|
Hill Castle
A hill castle or mountain castle is a castle built on a natural feature that stands above the surrounding terrain. It is a term derived from the German ''Höhenburg'' used in categorising castle sites by their topographical location. Hill castles are thus distinguished from lowland castles (''Niederungsburgen''). Hill castles may be further subdivided depending on their situation into the following: * Hilltop castle (''Gipfelburg''), that stands on the summit of a hill with steep drops on all sides. A special type is the rock castle or ''Felsenburg''. * Ridge castle (''Kammburg''), that is built on the crest of a ridge. * Hillside castle (''Hangburg''), that is built on the side of a hill and thus is dominated by rising ground on one side. * Spur castle (''Spornburg''), that is built on a hill spur surrounded by steep terrain on three sides and thus only needs to be defended on the one remaining side. When in the 10th and 11th centuries castles lost their pure fortress charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schachenstein Castle
The ruins of Schachenstein Castle (german: Burg Schachenstein) are located in the municipality of Thörl, above the village not far from the Thörlbach stream and north of Bruck an der Mur in the Styria, Austria. Schachenstein Castle was the last hill castle to be built in the Styria. Its primary role was as a fortified, lordly residence, thus no subjects were in service to the castle captains. The castle was never besieged, despite serious unrest such as the Baumkircher feud and Turkish raids. Location The site of castle was an outstanding choice: some 640 above sea level on rocks forming the southern spur of the ''Schöckelberg''. It is situated on an easily defended constriction of the road from Einodgräben to Mariazell, which was originally also guarded by a fortified gateway. Purpose The main purpose of the fortification was as a home and summer residence of the abbots of St. Lambrecht's Abbey as evinced by a large number of historic records. Subsequently, it was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles By Type
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocca (architecture)
A rocca (literally: "rock") is a type of Italian fortified stronghold or fortress, typically located on a hilltop, beneath or on which the inhabitants of a historically clustered village or town might take refuge at times of trouble. Generally under its owners' patronage, the settlement might hope to find prosperity in better times. A rocca might in reality be no grander than a fortified farmhouse. A more extensive rocca would be referred to as a castello. The rocca in Roman times would more likely be a site of a venerable cult than a dwelling, like the high place of Athens, its Acropolis. Though the earliest documentation is not earlier than the eleventh century, it was during the Lombard times that farming communities, which had presented a Roman pattern of loosely distributed farmsteads or self-sufficient Roman villa, moved from their traditional places on the fringes of the best arable lands in river valleys, where they were dangerously vulnerable from the Roman roads, to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland Castle
The term lowland castle or plains castle (german: Niederungsburg, Flachlandburg, Tieflandburg) describes a type of castle that is situated on a lowland, plain or valley floor, as opposed to one built on higher ground such as a hill spur. The classification is extensively used in Germany where about 34 percent of all castles are of the lowland type.Krahe, pp. 21-23 (2002) Because lowland castles do not have the defensive advantage of a site on higher ground, sites are chosen that are easy to defend, taking advantage, for example, of rivers, islands in lakes or marshes. Where such natural obstacles do not exist, artificially similar obstacles take on added significance. These include water-filled or dry moats, ramparts, palisades and curtain walls. In order to increase the height of the castle above the surrounding terrain, artificial earth mounds may be built (such as mottes), and fortified towers also fulfil this purpose. Castles of the Early Middle Ages (including Slavic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montechino Village
Montechino is a hamlet of forty inhabitants. It is a frazione of the comune of Gropparello, in the province of Piacenza, in Emilia-Romagna, Italy. Geography Montechino lies in the Val Riglio, part of the Val Nure. The village is above sea level, from Gropparello and from Piacenza. History For centuries, the feudal lords of the Nicelli family ruled much of the Val Nure. However, Montechino and its defensive fortress castle were controlled by the Confalonieri family, vassals of the Duke of Milan, Filippo Maria Visconti. Visconti had guaranteed the autonomy of the "Magnificent University of Val Nure", located near Montechino, in an effort to offset the power of the Nicelli. Further measures were implemented by the Duke in the form of tax relief, administrative autonomy and the power to appoint local judges. In 1492, the Confalonieri Family sold the castle of Montechino and its lands to Bartolino Nicelli, along with the title of Count and all attendant feudal rights. Economy Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montechino Italian Castle Piacenza
Montechino Castle is located in Montechino village, in the municipality of Gropparello, in the Riglio valley, province of Piacenza, Italy. It is situated on the crest of Monte Occhino hill, overlooking the Riglio river. History Montechino Castle was built in the 12th century as a strategic outpost to defend the Riglio valley. The castle controlled an important trade route between northern and southern Europe. It served those on pilgrimage to Rome or to Santiago de Compostela, in Galicia, Spain. According to the Enciclopedia Treccani, after returning from the Crusades the Confalonieri family from Piacenza took control of the castle in the early 12th century. In 1393 Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Duke of Milan, while solidifying his control of the area, conferred the feudal title of Count and the lands surrounding Montechino to the family as vassal allies. In 1492 they sold the castle and all its land in the valley to the aristocratic Nicelli family who continued to improve the proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
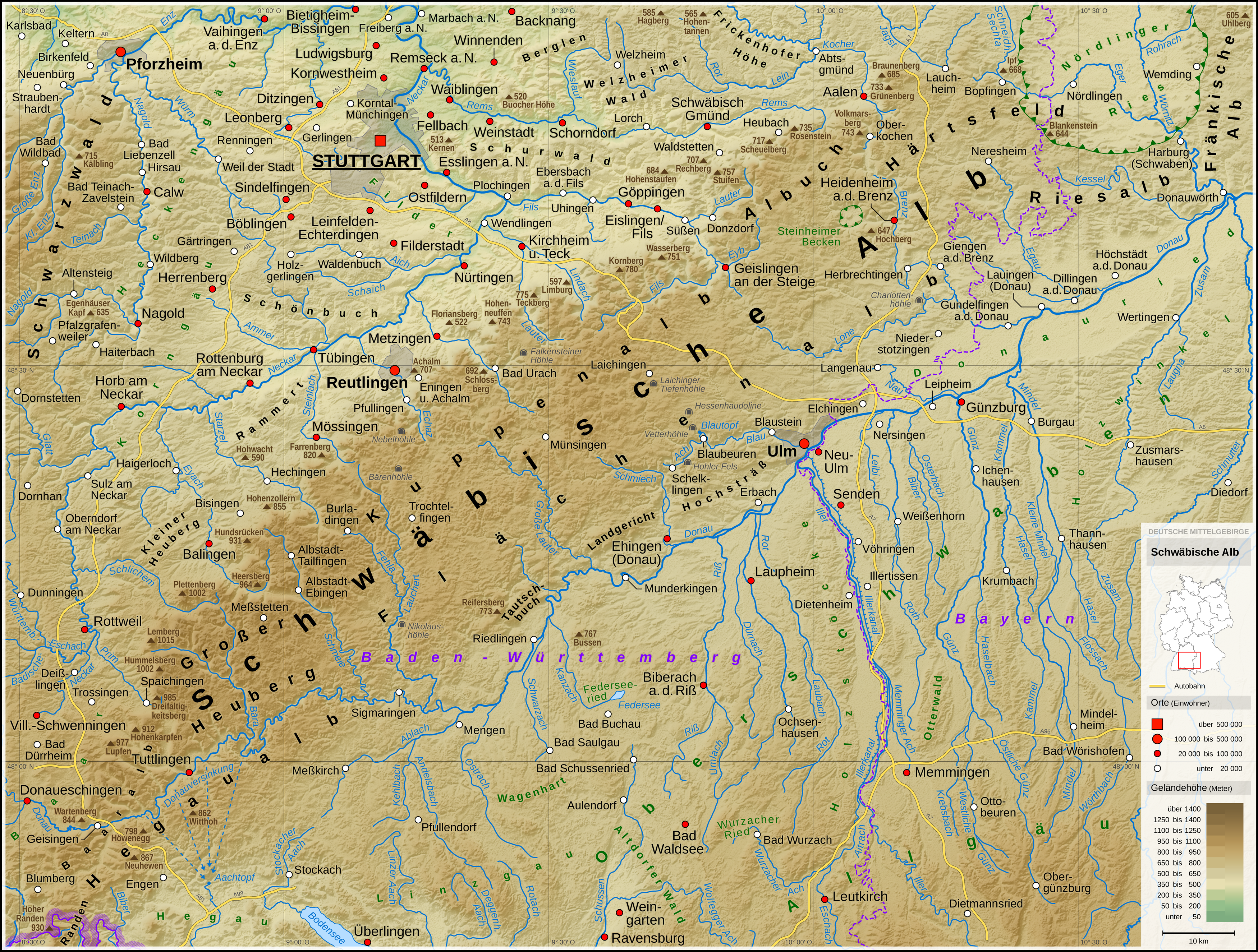
Swabian Jura
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of Swabia. The Swabian Jura occupies the region bounded by the Danube in the southeast and the upper Neckar in the northwest. In the southwest it rises to the higher mountains of the Black Forest. The highest mountain of the region is the Lemberg (). The area's profile resembles a high plateau, which slowly falls away to the southeast. The northwestern edge is a steep escarpment (called the Albtrauf or Albanstieg, rising up , covered with forests), while the top is flat or gently rolling. In economic and cultural terms, the Swabian Jura includes regions just around the mountain range. It is a popular recreation area. Geology The geology of the Swabian Jura is mostly limestone, which formed the seabed during the Jurassic period. The sea r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenzollern Castle
Hohenzollern Castle (german: Burg Hohenzollern ) is the ancestral seat of the imperial House of Hohenzollern. The third of three hilltop castles built on the site, it is located atop Mount Hohenzollern, above and south of Hechingen, on the edge of the Swabian Jura of central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The first castle on the mountain was constructed in the early 11th century. Over the years the House of Hohenzollern split several times, but the castle remained in the Swabian branch, the dynastic seniors of the Franconian-Brandenburgian cadet branch that later acquired its own imperial throne. This castle was completely destroyed in 1423 after a ten-month siege by the free imperial cities of Swabia. The second castle, a larger and sturdier structure, was constructed from 1454 to 1461, which served as a refuge for the Catholic Swabian Hohenzollerns, including during the Thirty Years' War. By the end of the 18th century it was thought to have lost its strategic importance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of 2.1 million (2,108,708 people). Slovenes constitute over 80% of the country's population. Slovene, a South Slavic language, is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. A sub-mediterranean climate reaches to the northern extensions of the Dinaric Alps that traverse the country in a northwest–southeast direction. The Julian Alps in the northwest have an alpine climate. Toward the northeastern Pannonian Basin, a continental climate is more pronounced. Ljubljana, the capital and largest city of Slovenia, is geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljubljana Castle
Ljubljana Castle ( sl, Ljubljanski grad, german: Laibacher Schloss) is a castle complex standing on Castle Hill above downtown Ljubljana, the capital of Slovenia. It is a key landmark of the town. Originally a medieval fortress, it was probably constructed in the 11th century and rebuilt in the 12th century. It acquired its present outline with an almost complete overhaul in the 15th century, whereas the majority of the buildings date to the 16th and 17th centuries. Initially a defense structure and since the first half of the 14th century the seat of the lords of Carniola, it was since the early 19th century used for various other purposes and today is used as a major cultural venue. The castle is depicted on the city's coat of arms, along with a dragon on top. History Ancient history According to archeological surveys, the area of the present castle has been settled continuously since 1200 BC, when the first settlements and later fortifications were built. The hill summit prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)