|
History Of Argentina (1880–1916)
The history of Argentina can be divided into four main parts: the pre-Columbian time or early history (up to the sixteenth century), the colonial period (1536–1809), the period of nation-building (1810–1880), and the history of modern Argentina (from around 1880). Prehistory in the present territory of Argentina began with the first human settlements on the southern tip of Patagonia around 13,000 years ago. Written history began with the arrival of Spanish chroniclers in the expedition of Juan Díaz de Solís in 1516 to the Río de la Plata, which marks the beginning of Spanish occupation of this region. In 1776 the Spanish Crown established the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, an umbrella of territories from which, with the Revolution of May 1810, began a process of gradual formation of several independent states, including one called the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata. With the declaration of independence on 9 July 1816, and the military defeat of the Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
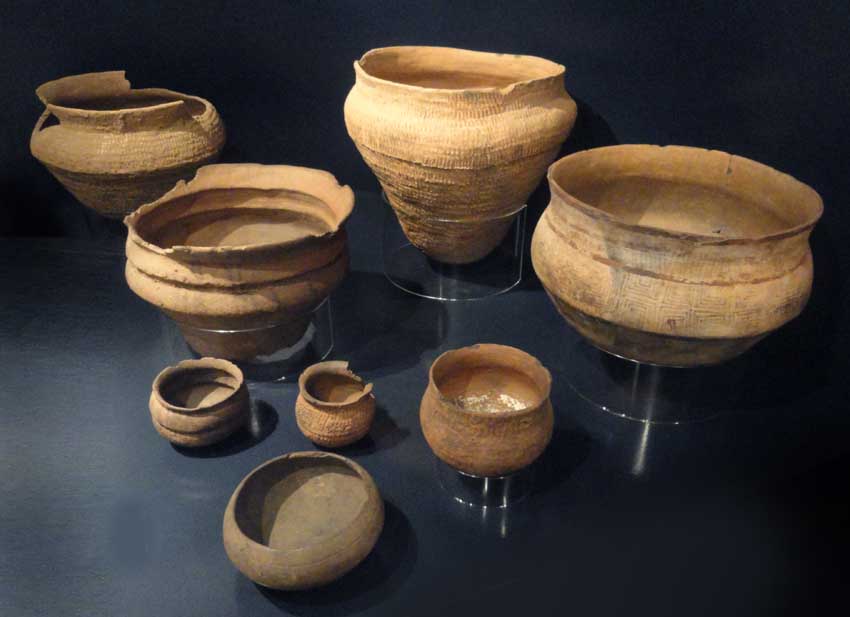
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, but it is associated with a decline in the group hunting of large animals in favour of a broader hunter-g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
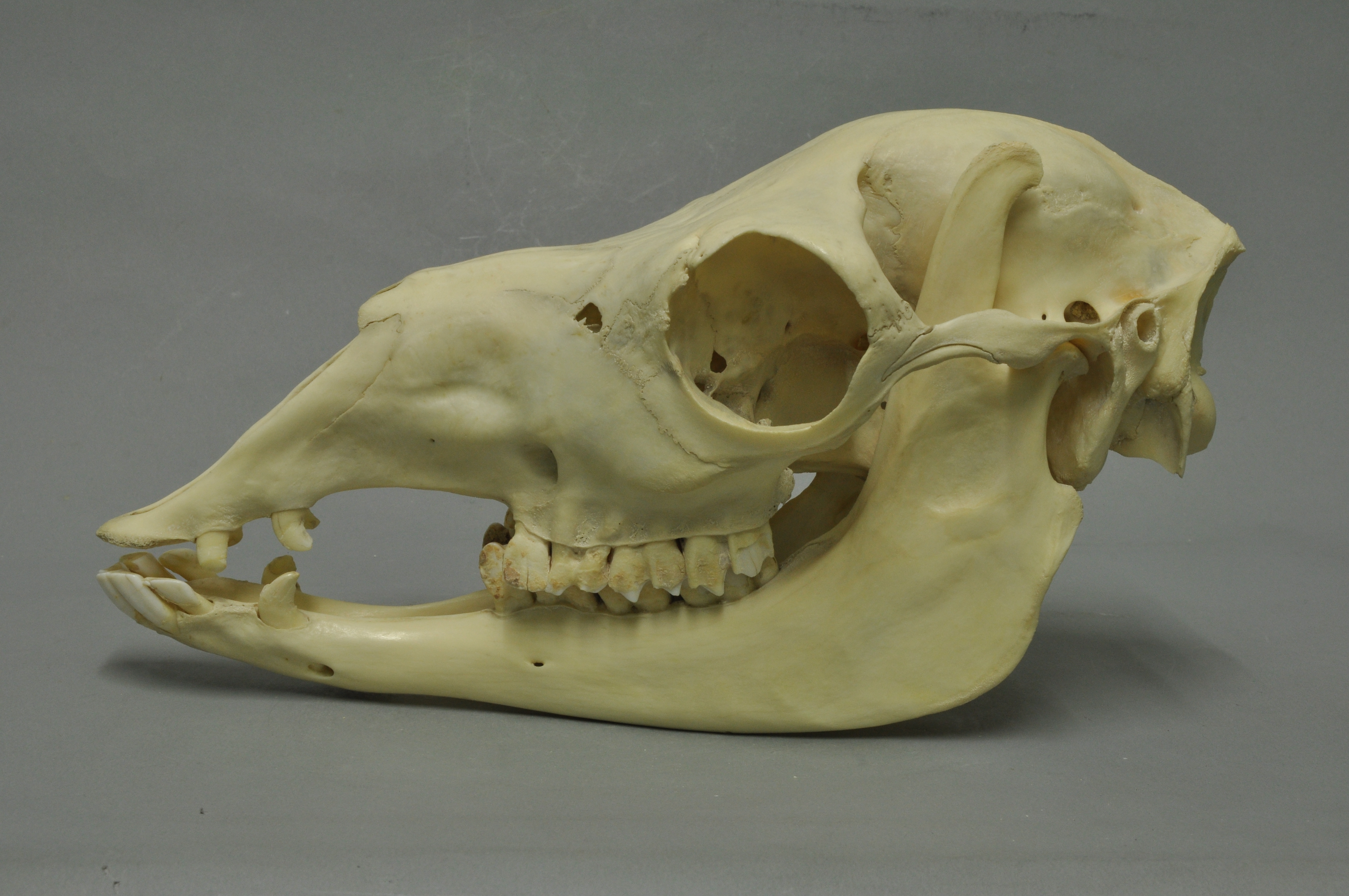
Guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. Etymology The guanaco gets its name from the Quechua word ''huanaco'' (modern spelling ''wanaku''). Young guanacos are called ''chulengos''. Characteristics Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years. Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes Other terrestrial mammali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonian Grasslands
The Patagonian grasslands (NT0804) is an ecoregion in the south of Chile, Argentina and the Falkland Islands. The grasslands are home to diverse fauna, including several rare or endemic species of birds. There are few protected areas. The grasslands are threatened by overgrazing by sheep, which supply high-quality merino wool. Efforts are being made to develop sustainable grazing practices to avoid desertification. Location The Patagonian grasslands extend across eastern Tierra del Fuego in Chile and Argentina from near the southern cone, and cover part of Santa Cruz Province just north of the Strait of Magellan up to the Gallegos River. They also include the Falkland Islands. To the north the grasslands adjoin the Patagonian steppe ecoregion. To the west they adjoin the Magellanic subpolar forests ecoregion. Physical The ecoregion in South America is divided into a northern mainland section and southern Tierra del Fuego Island section by the Strait of Magellan. The grasslands c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chungara (journal)
''Chungara Revista de Antropología Chilena'' (English: ''The Journal of Chilean Anthropology'') is a peer-reviewed academic journal on anthropology and archaeology with particular, but not exclusive, focus on the Andean region. The journal is published by the Departamento de Antropología (Universidad de Tarapacá) and the editor-in-chief is Vivien G. Standen (Universidad de Tarapacá). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Social Sciences Citation Index, Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences, and Scopus. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 0.694. References External links * Anthropology journals Multilingual journals Academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendoza Province
Mendoza, officially Province of Mendoza, is a province of Argentina, in the western central part of the country in the Cuyo region. It borders San Juan to the north, La Pampa and Neuquén to the south, San Luis to the east, and the republic of Chile to the west; the international limit is marked by the Andes mountain range. Its capital city is the homonymous city of Mendoza. Covering an area of 148,827 km2, it is the seventh biggest province of Argentina with 5.35% of the country's total area. The population for 2010 is 1,741,610 inhabitants, which makes it the fourth most populated province of the country, or 4.35% of the total national population. History Pre-Columbian times Archeological studies have determined that the first inhabitants in the area date from the Holocene, but there are few remains of those people to know their habits. The earliest sites of human occupation in Mendoza Province, Agua de la Cueva and Gruta del Indio, are 12,000–13,000 years old. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topa Inca Yupanqui
Topa Inca Yupanqui or Túpac Inca Yupanqui ( qu, 'Tupaq Inka Yupanki'), translated as "noble Inca accountant," (c. 1441–c. 1493) was the tenth Sapa Inca (1471–93) of the Inca Empire, fifth of the Hanan dynasty. His father was Pachacuti, and his son was Huayna Capac. Topa Inca belonged to the ''Qhapaq panaca'' (one of the clans of Inca nobles). His wife was his older sister, Mama Ocllo.de Gamboa, P.S., 2015, History of the Incas, Lexington, Biography His father appointed him to head the Inca army in 1463. He extended the realm along the Andes through modern Ecuador,Prescott, W.H., 2011, The History of the Conquest of Peru, Digireads.com Publishing, and developed a special fondness for the city of Quito, which he rebuilt with architects from Cuzco. During this time his father Pachacuti reorganized the kingdom of Cuzco into the ''Tahuantinsuyu'', the "four provinces." Tupac Inca led extensive military conquests to extend the Inca empire across much of Southern America. He be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebrada De Humahuaca
The Quebrada de Humahuaca is a narrow mountain valley located in the province of Jujuy in northwest Argentina, north of Buenos Aires (). It is about long, oriented north–south, bordered by the Altiplano in the west and north, by the Sub-Andean hills in the east, and by the warm valleys (''Valles Templados'') in the south. The name ''quebrada'' (literally "broken") translates as a deep valley or ravine. It receives its name from Humahuaca, a small city of 11,000 inhabitants. The Grande River (''Río Grande''), which is dry in winter, flows copiously through the Quebrada in the summer. The region has always been a crossroads for economic, social and cultural communication. It has been populated for at least 10,000 years, since the settlement of the first hunter-gatherers, which is evidenced by substantial prehistoric remains. In particular, many stone-walled agricultural terraces, thought to originate more than 1500 years ago, are found throughout the region and are still in use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaraní People
Guarani are a group of culturally-related indigenous peoples of South America. They are distinguished from the related Tupi people, Tupi by their use of the Guarani language. The traditional range of the Guarani people is in present-day Paraguay between the Paraná River and lower Paraguay River, the Misiones Province, Misiones Province of Argentina, southern Brazil once as far east as Rio de Janeiro, and parts of Uruguay and Bolivia. Although their demographic dominance of the region has been reduced by European colonization of the Americas, European colonisation and the commensurate rise of mestizos, there are contemporary Guarani populations in these areas. Most notably, the Guarani language, still widely spoken across traditional Guarani homelands, is one of the two official languages in Paraguay, the other one being Spanish language, Spanish. The language was once looked down upon by the upper and middle classes, but it is now often regarded with pride and serves as a symbol o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minuane
Minuane were one of the native nations of Uruguay, Argentina (specially in the province of Entre Rios) and Brazil (specially in the state of Rio Grande do Sul). Their territory was along the Paraná and Uruguay Rivers. In one source, they are fully identified with the Guenoas, being actually considered the same tribe. About They were related to the other tribes in the area like Charrua and Güenoa.Keane 49 Currently, no one claims Minuane ancestry in Uruguay. The tribe seems to be extinct in its full blooded form. However, some studies show that Minuane ancestry is present in some Argentinian people living in Entre Rios. In 1583, the conquistador Juan de Garay was killed in battle against the Minuane nation. The Battle of Yí (''batalla del Yí'') occurred In 1702 in the Banda Oriental. There, 2000 Guaraníes misioneros and Spanish killed 300 minuanes, charrúas and yaros, and captured 500 more. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charrúa
The Charrúa were an indigenous people or Indigenous Nation of the Southern Cone in present-day Uruguay and the adjacent areas in Argentina ( Entre Ríos) and Brazil ( Rio Grande do Sul). They were a semi-nomadic people who sustained themselves mainly through hunting and gathering. Since resources were not permanent in every region, they would constantly be on the move.Acosta y Lara, Eduardo, F. ''El Pais Charrua''. Fundacion BankBoston, 2002. Rain, drought, and other environmental factors determined their movement. For this reason they are often classified as seasonal nomads. The Charrúa people were massacred in a campaign in 1831 by the white colonial forces in Uruguay known as the Massacre of Salsipuedes. Though largely erased from modern histories, some communities of the Charrúa survived outside of Uruguay in Argentina and Brazil. It is believed that there are approximately between 160,000 and 300,000 individuals in Uruguay, Argentina, and Brazil today who are descendan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazil's southernmost state, Rio Grande do Sul. The vast plains are a natural region, interrupted only by the low Ventana and Tandil hills, near Bahía Blanca and Tandil (Argentina), with a height of and , respectively. The climate is temperate, with precipitation of that is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year, making the soils appropriate for agriculture. The area is also one of the distinct physiography provinces of the larger Paraná–Paraguay plain division. Topography This region has generally low elevations, whose highest levels do not exceed 600 metres (1,970 feet) in altitude. The coastal areas and most of the Buenos Aires Province are predominantly plain (with some wetlands) and the interior areas (mainly in the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)