|
High-grade Serous Carcinoma
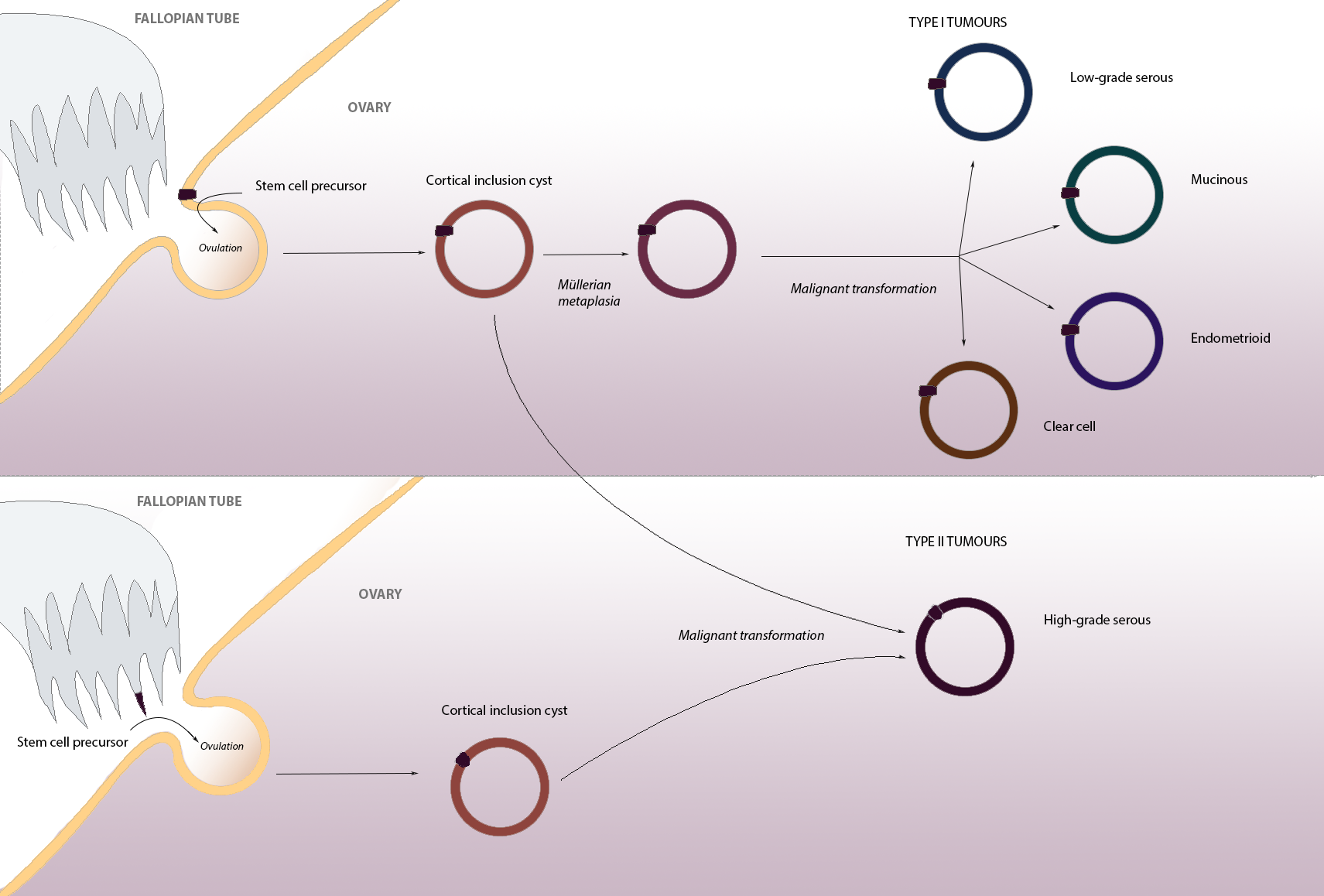
High-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC) is a type of tumour that arises from the serous epithelial layer in the abdominopelvic cavity and is mainly found in the ovary. HGSCs make up the majority of ovarian cancer cases and have the lowest survival rates. HGSC is distinct from low-grade serous carcinoma (LGSC) which arises from ovarian tissue, is less aggressive and is present in stage I ovarian cancer where tumours are localised to the ovary. Although originally thought to arise from the squamous epithelial cell layer covering the ovary, HGSC is now thought to originate in the Fallopian tube epithelium. HGSC is much more invasive than LGSC with a higher fatality rate - although it is more sensitive to platinum-based chemotherapy, possibly due to its rapid growth rate. In rare cases, HGSCs can develop from LGSCs, but generally the two types arise independently of each other. Risk factors Environmental risk factors The ‘incessant ovulation’ theory is suggested by the strong corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serous Membrane
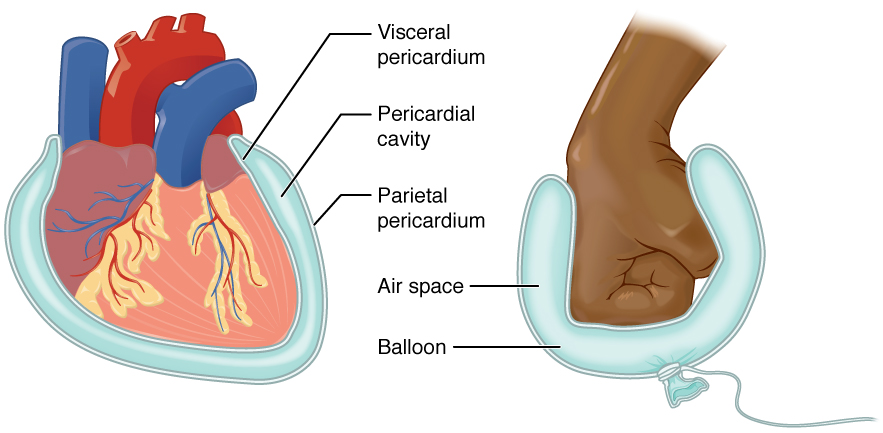
The serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth tissue membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous membrane that covers internal organs is called a ''visceral'' membrane; while the one that covers the cavity wall is called the ''parietal'' membrane. Between the two opposing serosal surfaces is often a potential space, mostly empty except for the small amount of serous fluid. The Latin anatomical name is '' tunica serosa''. Serous membranes line and enclose several body cavities, also known as serous cavities, where they secrete a lubricating fluid which reduces friction from movements. Serosa is entirely different from the adventitia, a connective tissue layer which binds together structures rather than reducing friction between them. The serous membrane covering the heart and lining the mediastinum is referred to as the pericardium, the sero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix "''peri-''" (περί; "around") and the suffix "''-cardion''" (κάρδιον; "heart"). Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). The fibrous pericardiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks"). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucinous Carcinoma
A mucinous neoplasm (also called colloid neoplasm) is an abnormal and excessive growth of tissue (neoplasia) with associated mucin (a fluid that sometimes resembles thyroid colloid). It arises from epithelial cells that line certain internal organs and skin, and produce mucin (the main component of mucus). A malignant mucinous neoplasm is called a mucinous carcinoma. For example, for ovarian mucinous tumors, approximately 75% are benign, 10% are borderline and 15% are malignant. Mucinous carcinoma Over 40 percent of all mucinous carcinomas are colorectal. When found within the skin, mucinous carcinoma is commonly a round, elevated, reddish, and sometimes ulcerated mass, usually located on the head and neck. File:Histopathology of mucinous invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.jpg, Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: Gross pathology (upper left) of mucinous carcinoma shows gelatinous areas. Histopathology shows clusters or nests of tumor cells floating in pools of extracellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear-cell Ovarian Carcinoma
Ovarian clear-cell carcinoma, or clear-cell carcinoma of the ovary, also called ovarian clear-cell adenocarcinoma, is one of several subtypes of ovarian carcinoma – a subtype of epithelial ovarian cancer, in contrast to non-epithelial cancers. According to research, most ovarian cancers start at the epithelial layer which is the lining of the ovary. Within this epithelial group ovarian clear-cell carcinoma makes up 5–10%. It was recognized as a separate category of ovarian cancer by the World Health Organization in 1973. Its incidence rate differs across various ethnic groups. Reports from the United States show that the highest rates are among Asians with 11.1% versus whites with 4.8% and blacks at 3.1%. These numbers are consistent with the finding that although clear-cell carcinomas are rare in Western countries they are much more common in parts of Asia. Background There are two subtypes of ovarian carcinoma – epithelial and nonepithelial; ovarian clear-cell carcinoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrioid Tumor
Endometrioid tumors are a class of tumor characterized by a resemblance to endometrium/ endometrial carcinoma, and over a third of cases have focal squamous differentiation. Ovary They are part of the surface epithelial tumor group of ovarian neoplasms (10–20% of which are the endometrioid type). Benign and borderline variants are rare, as the majority are malignant. There is an association with endometriosis and concurrent primary endometrial carcinoma ( endometrial cancer). On gross pathological examination, the tumor is cystic and may be solid and some arise in cystic endometriosis. In 40% of cases, endometrioid tumors are found bilaterally. Endometrium Endometrioid carcinoma can also arise in the endometrium. Grades 1 and 2 are considered "type 1" endometrial cancer, while grade 3 is considered "type 2". File:Pie chart of relative incidences of endometrial carcinoma.png, Relative incidences of endometrial carcinomas by histopathology, being endometrioid in a majori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramesonephric Duct
Paramesonephric ducts (or Müllerian ducts) are paired ducts of the embryo that run down the lateral sides of the genital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, they will develop to form the fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina. Development The female reproductive system is composed of two embryological segments: the urogenital sinus and the paramesonephric ducts. The two are conjoined at the sinus tubercle. Paramesonephric ducts are present on the embryo of both sexes. Only in females do they develop into reproductive organs. They degenerate in males of certain species, but the adjoining mesonephric ducts develop into male reproductive organs. The sex based differences in the contributions of the paramesonephric ducts to reproductive organs is based on the presence, and degree of presence, of Anti-Müllerian hormone. During the formation of the reproductive system, the paramesonephric ducts ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelomic Epithelium
Coelomic epithelium refers to the epithelium that lines the surface of the body wall and abdominal organs. It constitutes the outermost layer of the male and female gonads, thus forming the germinal epithelium of the female or of the male. It is also called the germinal epithelium of Waldeyer or sometimes the superficial epithelial cells in embryology. It is often encountered in the medical setting as an important source of various types of ovarian cancer, primary peritoneal serous cancer and endometriosis (coelomic metaplasia). , During gonadal sex Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones (ova, oft ... development, the coelomic epithelium, additionally with germ cells and mesenchymal cells make the indifferent gonad. As the coelomic epithelium is confronted with XY chromosomes, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murinae
The Old World rats and mice, part of the subfamily Murinae in the family Muridae, comprise at least 519 species. Members of this subfamily are called murines. In terms of species richness, this subfamily is larger than all mammal families except the Cricetidae and Muridae, and is larger than all mammal orders except the bats and the remainder of the rodents. Description The Murinae are native to Africa, Europe, Asia, and Australia. They are terrestrial placental mammals. They have also been introduced to all continents except Antarctica, and are serious pest animals. This is particularly true in island communities where they have contributed to the endangerment and extinction of many native animals. Two prominent murine species have become vital laboratory animals: the brown rat and house mouse are both used as medical subjects. The murines have a distinctive molar pattern that involves three rows of cusps instead of two, the primitive pattern seen most frequently in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicer
Dicer, also known as endoribonuclease Dicer or helicase with RNase motif, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene. Being part of the RNase III family, Dicer cleaves double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and pre-microRNA (pre-miRNA) into short double-stranded RNA fragments called small interfering RNA and microRNA, respectively. These fragments are approximately 20–25 base pairs long with a two-base overhang on the 3′-end. Dicer facilitates the activation of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which is essential for RNA interference. RISC has a catalytic component Argonaute, which is an endonuclease capable of degrading messenger RNA (mRNA). Discovery Dicer was given its name in 2001 by Stony Brook PhD student Emily Bernstein while conducting research in Gregory Hannon's lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Bernstein sought to discover the enzyme responsible for generating small RNA fragments from double-stranded RNA. Dicer's ability to generate around 22 nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTEN (gene)
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a phosphatase in humans and is encoded by the ''PTEN'' gene. Mutations of this gene are a step in the development of many cancers, specifically glioblastoma, lung cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. Genes corresponding to PTEN (orthologs) have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available. ''PTEN'' acts as a tumor suppressor gene through the action of its phosphatase protein product. This phosphatase is involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, preventing cells from growing and dividing too rapidly. It is a target of many anticancer drugs. The protein encoded by this gene is a phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase. It contains a tensin-like domain as well as a catalytic domain similar to that of the dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases. Unlike most of the protein tyrosine phosphatases, this protein preferentially dephosphorylates phosphoinositide substrates. It nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Knockout
A gene knockout (abbreviation: KO) is a genetic technique in which one of an organism's genes is made inoperative ("knocked out" of the organism). However, KO can also refer to the gene that is knocked out or the organism that carries the gene knockout. Knockout organisms or simply knockouts are used to study gene function, usually by investigating the effect of gene loss. Researchers draw inferences from the difference between the knockout organism and normal individuals. The KO technique is essentially the opposite of a gene knock-in. Knocking out two genes simultaneously in an organism is known as a double knockout (DKO). Similarly the terms triple knockout (TKO) and quadruple knockouts (QKO) are used to describe three or four knocked out genes, respectively. However, one needs to distinguish between heterozygous and homozygous KOs. In the former, only one of two gene copies (alleles) is knocked out, in the latter both are knocked out. Methods Knockouts are accomplished throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |