|
High River, Alberta
High River is a town within the Calgary Metropolitan Region of Alberta, Canada. It is approximately south of Calgary, at the junction of Alberta Highways 2 and 23. High River had a population of 14,324 in 2021. History The community takes its name from the Highwood River, which flows through the town. The area was originally inhabited largely by the Blackfoot First Nation, who called the site ''Ispitzee'' (or the "place of high trees along running water"). By 1870, after the arrival of the North-West Mounted Police and after Treaty Number 7 had been signed in 1877, settlers began arriving into the region.High River Downtown ARP Final Draft, O2 Planning + Design, page 25, Nov. 2014. Retrieved January 19, 2015 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Standard Time
The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time ( UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time ( UTC−06:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time at the 105th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory. In the United States, the exact specification for the location of time zones and the dividing lines between zones is set forth in the Code of Federal Regulations at 49 CFR 71. In the United States and Canada, this time zone is generically called Mountain Time (MT). Specifically, it is Mountain Standard Time (MST) when observing standard time, and Mountain Daylight Time (MDT) when observing daylight saving time. The term refers to the Rocky Mountains, which range from British Columbia to New Mexico. In Mexico, this time zone is known as the or ("Pacific Zone"). In the US and Canada, the Mountain Time Zone is to the east of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calgary And Edmonton Railway
The Calgary and Edmonton Railway (C&E) was an early pioneer railway in what was then the Northwest Territories, now Alberta, Canada. It connected the towns of Calgary and Strathcona (also called South Edmonton). Construction started in April 1890 and it opened August 1891. The line was the first major transportation connection for the isolated Edmonton settlement, and the development of the line was responsible for the creation of many railway towns along the line such as Red Deer and Wetaskiwin. It supplanted the Calgary and Edmonton Trail as the busiest transportation route along the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor. Initially, the northern terminus of the line was the old wooden Strathcona train station, a replica of which the Calgary and Edmonton Railway Station Museum operates, until the Edmonton, Yukon and Pacific Railway company was created to run a shortline across the North Saskatchewan River in 1902. In 1907 the new Strathcona Canadian Pacific Railway station became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Number 7
Treaty 7 is an agreement between the Crown and several, mainly Blackfoot, First Nation band governments in what is today the southern portion of Alberta. The idea of developing treaties for Blackfoot lands was brought to Blackfoot chief Crowfoot by John McDougall in 1875. It was concluded on September 22nd, 1877 and December 4th, 1877. The agreement was signed at the Blackfoot Crossing of the Bow River, at the present-day Siksika Nation reserve, approximately east of Calgary, Alberta. Chief Crowfoot was one of the signatories to Treaty 7. Another signing on this treaty occurred on December 4, 1877 to accommodate some Blackfoot leaders who were not present at the primary September 1877 signing. Treaty 7 is one of eleven Numbered Treaties signed between First Nations and the Crown between 1871 and 1921. The treaty established a delimited area of land for the tribes (a reserve), promised annual payments, provisions, or both, from the Crown to the tribes and promised continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackfoot Confederacy
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'' or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or " Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Blackfeet people: the '' Siksika'' ("Blackfoot"), the '' Kainai or Blood'' ("Many Chiefs"), and two sections of the Peigan or Piikani ("Splotchy Robe") – the Northern Piikani (''Aapátohsipikáni'') and the Southern Piikani (''Amskapi Piikani'' or ''Pikuni''). Broader definitions include groups such as the ''Tsúùtínà'' ( Sarcee) and ''A'aninin'' ( Gros Ventre) who spoke quite different languages but allied with or joined the Blackfoot Confederacy. Historically, the member peoples of the Confederacy were nomadic bison hunters and trout fishermen, who ranged across large areas of the northern Great Plains of western North America, specifically the semi-arid shortgrass prairie ecological region. They followed the bison herds as they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High River Station
High may refer to: Science and technology * Height * High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area * High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory * High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift took or takes place * Substance intoxication, also known by the slang description "being high" * Sugar high, a misconception about the supposed psychological effects of sucrose Music Performers * High (musical group), a 1974–1990 Indian rock group * The High, an English rock band formed in 1989 Albums * ''High'' (The Blue Nile album) or the title song, 2004 * ''High'' (Flotsam and Jetsam album), 1997 * ''High'' (New Model Army album) or the title song, 2007 * ''High'' (Royal Headache album) or the title song, 2015 * ''High'' (EP), by Jarryd James, or the title song, 2016 Songs * "High" (Alison Wonderland song), 2018 * "High" (The Chainsmokers song), 2022 * "High" (The Cure song), 1992 * "High" (David Hallyday song), 1988 * "Hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Calgary is situated at the confluence of the Bow River and the Elbow River in the south of the province, in the transitional area between the Rocky Mountain Foothills and the Canadian Prairies, about east of the front ranges of the Canadian Rockies, roughly south of the provincial capital of Edmonton and approximately north of the Canada–United States border. The city anchors the south end of the Statistics Canada-defined urban area, the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor. Calgary's economy includes activity in the energy, financial services, film and television, transportation and logistics, technology, manufacturing, aerospace, health and wellness, reta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calgary Metropolitan Region
The Calgary Metropolitan Region (CMR), also commonly referred to as the Calgary Region, is a conglomeration of municipalities centred on Calgary, the largest city in Alberta. With the Government of Alberta's establishment of the Calgary Metropolitan Region Board (CMRB) in 2017, the CMR's boundaries were legislated to include the City of Calgary, Foothills County to the south, Rocky View County to the west, north, and east, and a western portion of Wheatland County further to the east. Also within these boundaries are the cities of Airdrie and Chestermere, eight towns: Black Diamond, Cochrane, Crossfield, High River, Irricana, Okotoks, Strathmore, and Turner Valley, two villages: Beiseker and Longview, and two First Nations communities: Tsuu T'ina 145 and Eden Valley 216. Not all of these, however, are administrative members of the CMRB. The Calgary census metropolitan area (CMA) as delineated by Statistics Canada is smaller than the CMR. The Calgary CMA include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highwood River
The Highwood River is a tributary of the Bow River in southwestern Alberta, Canada. Course The Highwood originates in the Canadian Rockies in Peter Lougheed Provincial Park, in the Highwood Pass below Mount Arethusa. It flows south and is paralleled by the Kananaskis Trail between Elbow-Sheep Wildland Provincial Park, Don Getty Wildland Provincial Park, and ''Emerson Creek Park''. It turns east and flows along Highway 541 and through the community of Longview. Continuing east, it passes through High River, ending when it enters the Bow River southeast of Calgary. Recreation The river is known for flyfishing. A variety of trout species live in the river, including native bull trout. In springtime when the snow is melting the river offers white water rafting. Flooding The Highwood River is subject to frequent flooding. Flood events of exceptional magnitude occurred in 1894, 1899, 1902, 1908, 1912, 1923, 1929, 1932, 1942, 1995, 2005 and 2013. Most recently during the 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Highway 23
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 23, commonly referred to as Highway 23, is a highway in southern Alberta, Canada, east of Highway 2 that serves as an alternate route between Calgary and Lethbridge. It begins at Highway 3 (Crowsnest Highway) west of Lethbridge near the Hamlet of Monarch and shares a short concurrency with Highway 3A. It continues north and passes by the Villages of Nobleford, Barons, and Carmangay before it crosses the Little Bow River. It continues north, passing through the Hamlet of Kirkcaldy and Town of Vulcan before it meets the junction of Highway 24 and Highway 542. From there, the highway turns west and passes near just north of the Hamlet of Brant and just south of the Hamlet of Blackie before skirting Frank Lake. It intersects Highway 2 and enters the Town of High River along 12 Avenue SE before becoming Highway 2A at 10 Street SE. In tandem with Highway 519, the southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
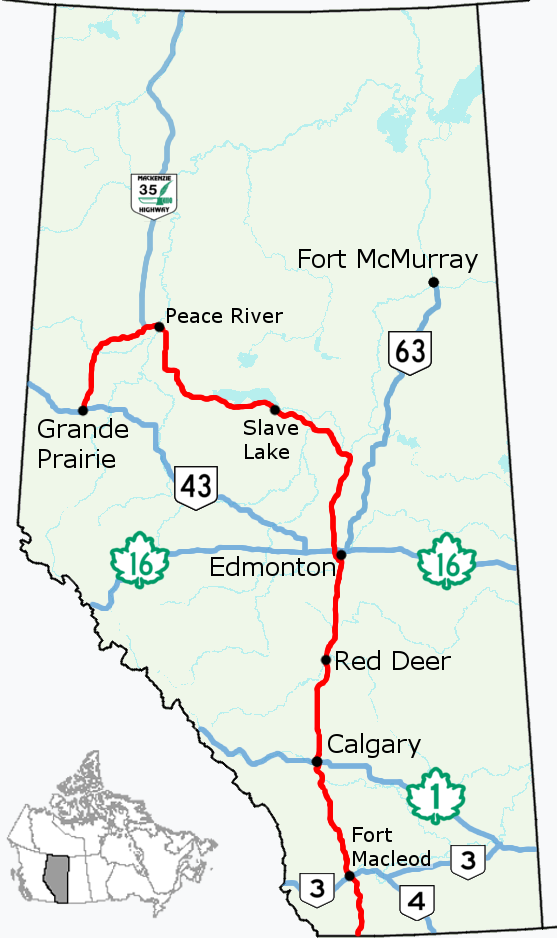
Alberta Highway 2
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 2, commonly referred to as Highway 2 or the Queen Elizabeth II Highway, is a major highway in Alberta that stretches from the Canada–United States border through Calgary and Edmonton to Grande Prairie. Running primarily north to south for approximately , it is the longest and busiest highway in the province carrying more than 170,000 vehicles per day near Downtown Calgary. The Fort Macleod—Edmonton section forms a portion of the CANAMEX Corridor that links Alaska to Mexico. More than half of Alberta's 4 million residents live in the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor created by Highway 2. U.S. Route 89 enters Alberta from Montana and becomes Highway 2, a two-lane road that traverses the foothills of southern Alberta to Fort Macleod where it intersects Highway 3 and becomes divided. In Calgary, the route is a busy freeway named Deerfoot Trail that continues into central Alberta as the Queen E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area Codes 587, 825, And 368
Area codes 587, 825, and 368 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) for the entire Canadian province of Alberta. They form an overlay with both of the previously existing area code 403 of southern Alberta, and northern Alberta's 780. Telephone numbers in area code 587 were allocated starting in late 2008. The complex overlay involving a total of five area codes in Alberta mandated ten-digit dialing throughout Alberta. History Prior to 1997, numbering plan area 403 comprised Alberta, Yukon and the Northwest Territories, as well as a very small western portion of what is today Nunavut (which split off from the Northwest Territories on 1 April 1999). In 1997, area code 403 began serving exclusively Alberta, with all other portions of 403 (as well as the portion of area code 819 that had served the region that is today's Nunavut but at the was still part of the Northwest Territories) splitting off into a new area code 867. In January 1999, the northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
2018.png)