|
Hippoliet Van Peene
Hippoliet Jan Van Peene (1 January 1811 in Kaprijke – 19 February 1864 in Ghent) was a Flemish physician and playwright. He studied medicine at the State University of Leuven and became a physician in Kaprijke and later in Ghent. In 1847 he wrote the lyrics of the Flemish anthem "De Vlaamse Leeuw "" (; The Flemish Lion) is the official anthem of Flanders, a region and community in Belgium. Composition The words of this anthem were written in July 1847 by Hippoliet Van Peene (1811–1864) who was clearly inspired by the song ''Sie s ..." of which the music was composed by Karel Miry. He was the first modern Flemish playwright and he wrote 35 theatre plays, which in his time were performed by ''Broedermin en Taelyver'' in Ghent. At the inauguration of the Minard Theatre in 1847, his ''Brigitta of de Twee Vondelingen'' was performed. Bibliography * ''Keizer Karel en de Berchemsche Boer'', comedy, 1841 * ''Jacob van Artevelde'', historical drama, 1841 * ''Willem van Dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippoliet Van Peene
Hippoliet Jan Van Peene (1 January 1811 in Kaprijke – 19 February 1864 in Ghent) was a Flemish physician and playwright. He studied medicine at the State University of Leuven and became a physician in Kaprijke and later in Ghent. In 1847 he wrote the lyrics of the Flemish anthem "De Vlaamse Leeuw "" (; The Flemish Lion) is the official anthem of Flanders, a region and community in Belgium. Composition The words of this anthem were written in July 1847 by Hippoliet Van Peene (1811–1864) who was clearly inspired by the song ''Sie s ..." of which the music was composed by Karel Miry. He was the first modern Flemish playwright and he wrote 35 theatre plays, which in his time were performed by ''Broedermin en Taelyver'' in Ghent. At the inauguration of the Minard Theatre in 1847, his ''Brigitta of de Twee Vondelingen'' was performed. Bibliography * ''Keizer Karel en de Berchemsche Boer'', comedy, 1841 * ''Jacob van Artevelde'', historical drama, 1841 * ''Willem van Dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
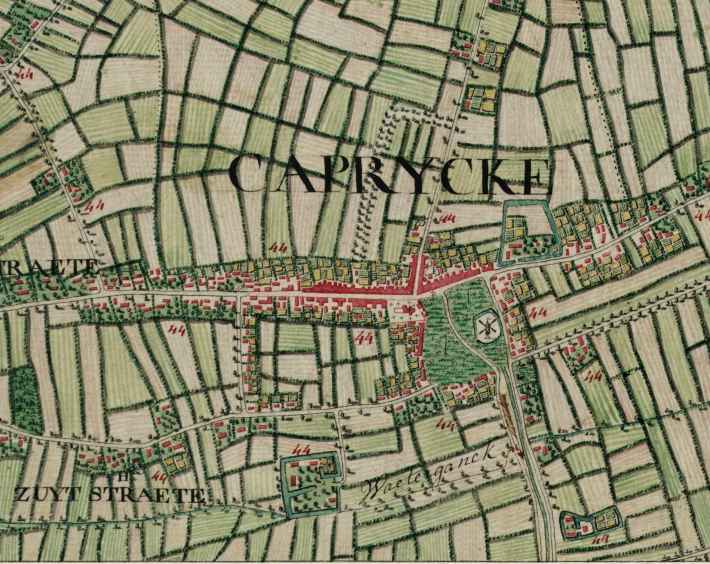
Kaprijke
Kaprijke () is a municipality in the Belgian province of East Flanders. The municipality comprises the towns of Kaprijke proper and . In 2021, Kaprijke had a total population of 6,508. History The name Kaprijke comes from Gallo-Roman name "Capricum" which means "Land of Caprius". It used to be the site of a Roman garrison, which can still be seen at the square in front of the old town hall. Kaprijke received city rights in 1240 by Joan, Countess of Flanders. During the 14th and 15th century, the cloth industry flourished in Kaprijke. However, during the period of religious strife during the 16th century, the merchants and cloth makers withdrew to safer locations. Following the resolution of the problems, the merchants and weavers did not return, leading up to the decline of the city of Kaprijke into a rural village during the 17th and 18th centuries. Kaprijke is known for its beautiful castle built in 1550, Hof ter Kruisen. It was commissioned by Andries of Baviere and fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in size only by Brussels and Antwerp. It is a port and university city. The city originally started as a settlement at the confluence of the Rivers Scheldt and Leie and in the Late Middle Ages became one of the largest and richest cities of northern Europe, with some 50,000 people in 1300. The municipality comprises the city of Ghent proper and the surrounding suburbs of Afsnee, Desteldonk, Drongen, Gentbrugge, Ledeberg, Mariakerke, Mendonk, Oostakker, Sint-Amandsberg, Sint-Denijs-Westrem, Sint-Kruis-Winkel, Wondelgem and Zwijnaarde. With 262,219 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019, Ghent is Belgium's second largest municipality by number of inhabitants. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education. Geographically, Flanders is mainly flat, and has a small section of coast on the North Sea. It borders the French department of Nord to the south-west near the coast, the Dutch provinces of Zeeland, North Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State University Of Leuven
The State University of Leuven was a university founded in 1817 in Leuven in Belgium, then part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. It was distinct from the Old University of Leuven (1425-1797) and from the Catholic University of Leuven, which moved from Mechlin to Leuven after the State University had been closed in 1835. History The State University of Leuven was founded by King William I of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1817 in Leuven. This continued the history of having a major university in Leuven, with the Old University of Leuven having been active from 1425 to 1797, and the State University used the same campus and facilities and a dozen of professors of the Old University taught there and have resumed the courses they had given in the venerable medieval Alma Mater, as : * Xavier Jacquelart, who was also a professor in the former University of Leuven * Jean Philippe Debruyn, of Louvain, licensed in both rights, born December 12, 1766, professor in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Vlaamse Leeuw
"" (; The Flemish Lion) is the official anthem of Flanders, a region and community in Belgium. Composition The words of this anthem were written in July 1847 by Hippoliet Van Peene (1811–1864) who was clearly inspired by the song ''Sie sollen ihn nicht haben, / den freien Deutschen Rhein, / So lang sich Herzen laben / An seinem Feuerwein'' (They must never get our free German Rhine, As long as hearts relish its fiery wine) by the German author Nikolaus Becker. The music, by Karel Miry (1823–1899), is apparently influenced by Robert Schumann's ''Sonntags am Rhein.'' Like France's Marseillaise, ''De Vlaamse Leeuw'' is a nationalist battle song. Franco-Belgian political tension in the mid-19th century made the Flemish public mood ripe for such an expression of regional feeling. At the time, it was not meant as anti-Belgian (as it often came to be seen by Flemish separatists and their Belgicist opponents), for the "enemy" it refers to is Belgium's southwestern neighbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karel Miry
Karel Miry (14 August 1823 – 5 October 1889) was a Belgian composer. He was one of the first Belgian composers to write operas to librettos in Dutch and is known as the composer of the music for De Vlaamse Leeuw, the national anthem of Flanders, for which Hippoliet van Peene wrote the lyrics. Karel Miry was born and died in Ghent, where he studied the violin with Jean Andries and harmony and composition with Martin Joseph Mengal at the Royal Conservatory. He completed his studies at the Royal Conservatory of Brussels, where he was a student of François-Auguste Gevaert. Miry succeeded Andries as a professor of harmony and counterpoint in 1857, and in 1871 he became the assistant director under Adolphe Samuel of the conservatory. In 1875, he was appointed as inspector of music at the municipal schools of Ghent; in 1881 the state-aided schools were added to his responsibility. Karel Miry died in 1889 in Ghent. Miry was well known for his operas, operettas, vaudevilles, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1811 Births
Events January–March * January 8 – An unsuccessful slave revolt is led by Charles Deslondes, in St. Charles and St. James Parishes, Louisiana. * January 17 – Mexican War of Independence – Battle of Calderón Bridge: A heavily outnumbered Spanish force of 6,000 troops defeats nearly 100,000 Mexican revolutionaries. * January 22 – The Casas Revolt begins in San Antonio, Spanish Texas. * February 5 – British Regency: George, Prince of Wales becomes prince regent, because of the perceived insanity of his father, King George III of the United Kingdom. * February 19 – Peninsular War – Battle of the Gebora: An outnumbered French force under Édouard Mortier routs and nearly destroys the Spanish, near Badajoz, Spain. * March 1 – Citadel Massacre in Cairo: Egyptian ruler Muhammad Ali kills the last Mamluk leaders. * March 5 – Peninsular War – Battle of Barrosa: A French attack fails, on a larger Anglo-Portugue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1864 Deaths
Events January–March * January 13 – American songwriter Stephen Foster (" Oh! Susanna", "Old Folks at Home") dies aged 37 in New York City, leaving a scrap of paper reading "Dear friends and gentle hearts". His parlor song "Beautiful Dreamer" is published in March. * January 16 – Denmark rejects an Austrian-Prussian ultimatum to repeal the Danish Constitution, which says that Schleswig-Holstein is part of Denmark. * January 21 – New Zealand Wars: The Tauranga campaign begins. * February – John Wisden publishes '' The Cricketer's Almanack for the year 1864'' in England; it will go on to become the major annual cricket reference publication. * February 1 – Danish-Prussian War (Second Schleswig War): 57,000 Austrian and Prussian troops cross the Eider River into Denmark. * February 15 – Heineken brewery founded in Netherlands. * February 17 – American Civil War: The tiny Confederate hand-propelled submarine '' H. L. Hun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish Activists
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; it is spoken by Flemings, the dominant ethnic group of the region. Outside of Flanders, it is also spoken to some extent in French Flanders and the Dutch Zeelandic Flanders. Terminology The term ''Flemish'' itself has become ambiguous. Nowadays, it is used in at least five ways, depending on the context. These include: # An indication of Dutch written and spoken in Flanders including the Dutch standard language as well as the non-standardized dialects, including intermediate forms between vernacular dialects and the standard. Some linguists avoid the term ''Flemish'' in this context and prefer the designation ''Belgian-Dutch'' or ''South-Dutch'' # A synonym for the so-called intermediate language in Flanders region, the # An indicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish Writers
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; it is spoken by Flemings, the dominant ethnic group of the region. Outside of Flanders, it is also spoken to some extent in French Flanders and the Dutch Zeelandic Flanders. Terminology The term ''Flemish'' itself has become ambiguous. Nowadays, it is used in at least five ways, depending on the context. These include: # An indication of Dutch written and spoken in Flanders including the Dutch standard language as well as the non-standardized dialects, including intermediate forms between vernacular dialects and the standard. Some linguists avoid the term ''Flemish'' in this context and prefer the designation ''Belgian-Dutch'' or ''South-Dutch'' # A synonym for the so-called intermediate language in Flanders region, the # An indica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |