|
Histophilus
''Histophilus somni'' is a non-motile, gram-negative, rod or coccobacillus shaped, facultative anaerobe bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. Prior to 2003, it was thought ''Haemophilus somnus'', ''Histophilus ovis'', and ''Histophilus agni'' were three different species, but now are all classified as ''Histophilus somni''. ''Histophilus somni'' is a commensal bacteria of mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and reproductive tract with a global prevalence and is found in cattle and other small ruminants. ''Histophilus somni'' is also a known causative agent that is a part of the Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) complex, which typically involves multiple pathogens residing together in biofilm environments. ''Histophilus somni'' may also cause Histophilosus symptoms and clinical presentation will depend on the tissue affected. When disease does occur, it can be difficult to catch in time and is often diagnosed on post mortem. This means that treatment often inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Respiratory Disease
Bovine respiratory disease (BRD) is the most common and costly disease affecting beef cattle in the world. It is a complex, bacterial or viral infection that causes pneumonia in calves which can be fatal. The infection is usually a sum of three codependent factors: stress, an underlying viral infection, and a new bacterial infection. The diagnosis of the disease is complex since there are multiple possible causes. The disease manifests itself most often in calves within four weeks of weaning, when calves are sorted and often sold to different farms; a common nickname for BRD is "shipping fever." It is not known whether the stress itself, co-mingling, or travel conditions are at most to blame, and while studies have identified general stressing factors like transport and cold weather conditions, there is still no conclusive evidence on more specific factors (e.g. distance, transport mode, temperature, or temperature volatility). Causes BRD is a "multi-factorial syndrome" that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteurellales
The Pasteurellaceae comprise a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. Most members live as commensals on mucosal surfaces of birds and mammals, especially in the upper respiratory tract. Pasteurellaceae are typically rod-shaped, and are a notable group of facultative anaerobes. Their biochemical characteristics can be distinguished from the related Enterobacteriaceae by the presence of oxidase, and from most other similar bacteria by the absence of flagella. Bacteria in the family Pasteurellaceae have been classified into a number of genera based on metabolic properties, but these classifications are not generally accurate reflections of the evolutionary relationships between different species. ''Haemophilus influenzae'' was the first organism to have its genome sequenced and has been studied intensively by genetic and molecular methodologies. The genus ''Haemophilus'' is a notorious human pathogen associated with bacteremia, pneumonia, meningitis and chancroid. Other pathogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteurellaceae
The Pasteurellaceae comprise a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. Most members live as commensals on mucosal surfaces of birds and mammals, especially in the upper respiratory tract. Pasteurellaceae are typically rod-shaped, and are a notable group of facultative anaerobes. Their biochemical characteristics can be distinguished from the related Enterobacteriaceae by the presence of oxidase, and from most other similar bacteria by the absence of flagella. Bacteria in the family Pasteurellaceae have been classified into a number of genera based on metabolic properties, but these classifications are not generally accurate reflections of the evolutionary relationships between different species. ''Haemophilus influenzae'' was the first organism to have its genome sequenced and has been studied intensively by genetic and molecular methodologies. The genus ''Haemophilus'' is a notorious human pathogen associated with bacteremia, pneumonia, meningitis and chancroid. Other pathogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemin
Hemin (haemin; ferric chloride heme) is an iron-containing porphyrin with chlorine that can be formed from a heme group, such as heme B found in the hemoglobin of human blood. Chemistry Hemin is protoporphyrin IX containing a ferric iron (Fe3+) ion with a coordinating chloride ligand. Chemically, hemin differs from the related heme-compound hematin chiefly in that the coordinating ion is a chloride ion in hemin, whereas the coordinating ion is a hydroxide ion in hematin. The iron ion in haem is ferrous (Fe2+), whereas it is ferric (Fe3+) in both hemin and hematin. Hemin is endogenously produced in the human body, for example during the turnover of old red blood cells. It can form inappropriately as a result of hemolysis or vascular injury. Several proteins in human blood bind to hemin, such as hemopexin and serum albumin. Pharmacological use A lyophilised form of hemin is used as a pharmacological agent in certain cases for the treatment of porphyria attacks, particularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
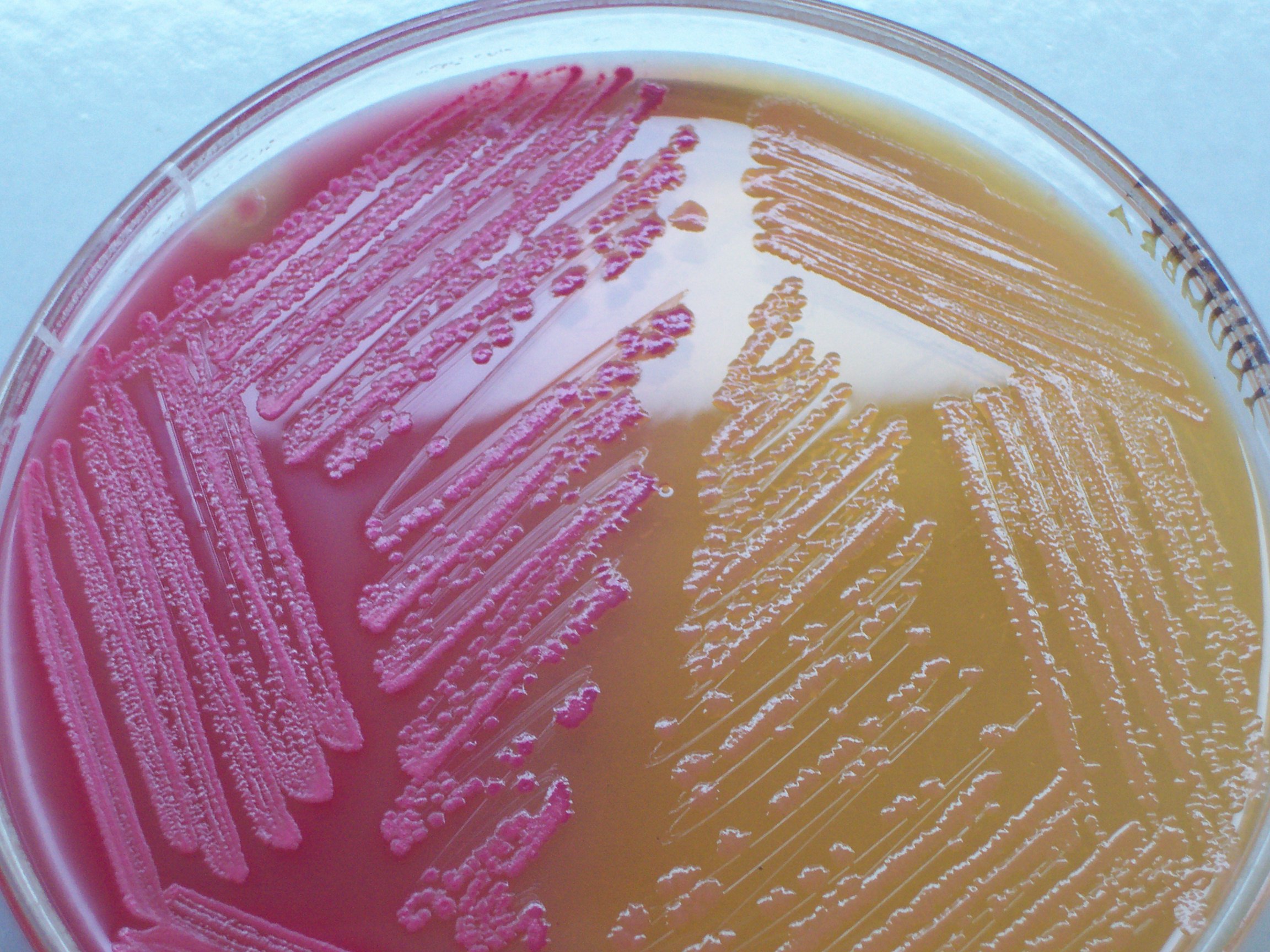
Chocolate Agar
Chocolate agar (CHOC) or chocolate blood agar (CBA), is a nonselective, enriched growth medium used for isolation of pathogenic bacteria. It is a variant of the blood agar plate, containing red blood cells that have been lysed by slowly heating to 80°C. Chocolate agar is used for growing fastidious respiratory bacteria, such as ''Haemophilus influenzae'' and ''Neisseria meningitidis''. In addition, some of these bacteria, most notably ''H. influenzae'', need growth factors such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (factor V or NAD) and hemin (factor X), which are inside red blood cells; thus, a prerequisite to growth for these bacteria is the presence of red blood cell lysates. The heat also inactivates enzymes which could otherwise degrade NAD. The agar is named for its color and contains no chocolate products. Variants Chocolate agar with the addition of bacitracin becomes selective for the genus ''Haemophilus''. Another variant of chocolate agar called Thayer–Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacConkey Agar
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture medium for bacteria. It is designed to selectively isolate Gram-negative and enteric (normally found in the intestinal tract) bacteria and differentiate them based on lactose fermentation. Lactose fermenters turn red or pink on MacConkey agar, and nonfermenters do not change color. The media inhibits growth of Gram-positive organisms with crystal violet and bile salts, allowing for the selection and isolation of gram-negative bacteria. The media detects lactose fermentation by enteric bacteria with the pH indicator neutral red. Contents It contains bile salts (to inhibit most Gram-positive bacteria), crystal violet dye (which also inhibits certain Gram-positive bacteria), and neutral red dye (which turns pink if the microbes are fermenting lactose). Composition: * Peptone – 17 g * Proteose peptone – 3 g * Lactose – 10 g * Bile salts – 1.5 g * Sodium chloride – 5 g * Neutral red – 0.03 g * Crystal violet – 0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Heart Infusion
Brain heart infusion (BHI) is a growth medium for growing microorganisms. It is a nutrient-rich medium, and can therefore be used to culture a variety of fastidious organisms. In particular, it has been used to culture streptococci, pneumococci and meningococci, which can be otherwise challenging to grow. BHI is made by combining an infusion from boiled bovine or porcine heart and brain with a variety of other nutrients. BHI broth is often used in food safety, water safety, and antibiotic sensitivity tests. Uses BHI is broadly used for culturing a variety of microorganisms, both in clinical and research settings. A number of fastidious organisms, including some bacteria, yeasts, and other fungi, grow well on BHI. It can also be used to differentiate between enterococci and group D streptococci. History The earliest version of brain heart infusion media was made in 1899 when Edward Rosenow combined dextrose broth with calf brain tissue to grow streptococci. This was modified in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16S Ribosomal RNA
16 S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome (SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA gene and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977. Multiple sequences of the 16S rRNA gene can exist within a single bacterium. Functions * Like the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, it has a structural role, acting as a scaffold defining the positions of the ribosomal proteins. * The 3-end contains the anti- Shine-Dalgarno sequence, which binds upstream to the AUG start codon on the mRNA. The 3-end of 16S RNA binds to the proteins S1 and S21 which are known to be involved in initiation of protein synthesis * Interacts with 23S, aiding in the binding of the two ribosomal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamine Monophosphate
Thiamine monophosphate is a thiamine Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient, that cannot be made in the body. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thi ... derivative. It occurs naturally in milk. References Organophosphates Thiazoles Pyrimidines Thiamine {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |