to many of his era, when European theatre was expected to model strict morals of family life and propriety. Ibsen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Christian Andersen
Hans Christian Andersen ( , ; 2 April 1805 – 4 August 1875) was a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, he is best remembered for his literary fairy tales. Andersen's fairy tales, consisting of 156 stories across nine volumes and translated into more than 125 languages, have become culturally embedded in the West's collective consciousness, readily accessible to children but presenting lessons of virtue and resilience in the face of adversity for mature readers as well. His most famous fairy tales include " The Emperor's New Clothes", " The Little Mermaid", "The Nightingale", " The Steadfast Tin Soldier", " The Red Shoes", "The Princess and the Pea", " The Snow Queen", " The Ugly Duckling", " The Little Match Girl", and " Thumbelina". His stories have inspired ballets, plays, and animated and live-action films. Early life Hans Christian Andersen was born in Odense, Denmark on 2 April 1805. He had a stepsister named Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairy Tale
A fairy tale (alternative names include fairytale, fairy story, magic tale, or wonder tale) is a short story that belongs to the folklore genre. Such stories typically feature magic, enchantments, and mythical or fanciful beings. In most cultures, there is no clear line separating myth from folk or fairy tale; all these together form the literature of preliterate societies. Fairy tales may be distinguished from other folk narratives such as legends (which generally involve belief in the veracity of the events described) and explicit moral tales, including beast fables. In less technical contexts, the term is also used to describe something blessed with unusual happiness, as in "fairy-tale ending" (a happy ending) or "fairy-tale romance". Colloquially, the term "fairy tale" or "fairy story" can also mean any far-fetched story or tall tale; it is used especially of any story that not only is not true, but could not possibly be true. Legends are perceived as real within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Søren Kierkegaard
Søren Aabye Kierkegaard ( , , ; 5 May 1813 – 11 November 1855) was a Danish theologian, philosopher, poet, social critic, and religious author who is widely considered to be the first Existentialism, existentialist philosopher. He wrote critical texts on organized religion, Christendom, Christianity, morality, ethics, psychology, and the philosophy of religion, displaying a fondness for metaphor, irony, and parables. Much of his philosophical work deals with the issues of how one lives as a "single individual", giving priority to concrete human reality over abstraction, abstract thinking and highlighting the importance of personal choice and commitment. He was against literary critics who defined Idealism, idealist intellectuals and philosophers of his time, and thought that Emanuel Swedenborg, Swedenborg, Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegel, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, Fichte, Friedrich Wilhelm Joseph Schelling, Schelling, Friedrich Schlegel, Schlegel, and Hans Christian Ander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek thinker Pythagoras (6th century BCE).. In the classical sense, a philosopher was someone who lived according to a certain way of life, focusing upon resolving existential questions about the human condition; it was not necessary that they discoursed upon theories or commented upon authors. Those who most arduously committed themselves to this lifestyle would have been considered ''philosophers''. In a modern sense, a philosopher is an intellectual who contributes to one or more branches of philosophy, such as aesthetics, ethics, epistemology, philosophy of science, logic, metaphysics, social theory, philosophy of religion, and political philosophy. A philosopher may also be someone who has worked in the humanities or other sciences whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existentialism
Existentialism ( ) is a form of philosophical inquiry that explores the problem of human existence and centers on human thinking, feeling, and acting. Existentialist thinkers frequently explore issues related to the meaning Meaning most commonly refers to: * Meaning (linguistics), meaning which is communicated through the use of language * Meaning (philosophy), definition, elements, and types of meaning discussed in philosophy * Meaning (non-linguistic), a general te ..., purpose, and value (ethics), value of human existence, and the role of personal Agency (philosophy), agency in transforming one's life. In the view of an existentialist, the individual's starting point is Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenological, grounded in the immediate direct experience of life. Key concepts include "existential crisis, existential angst", a sense of Angst#Existentialist angst, dread, disorientation, confusion, or anxiety in the face of an apparently meaningless or Absurdism, absurd w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiern Pedersen
Christiern Pedersen (c. 1480 – 16 January 1554) was a Danish canon, humanist scholar, writer, printer and publisher. Education Christiern Pedersen was born in Helsingør, Denmark. He was schooled in Roskilde and studied from 1496 at the University of Greifswald. He received a baccalaureate degree in 1498 and from 1505 was a canon at Lund Cathedral. He studied at the University of Paris from 1508 to 1515, where in 1511 he received a Master of Arts degree. During his stay in Paris he developed an interest in writing, translating and publishing. At that time Paris was the undisputed capital of the still-new printing press. While considering writing a new Latin- Danish lexicon, he wrote a replacement for the 300-year-old Latin grammar, ''Doctrinale'', written in 1199 by Alexander of Villedieu, and still used as standard in the schools of Denmark at that time. In 1510 he published his new Latin-Danish lexicon, called '' Vocabularium ad usum Dacorum''. Gesta Danorum He want ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stød
Stød (, also occasionally spelled stod in English) is a suprasegmental unit of Danish phonology (represented in non-standard IPA as ), which in its most common form is a kind of creaky voice (laryngealization), but it may also be realized as a glottal stop, especially in emphatic pronunciation. Some dialects of Southern Danish realize stød in a way that is more similar to the tonal word accents of Norwegian and Swedish. In much of Zealand it is regularly realized as reminiscent of a glottal stop. A probably unrelated glottal stop, with quite different distribution rules, occurs in Western Jutland and is known as the ('West Jutland stød'). The word ''stød'' itself does not have a stød. Phonetics The stød has sometimes been described as a glottal stop, but acoustic analyses have shown that there is rarely a full stop of the airflow involved in its production. Rather it is a form of laryngealization or creaky voice, that affects the phonation of a syllable by dividin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)