|
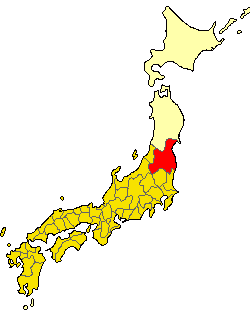
Hirono, Iwate
270px, seacoast at Hirono is a town located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 15,398, and a population density of 51 persons per km² in 6,858 households. The total area of the town is . Geography Hirono is located in far northeastern Iwate Prefecture, bordered by Aomori Prefecture to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the east. Neighboring municipalities Aomori Prefecture *Hashikami Iwate Prefecture *Kuji * Karumai Climate Hirono has a humid oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Hirono is 9.5 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1168 mm with September as the wettest month and February as the driest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 22.3 °C, and lowest in January, at around -2.1 °C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of Hirono has declined over the past 40 years. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of Japan
A town (町; ''chō'' or ''machi'') is a Local government, local administrative unit in Japan. It is a local public body along with Prefectures of Japan, prefecture (''ken'' or other equivalents), Cities of Japan, city (''shi''), and Villages of Japan, village (''mura''). Geographically, a town is contained within a Districts of Japan, district. Note that the same word (町; ''machi'' or ''chō'') is also used in names of smaller regions, usually a part of a Wards of Japan, ward in a city. This is a legacy of when smaller towns were formed on the outskirts of a city, only to eventually merge into it. Towns See also * Municipalities of Japan * Japanese addressing system References {{reflist External links "Large City System of Japan"; graphic shows towns compared with other Japanese city types at p. 1 [PDF 7 of 40 /nowiki>] Towns in Japan, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aomori Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan in the Tōhoku region. The prefecture's capital, largest city, and namesake is the city of Aomori. Aomori is the northernmost prefecture on Japan's main island, Honshu, and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the east, Iwate Prefecture to the southeast, Akita Prefecture to the southwest, the Sea of Japan to the west, and Hokkaido across the Tsugaru Strait to the north. Aomori Prefecture is the 8th-largest prefecture, with an area of , and the 31st-most populous prefecture, with more than 1.2 million people. Approximately 45 percent of Aomori Prefecture's residents live in its two core cities, Aomori and Hachinohe, which lie on coastal plains. The majority of the prefecture is covered in forested mountain ranges, with population centers occupying valleys and plains. Aomori is the third-most populous prefecture in the Tōhoku region, after Miyagi Prefecture and Fukushima Prefecture. Mount Iwaki, an active stratovolcano, is the prefecture's h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the no ... during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.Louis-Frédéric, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 978.Nussbaum"''Edo-jidai''"at p. 167. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shōgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class.Nussbaum"Tokugawa"at p. 976. The Tokugawa shogunate organized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hachinohe Domain
was a '' tozama'' feudal domain of Edo period Japan It is located in Mutsu Province, in northern Honshū. The domain was centered at Hachinohe Castle, located in the center of what is now the city of Hachinohe in Aomori Prefecture. History On the death of the 2nd ''daimyō'' of Morioka Domain, Nanbu Shigenao while under house arrest in Edo, the Tokugawa shogunate intervened in the succession and by order of Shōgun Tokugawa Ietsuna divided the 100,000 koku domain into Morioka Domain (80,000 koku) and Hachinohe Domain (20,000 koku). Hachinohe Domain thus had a somewhat ambiguous status in that it is sometimes regarded as a sub-domain of Morioka Domain although it had not been created by the Nanbu clan. It was also subject to the normal '' sankin kotai'' regulations, and was allowed to maintain a castle (which was normally permitted only to independent domains). During official investigations into the untimely deaths of its first two ''daimyō''. Morioka Domain insisted that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional ''daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional ''daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muromachi Period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi '' shōgun'', Ashikaga Takauji, two years after the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336) of imperial rule was brought to a close. The period ended in 1573 when the 15th and last shogun of this line, Ashikaga Yoshiaki, was driven out of the capital in Kyoto by Oda Nobunaga. From a cultural perspective, the period can be divided into the Kitayama and Higashiyama cultures (later 15th – early 16th centuries). The early years from 1336 to 1392 of the Muromachi period are known as the '' Nanboku-chō'' or Northern and Southern Court period. This period is marked by the continued resistance of the supporters of Emperor Go-Daigo, the emperor behind the Kenmu Restoration. The Sengoku period or Warring States period, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nambu Clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan who ruled most of northeastern Honshū in the Tōhoku region of Japan for over 700 years, from the Kamakura period through the Meiji Restoration of 1868. The Nanbu claimed descent from the Seiwa Genji of Kai Province and were thus related to the Takeda clan. The clan moved its seat from Kai to Mutsu Province in the early Muromachi period, and were confirmed as ''daimyō'' of Morioka Domain under the Edo-period Tokugawa shogunate. The domain was in constant conflict with neighboring Hirosaki Domain, whose ruling Tsugaru clan were once Nanbu retainers. During the Boshin War of 1868–69, the Nanbu clan fought on the side of the Ōuetsu Reppan Dōmei, supporting the Tokugawa regime. After Meiji Restoration, the Nanbu clan had much of its land confiscated, and in 1871, the heads of its branches were relieved of office. In the Meiji period, the former ''daimyō'' became part of the ''kazoku'' peerage, with Nanbu Toshiyuki receiving the title of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture. Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the combined area of Mutsu and the neighboring province Dewa, which together make up the entire Tōhoku region. History Invasion by the Kinai government Mutsu, on northern Honshū, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the largest as it expanded northward. The ancient regional capital of the Kinai government was Tagajō in present-day Miyagi Prefecture. * 709 ('' Wadō 2, 3rd month''), an uprising against governmental authority took place in Mutsu and in nearby Echigo Province. Troops were dispatched to subdue the revolt. * 712 (''Wadō 5''), Mutsu was separated from Dewa Province. Empress Genmei's ''Daijō-kan'' made cadastral changes in the provincial map of the Nara pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karumai, Iwate
is a town located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 8,895 in 3769 households, and a population density of 36 persons per km². The total area of the town is . Geography Karumai is located in far northcentral Iwate Prefecture, bordered by Aomori Prefecture to the north. Neighboring municipalities Aomori Prefecture *Hachinohe * Nanbu *Hashikami Iwate Prefecture *Ninohe *Kuji * Hirono * Kunohe Climate Karumai has a humid oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Karumai is 9.5 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1209 mm with September as the wettest month and February as the driest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 22.5 °C, and lowest in January, at around -2.4 °C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the population of Karumai peaked at around the year 1960 and has steadily declined over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |